Abstract
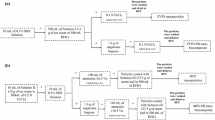
Lime was physically blended with Waste Activated Sludge (W.A.S) in various proportions. These blends were hydrated, dried, ground, and sieved to size of utmost 200 μm. The sorbents were then used in fixed-bed reactor for dry desulfurization tests. It was found that the blends had higher sorption capacities than lime alone which means that W.A.S augmented lime's sorption capacity. Higher surface area and porosity of the blended sorbents compared to lime was the main cause of the improved sorption capacity, a conclusion supported by Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area analysis (surface area increment with sorption capacity) and scanning electron microscopy imaging (rough morphology being formed). This higher surface area and porosity was caused by pozzolanic reaction between lime and the alumina silicate constituents of W.A.S. The products of this reaction are high surface area, complex calcium alumina silicates.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari, A., Bagreev, A., & Bandosz, T. J. (2005). Effect of adsorbent composition on H2S removal on sewage sludge-based materials enriched with carbonaceous phase. Carbon, 43(5), 1039–1048.
Bagreev, A., Bandosz, T. J., & Locke, D. C. (2001). Pore structure and surface chemistry of adsorbents obtained by pyrolysis of sewage sludge-derived fertilizer. Carbon, 39(13), 1971–1979.
Dahlan, I., Lee, K. T., Kamaruddin, A. H., & Mohamed, A. R. (2009). Selection of metal oxides in the preparation of rice husk ash (RHA)/CaO sorbent for simultaneous SO2 and NO removal. J Hazard Mater, 166(2–3), 1556–1559.
Garea, A., Fernández, I., Viguri, J. R., Ortiz, M. I., Fernández, J., Renedo, M. J., et al. (1997). Fly ash/calcium hydroxide mixtures for SO2 removal: structural properties and maximum yield. Chem Eng J, 66(3), 171–179.
Institute, W. C. (2009). The coal resource—a comprehensive overview of coal. London: World Coal Institute.
Kamall, R. (2000). In D. o. T. a. Industry (Ed.), Flue gas desulfurization (FGD) technologies, vol. 12 (p. 15). London: Department of Trade and Industry.
Karatepe, N., Erdogan, N., Ersoy-Meriçboyu, A., & Küçükbayrak, S. (2004). Preparation of diatomite/Ca(OH)2 sorbents and modelling their sulphation reaction. Chem Eng Sci, 59(18), 3883–3889.
Lee, K. T., Matlina Mohtar, A., Zainudin, N. F., Bhatia, S., & Mohamed, A. R. (2005). Optimum conditions for preparation of flue gas desulfurization absorbent from rice husk ash. Fuel, 84(2–3), 143–151.
Lee, K. T., Bhatia, S., Mohamed, A. R., & Chu, K. H. (2006). Optimizing the specific surface area of fly ash-based sorbents for flue gas desulfurization. Chemosphere, 62(1), 89–96.
Li, Y., & Sadakata, M. (1999). Study of gypsum formation for appropriate dry desulfurization process of flue gas. Fuel, 78(9), 1089–1095.
Lin, R.-B., Shih, S.-M., & Liu, C.-F. (2003). Characteristics and reactivities of Ca(OH)2/silica fume sorbents for low-temperature flue gas desulfurization. Chem Eng Sci, 58(16), 3659–3668.
Seredych, M., Strydom, C., & Bandosz, T. J. (2008). Effect of fly ash addition on the removal of hydrogen sulfide from biogas and air on sewage sludge-based composite adsorbents. Waste Manag, 28(10), 1983–1992.
Tourism, D. o. E. A. a. (2006). South Africa Environment Outlook. In D. o. E. A. a. Tourism (Ed.), (pp. 51). Pretoria
Zainudin, N. F., Lee, K. T., Kamaruddin, A. H., Bhatia, S., & Mohamed, A. R. (2005). Study of adsorbent prepared from oil palm ash (OPA) for flue gas desulfurization. Sep Purif Technol, 45(1), 50–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maina, P., Mbarawa, M. Waste Activated Sludge as an Additive for Increment of Lime Sorption Capacity. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 267–273 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0856-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0856-z