Abstract
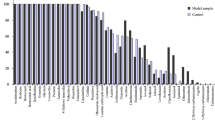
In the present work, the effectiveness of conventional wastewater treatments (activated sludge and oxidation ditches) and low-cost wastewater treatments (trickling filter beds, anaerobic lagooning and constructed wetlands) in the removal of pharmaceutically active compounds has been studied. To evaluate the efficiency of removal, 16 pharmaceutically active compounds belonging to seven therapeutic groups (anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, antiepileptic drugs, β-blockers, nervous stimulants, estrogens and lipid regulators) have been monitored during 1-year period in influent and effluent wastewater from 11 wastewater treatment plants of Spain. Mean removal rates of pharmaceutically active compounds achieved in conventional wastewater treatments were slightly higher than those achieved in low-cost treatments, being 64% and 55%, respectively. Ibuprofen, naproxen, salicylic acid and caffeine were the pharmaceutical compounds most efficiently removed, regardless the wastewater treatment applied, with removal rates up to 99%. Anaerobic lagooning was the less effective treatment for the removal of the most persistent compounds: carbamazepine and propranolol.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Camacho-Muñoz, D., Martín, J., Santos, J. L., Aparicio, I., & Alonso, E. (2009). An affordable method for the simultaneous determination of the most studied pharmaceutical compounds as wastewater and surface water pollutants. Journal of Separation Science, 32, 3064–3073.
Camacho-Muñoz, D., Martín, J., Santos, J. L., Aparicio, I., & Alonso, E. (2010a). Occurrence, temporal evolution and risk assessment of pharmaceutically active compounds in Doñana Park (Spain). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183, 602–608.
Camacho-Muñoz, M. D., Santos, J. L., Aparicio, I., & Alonso, E. (2010b). Presence of pharmaceutically active compounds in Doñana Park (Spain) main watersheds. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177, 1159–1162.
Conkle, J. L., White, J. R., & Metcalfe, C. D. (2008). Reduction of pharmaceutically active compounds by lagoon wetland wastewater treatment system in Southeast Louisiana. Chemosphere, 73, 1741–1748.
Díaz-Cruz, M., López de Alda, M. J., & Barceló, D. (2003). Environmental behavior and analysis of veterinary and human drugs in soils, sediments and sludge. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 22, 340–351.
Dordio, A., Palace, A. J., Martins, D., Barrocas, C., & Pinto, A. P. (2010). Removal of pharmaceuticals in microcosm constructed wetlands using Typha spp. and LECA. Bioresource Technology, 101, 886–892.
Farré, M., Ferrer, I., Ginebreda, A., Figueras, M., Olivella, L., Tirapu, L., Vilanova, M., & Barceló, D. (2001). Determination of drugs in surface water and wastewater samples by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: methods and preliminary results including toxicity studies with Vibrio fischeri. Journal of Chromatography. A, 938, 187–197.
García, J., Rousseau, D. P. L., Morató, J., Lesage, E., Matamoros, V., & Bayona, J. M. (2010). Contaminant removal processes in subsurface-flow constructed wetlands: a review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 561–661.
Göbel, A., McArdell, C. S., Joss, A., Siegrist, H., & Giger, W. (2007). Fate of sulfonamides, macrolides, and trimethorprim in different wastewater treatment technologies. Science of the Total Environment, 372, 361–371.
Hashimoto, T., Onda, K., Nakamura, Y., Tada, K., Miya, A., & Murakami, T. (2007). Comparison of natural estrogen removal efficiency in the conventional activated sludge process and the oxidation ditch process. Water Research, 41, 2117–2126.
Hijosa-Valsero, M., Matamoros, V., Martín-Villacorta, J., Bécares, E., & Bayona, J. M. (2010a). Assessment of full-scale natural systems for the removal of PPCPs from wastewater in small communities. Water Research, 44, 1429–1439.
Hijosa-Valsero, M., Matamoros, V., Sidrach-Cardona, R., Martín-Villacorta, J., Bécares, E., & Bayona, J. M. (2010b). Comprehensive assessment of the design configuration of constructed wetlands for the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from urban wastewaters. Water Research, 44, 3669–3678.
Jones, O. A. H., Voulvoulis, N., & Lester, J. N. (2007). The occurrence and removal of selected pharmaceutical compounds in a sewage treatment works utilizing activated sludge treatment. Environmental Pollution, 145, 738–744.
