Abstract
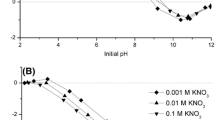
The modification effects of hematite with aluminum hydroxide were investigated on the removal of fluoride ions from water using batch experiments. The effects of pH, contact time, fluoride concentration, and the dose of sorbent on the sorption of fluoride ions by a modified hematite were studied. Characterization of hematite before and after the modification with aluminum hydroxide was studied by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller. Equilibrium was reached in 48 h of contact time and the maximum sorption of fluoride was found in the pHeq range between 2.34 and 6.26. The Elovich model described the kinetic sorption processes and the Langmuir–Freundlich model, the sorption isotherm process. These results indicated that the sorption mechanism was chemisorption on a heterogeneous material.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikary, S. K., Tipnis, U. K., Harkare, W. P., & Govindan, K. P. (1989). Defluoridation during desalination of brackish water by electrodialysis. Desalination, 71(3), 301–312.
Bitton, G. (1998). Formula handbook for environmental engineers and scientist. New York, NY: Wiley.
Chaturvedi, K., Pathak, B. N., & Singh, V. N. (1988). Fluoride removal from water by adsorption on china clay. Applied Clay Science, 3(4), 337–346.
Chen, L., Wu, H., Wang, T., Jin, Y., Zhang, Y., & Dou, X. (2009). Granulation of Fe–Al–Ce nano-adsorbent for fluoride removal from drinking water by spray coating on sand in fluidized bed. Powder Technology, 193(1), 56–64.
Cortés-Martínez, R., Martínez-Miranda, V., Solache-Ríos, M., & García-Sosa, I. (2004). Evaluation of natural and surfactant-modified zeolites in the removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions. Separation Science and Technology, 39(11), 2711–2730.
Durmaz, F., Kara, H., Cengeloglu, Y., & Ersoz, M. (2005). Fluoride removal by donnan dialysis with anion exchange membranes. Desalination, 177(1/3), 51–57.
Emamjomeh, M. M., & Sivakumar, V. (2009). Fluoride removal by a continuous flow electrocoagulation reactor. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(2), 1204–1212.
Garmes, H., Persin, F., Sandeaux, J., Pourcelly, G., & Mountadar, M. (2002). Defluoridation of groundwater by a hybrid process combining adsorption and Donnan dialysis. Desalination, 145(1/3), 287–291.
Ghorai, S., & Pant, K. K. (2004). Equilibrium, kinetics and breakthrough studies for adsorption of fluoride on activated alumina. Separation and Purification Technology, 42(3), 265–271.
Gopal, V., & Elango, K. P. (2007). Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of fluoride onto plaster of Paris. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141(1), 98–105.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (2002). Application of kinetics models to the sorption of copper (II) on to peat. Adsorption Science and Technology, 20(8), 797–815.
Ho, Y. S., Ng, J. C. Y., & McKay, G. (2001). Removal of lead (II) from effluents by sorption on peat using second-order kinetics. Separation Science and Technology, 36(2), 241–261.
Hu, K., & Dickson, M. J. (2006). Nanofiltration membrane performance of fluoride removal from water. Journal of Membrane Science, 279(1/2), 529–538.
Jain, S., & Jayaram, R. V. (2009). Removal of fluoride from contaminated drinking water using unmodified and aluminium hydroxide impregnated blue lime stone waste. Separation Science and Technology, 44(6), 1436–1451.
Jiménez-Nuñez, M. L., Solache-Rios, M., & Olguín, M. T. (2010). Fluoride sorption from aqueous solutions and drinking water by magnesium, cobalt, and nickel hydrotalcite-like compounds in batch and column systems. Separation Science and Technology, 45(6), 786–793.
Jiménez-Reyes, M., & Solache-Ríos, M. (2010). Sorption behavior of fluoride ions from aqueous solutions by hydroxyapatite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 180(1/3), 297–302.
Joshi, S. V., Mehta, S. H., Rao, A. P., & Rao, A. V. (1992). Estimation of sodium fluoride using HPLC in reverse osmosis experiments. Water Treatment, 10, 307–312.
Kang, W. H., Kim, E. I., & Park, J. Y. (2007). Fluoride removal capacity of cement paste. Desalination, 202(1/3), 38–44.
Kemer, B., Ozdes, D., Gundogdu, A., Bulut, V. N., Duran, C., & Soylak, M. (2009). Removal of fluoride ions from aqueous solution by waste mud. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168(2/3), 888–894.
King, P., Rakesh, N., Beenalahari, S., Kumar, Y. P., & Prasad, V. S. R. K. (2007). Removal of lead from aqueous solution using Syzygium cumini L: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 142(1/2), 340–347.
