Abstract
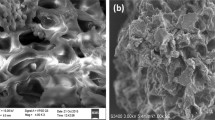
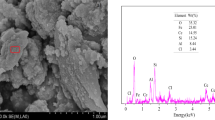
The adsorption of Brilliant Blue FCF from aqueous solution was evaluated using a Fe-zeolitic tuff. The adsorbent was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, IR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. Sorption kinetic, isotherms, dose and pH effects were determined and the adsorption behavior was analyzed. Kinetic pseudo-first order and linear isotherm models were successfully applied to the experimental results, indicating that the sorption mechanism is physisorption. Experiments in columns were performed and breakpoint was found in 100 min using a concentration of 5 mg/l.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansal, R. C., Donnet, J. B., & Stoeckli, F. (1988). Active carbon. New York: Dekker.
Berber-Mendoza, M. S., Leyva-Ramos, R., Alonso-Davila, P., Fuentes-Rubio, L., & Guerrero-Coronado, R. M. (2006). Comparison of isotherms for the ion exchange of Pb(II) from aqueous solution onto homoionic clinoptilolite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 301, 40–45.
Breck, D. (1973). Zeolite molecular sieves. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
Bullent, A., Turan, M., Ozdemir, O., & Celik, M. S. (2004). Color removal of reactive dyes from water by clinoptilolite. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, 39, 1251–1261.
Cortés, R., Martínez, V., & Solache, M. (2004). Evaluation of natural and surfactant-modified zeolites in the removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions. Separation Science and Technology, 39, 2711–2730.
Díaz-Nava, M. C., Olguín, M. T., Solache-Ríos, M., Alarcón-Herrera, M. T., & Aguilar-Elguezabal, A. (2005). Characterization and improvement of ion exchange capacities of Mexican clinoptilolite-rich tuffs. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrolytic Chemistry, 51, 231–240.
Doula, M. (2007). Synthesis of a clinoptilolite–Fe system with high Cu sorption capacity. Chemosphere, 67, 731–740.
El, A., Bassam, M., Bassam, E. A., & Ali, M. F. (2005). Handbook of industrial chemistry: Organic chemicals. New York: McGraw-Hill.
García-Mendieta, A., Solache-Ríos, M., & Olguín, M. T. (2003). Comparison of phenol and 4-chlorophenol adsorption in activated carbon with different physical properties. Separation Science and Technology, 38, 2549–2564.
García-Mendieta, A., Solache-Ríos, M., & Olguín, M. T. (2009). Evaluation of the sorption properties of a Mexican clinoptilolite-rich tuff for iron, manganese and iron–manganese systems. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 118, 489–495.
Günay, A., Arslankaya, E., & Tosun, I. (2007). Lead removal from aqueous solution by natural and pretreated clinoptilolite: adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 146, 362–371.
Gutiérrez, S. E., Solache-Ríos, M., & Colin, A. (2009). Sorption of indigo carmine by a Fe-zeolitic tuff and carbonaceous material from pirolyzed sewage sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170, 1227-1235.
Haggerty, G. M., & Bowman, R. S. (1994). Sorption of chromate and other inorganic anions by organo-zeolite. Environment Science & Technology, 28, 452–458.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (2002). Application of kinetic models to the sorption of copper (II) on to peat. Adsorption Science and Technology, 20, 797–813.
Ho, Y. S., Chiu, W. T., Hsu, C. S., & Huang, C. T. (2004). Sorption of lead ions from aqueous solution using tree fern as a sorbent. Hydrometallurgy, 73, 55–61.
Kasiri, M. B., Aleboyeh, H., & Aleboyeh, A. (2008). Degradation of Acid Blue 74 using Fe-ZSM5 zeolite as a heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst. Applied Catalysis, 84, 9–15.
Malkoc, E., Nuhoglu, Y., & Abali, Y. (2006). Cr (VI) adsorption by waste acorn of Quercus ithaburensis in fixed beds: prediction of breakthrough curves. Chemical Engineering Journal, 119, 61–68.
Mittal, A. (2006). Use of hen feathers as potential adsorbent for the removal of a hazardous dye, Brilliant Blue FCF, from wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 128, 233–239.
Mumpton, F. A., & Orsmy, W. C. (1976). Morphology of zeolites in sedimentary rocks by scanning electron microscopy. Clays and Clay Minerals, 24, 1–23.
Netpradit, S., Thiravetyan, P., & Towprayoon, S. (2004). Evaluation of metal hydroxide sludge for reactive dye adsorption in a fixed-bed column system. Water Research, 38, 71–78.
San-Miguel, G., Lambert, S. D., & Graham, N. J. D. (2001). The regeneration of field-spent granular-activated carbons. Water Research, 35, 2740–2748.
Sprynskyy, M., Buszewski, B., Terzyk, A., & Namie’snik, J. (2006). Study of the selection mechanism of heavy metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Cd2+) adsorption on clinoptilolite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 304, 21–28.
Solache-Ríos, M. J., Villalva-Coyote, R., & Díaz-Nava, M. C. (2010). Sorption and desorption of remazol yellow by a Fe-zeolitic tuff. Journal of the Mexican Chemical Society, 54, 58–66.
Torres-Pérez, J., Solache-Ríos, M., & Colín-Cruz, A. (2008). Sorption and desorption of dye remazol yellow onto a Mexican surfactant-modified clinoptilolite-rich tuff and a carbonaceous material from pyrolysis of sewage sludge. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 187, 303–313.
Trgo, M., & Perić, J. (2003). Interaction of the zeolitic tuff with Zn-containing simulated pollutant solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 260, 166–175.
Tsitsishvili, G. V., Andronikashvili, T. G., Kirov, G. N., & Filizova, L. D. (1992). Natural zeolites, ed., Chichester, UK: Ellis Horwood.
Wang, S., & Ariyanto, E. (2007). Competitive adsorption of malachite green and Pb ions on natural zeolite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 314, 25–31.
Wang, S., Boyjoo, Y., Choueib, A., & Zhu, Z. H. (2005). Removal of dyes from aqueous solution using fly ash and red mud. Water Research, 39, 129–138.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge financial support from CONACYT, project 131174Q.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinedo-Hernández, S., Díaz-Nava, C. & Solache-Ríos, M. Sorption Behavior of Brilliant Blue FCF by a Fe-Zeolitic Tuff. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 467–475 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0877-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0877-7