Kasprzyk-Hordern, B., Dinsdale, R. M., & Guwy, A. J. (2008). The occurrence of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs in surface water in South Wales, UK. Water Research, 42, 3498–3518.
Kasprzyk-Hordern, B., Dinsdale, R. M., & Guwy, A. J. (2009). The removal of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs during wastewater treatment and its impact on the quality of receiving waters. Water Research, 43, 363–380.
Lacey, C., McMahon, G., Bones, J., Barron, L., Morrisey, A., & Tobin, J. M. (2008). An LC-MS method for the determination of pharmaceutical compounds in wastewater treatment plant influent and effluent samples. Talanta, 75, 1089–1097.
Lajeunesse, A., & Gagnon, C. (2007). Determination of acidic pharmaceutical products and carbamazepine in roughly primary-treated wastewater by solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 87, 565–578.
Lindqvist, N., Tuhkanen, T., & Kronberg, L. (2005). Occurrence of acidic pharmaceuticals in raw and treated sewages and in receiving waters. Water Research, 39, 2219–2228.
Matamoros, V., Puigagut, J., García, J., & Bayona, J. M. (2007). Behavior of selected priority organic pollutants in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands: a preliminary screening. Chemosphere, 69, 1374–1380.
Matamoros, V., Hijosa, M., & Bayona, J. M. (2009). Assessment of the pharmaceutical active compounds removal in wastewater treatment systems at enantiomeric level. Ibuprofen and naproxen. Chemosphere, 75, 200–205.
Radjenović, J., Petrović, M., & Barceló, D. (2009). Complementary mass spectrometry and bioassays for evaluating pharmaceutical-transformation products in treatment of drinking water and wastewater. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 28, 562–580.
Rauch-Williams, T., Hoppe-Jones, C., & Drewes, J. E. (2010). The role of organic matter in the removal of emerging trace organic chemicals during managed aquifer recharge. Water Research, 44, 449–460.
Santos, J. L., Aparicio, I., Alonso, E., & Callejón, M. (2005). Simultaneous determination of pharmaceutically active compounds in wastewater samples by solid phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array and fluorescence detectors. Analytica Chimica Acta, 550, 116–122.
Santos, J. L., Aparicio, I., Callejón, M., & Alonso, E. (2008). Occurrence of pharmaceutically active compounds during 1-year period in wastewaters from four wastewater treatment plants in Seville (Spain). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 1509–1516.
Sui, Q., Huang, J., Deng, S., Yu, G., & Fan, Q. (2010). Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals, caffeine and DEET in wastewater treatment plants of Beijing, China. Water Research, 44, 417–426.
Tauxe-Wuersch, A., De Alencastro, L. F., Grandjean, D., & Tarradellas, J. (2005). Occurrence of several acidic drugs in sewage treatment plants in Switzerland and risk assessment. Water Research, 39, 1761–1772.
Ternes, T., Bonerz, M., & Schmidt, T. (2001). Determination of neutral pharmaceuticals in wastewater and rivers by liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography. A, 938, 175–185.
Ternes, T., Meisenheimer, M., McDowell, D., Sacher, F., Brauch, H., Haist-Gulde, B., Preuss, G., Wilme, U., & Zulei-Seibert, N. (2002). Removal of pharmaceuticals during drinking water treatment. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 3855–3863.
Tsoumanis, C. M., Giokas, D. L., & Vlessidis, G. (2010). Monitoring and classification of wastewater quality using supervised pattern recognition techniques and deterministic resolution of molecular absorption spectra based on multiwavelenght UV spectra deconvolution. Talanta, 82, 575–581.
Vieno, N., Tuhkanen, T., & Kronberg, L. (2007). Elimination of pharmaceuticals in sewage treatment plants in Finland. Water Research, 41, 1001–1012.
Zorita, S., Martensson, L., & Mathiasson, L. (2009). Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals in a municipal sewage treatment system in the south of Sweden. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 2760–2770.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the financial support received from the Agencia Andaluza del Agua (Consejería de Medio Ambiente, Junta de Andalucía, Spain) and from the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain (Project No. CGL2007-62281).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camacho-Muñoz, D., Martín, J., Santos, J.L. et al. Effectiveness of Conventional and Low-Cost Wastewater Treatments in the Removal of Pharmaceutically Active Compounds. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 2611–2621 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1053-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1053-9