Ku, Y., & Chiou, H. M. (2002). The adsorption of fluoride ion from aqueous solution by activated alumina. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 133(1/4), 349–361.
Liao, X., & Shi, B. (2005). Adsorption of fluoride on zirconium (IV)-impregnated collagen fiber. Environmental Science and Technology, 39(12), 4628–4632.
Maliyekkal, S. M., Sharma, A. K., & Philip, L. (2006). Manganese-oxide-coated alumina: a promising sorbent for defluoridation of water. Water Research, 40(19), 3497–3506.
Mathialagan, T., & Viraraghavan, T. (2003). Adsorption of cadmium from aqueous solutions by vermiculite. Separation Science and Technology, 38(1), 57–76.
Min, Y., Hashimoto, T., Hoshi, N., & Myoga, H. (1999). Fluoride removal in a fixed bed packed with granular calcite. Water Research, 33(16), 3395–3402.
Mineral Information Institute. (2009). IRON ORE: hematite. USA: Magnetite & Taconite.
Mohan, S. V., Ramanaiah, S. V., Rajkumar, B., & Sarma, P. N. (2007). Biosorption of fluoride from aqueous phase onto algal Spirogyra IO1 and evaluation of adsorption kinetics. Bioresource Technology, 98(5), 1006–1011.
Mohapatra, D., Mishra, D. P., Mishra, S., Chaudhury, G. R., & Das, R. P. (2004). Use of oxide minerals to abate fluoride from water. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 275(2), 365–359.
Piñón-Miramontes, M., Bautista-Margulis, R., & Pérez-Hernández, A. (2003). Removal of arsenic and fluoride from drinking water with cake alum and a polymeric anionic flocculent. International Society for Fluoride Research, 36(2), 122–128.
Ruixia, L., Jinlong, G., & Hongxiao, T. (2002). Adsorption of fluoride, phosphate, and arsenate ions on a new type of ion exchange fiber. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 248(2), 268–274.
Sarkar, M., Banerjee, A., & Pramanik, P. (2006). Kinetic and mechanism of fluoride removal using laterite. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 45(17), 5920–5927.
Shuibo, X., Chun, Z., Xinghuo, Z., Jing, Y., Xiaojian, Z., & Jingsong, W. (2009). Removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution by adsorption of hematite. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 100(2), 162–166.
Solangi, I. B., Memon, S., & Bhanger, M. I. (2009). Removal of fluoride from aqueous environment by modified Amberlite resin. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171(1/3), 815–819.
Sujana, M. G., Pradhan, H. K., & Anand, S. (2009). Studies on sorption of some geomaterials for fluoride removal from aqueous solutions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(1), 120–125.
Sundaram, C. S., Viswanathan, N., & Meenakshi, S. (2008). Defluoridation chemistry of synthetic hydroxyapatite at nano scale: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 155(1/2), 206–215.
Susheela, A. K., Kumar, A., Betnagar, M., & Bahadur, M. (1993). Prevalence of endemic fluorosis with gastro-intestinal manifestations in people living in some North-Indian villages. Fluoride, 26(2), 97–104.
Tor, A., Danaoglu, N., Arslan, G., & Cengeloglu, Y. (2009). Removal of fluoride from water by using granular red mud: batch and column studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164(1), 271–278.
Wasay, S. A., Haron, J. M., & Tokunaga, S. (1996). Adsorption of fluoride, phosphate and arsenate ions on lanthanum-impregnated silica gel. Water Environment Research, 68(3), 295–300.
World Health Organization, WHO. (2008). Guidelines for drinking-water quality; volume 1. Recommendations. 3rd ed, Geneva.
World Health Organization, WHO. (2010). Naturally ocurring hazards. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/naturalhazards/en/print.html. Accessed 30 June 2010
Yadav, K., Kaushik, C. P., Haritash, A. K., Kansal, A., & Rani, N. (2006). Defluoridation of groundwater using brick powder as an adsorbent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 128(2/3), 289–293.
Yao, R., Meng, F., Zhang, L., Ma, D., & Wang, M. (2009). Defluoridation of water using neodymium-modified chitosan. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165(9), 454–460.
Zhao, Y., Li, X., Lui, L., & Chen, F. (2008). Fluoride removal by Fe(III)-loaded ligand exchange cotton cellulose adsorbent from drinking water. Carbohydrate Polymers, 72(1), 144–150.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support from CONACYT, project 131174Q and scholarship Grant No. 328367 for ATS and thanks Guadalupe Vazquez Mejia for drinking water characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teutli-Sequeira, A., Solache-Ríos, M. & Balderas-Hernández, P. Modification Effects of Hematite with Aluminum Hydroxide on the Removal of Fluoride Ions from Water. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 319–327 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0860-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0860-3