Abstract
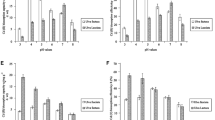
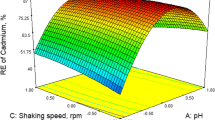
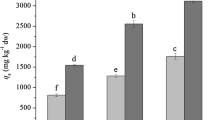
Brown algae Sargassum sinicola and Sargassum lapazeanum were tested as cadmium biosorbents in coastal environments close to natural and enriched areas of phosphorite ore. Differences in the concentration of cadmium in these brown algae were found, reflecting the bioavailability of the metal ion in seawater at several sites. In the laboratory, maximum biosorption capacity (q max) of cadmium by these nonliving algae was determined according to the Langmuir adsorption isotherm as 62.42 ± 0.44 mg g−1 with the affinity constant (b) of 0.09 and 71.20 ± 0.80 with b of 0.03 for S. sinicola and S. lapazeanum, respectively. Alginate yield was 19.16 ± 1.52% and 12.7 ± 1.31%, respectively. Although S. sinicola had far lower biosorption capacity than S. lapazeanum, the affinity for cadmium for S. sinicola makes this alga more suitable as a biosorbent because of its high q max and large biomass on the eastern coast of the Baja California Peninsula. Sargassum biomass was estimated at 180,000 t, with S. sinicola contributing to over 70%.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade, S., Medina, M. H., Moffett, J. W., & Correa, J. A. (2006). Cadmium-Copper antagonism in seaweeds inhabiting coastal areas affected by copper mine waste disposals. Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 4382–4387.
Baoli, W., & Congquiang, L. (2004). Factors controlling the distribution of trace metals in macroalgae. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 23, 366–372.
Casas-Valdez, M. (2009). El alga marina Sargassum (Sargassaceae) en el desarrollo regional. In: Urciaga-García, J. Lluch-Belda, D., Beltrán-Morales, L. F. (Eds.), Recursos marinos y servicios ambientales en el desarrollo regional (pp. 139–156). La Paz, B.C.S., Mexico: CIBNOR
Chapman, V. J., & Chapman, D. J. (1980). Seaweeds and their uses (3rd ed.). London: Chapman & Hall.
COREMI (2000). Geological-mining monograph of the State of Baja California Sur. Consejo de Recursos Minerales, Publication M-24e, Mexico
Davis, T. A., Volesky, B., & Vieira, R. H. S. F. (2000). Sargassum seaweed as biosorbent for heavy metals. Water Research, 34, 4270–4278.
Davis, T. A., Llanes, F., Volesky, B., & Mucci, A. (2003a). Metal selectivity of Sargassum spp. and their alginate in relation to their a-L-guluronic acid content and conformation. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 261–267.
Davis, T. A., Volesky, B., & Mucci, A. (2003b). A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Research, 37, 431–4330.
Davis, T. A., Ali, F. C., Giannitti, E., Volesky, B., & Mucci, A. (2004). Cadmium biosorption by S. fluitans: treatment, resilience and uptake relative to other Sargassum spp. and brown algae. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 39, 183–189.
Figueira, M. M., Volesky, B., & Mathieu, H. J. (1999). Instrumental analysis study of iron species biosorption by Sargassum biomass. Environmental Science & Technology, 33, 1840–1846.
Hashim, M. A., & Chu, K. H. (2004). Biosorption of cadmium by brown, green and red seaweeds. Chemical Engineering Journal, 97, 249–255.
Haug, A. (1965). Alginic acid. In R. L. Whistler & L. M. Wofrom (Eds.), Methods in carbohydrate chemistry, analysis and preparation of sugars (Vol. 5, pp. 69–73). New York: Academic.
Haug, A., Larsen, B., & Smidsrod, O. (1966). A study of the constitution of alginic acid by partial acid hydrolysis. Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 20, 183–190.
Hernández-Carmona, G. (1985). Variación estacional del contenido de alginatos en tres especies de feofitas de Baja California Sur, México. Investigaciones Marinas CICIMAR, 2, 30–45.
Hernández-Carmona, G., McHugh, D. J., Arvizu-Higuera, D. L., & Rodríguez-Montesinos, Y. E. (1999a). Pilot plant scale extraction of alginate from Macrocystis pyrifera. 1. Effect of pre-extraction treatments on yield and quality of alginate. Journal of Applied Phycology, 10, 507–513.
Hernández-Carmona, G., McHugh, D. J., & López-Gutierrez, F. (1999b). Pilot plant scale extraction of alginate from Macrocystis pyrifera. 2. Studies on extraction conditions and methods of separating the alkaline-insoluble residue. Journal of Applied Phycology, 11, 493–502.
Huerta-Díaz, M. A., De León-Chavira, F., Lares, M. L., Chee-Barragán, A., & Siqueiros-Valencia, A. (2007). Iron, manganese and trace metal concentrations in seaweeds from the central west coast of the Gulf of California. Applied Geochemistry, 22, 1380–1392.
Knauer, K., Ahner, B., Xue, H. B., & Sigg, L. (1997). Metal and phytochelatin content in phytoplankton from freshwater lakes with different metal concentrations. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17, 2444–2452.
Lockwood, M. P. (1976). Effects of pollutants on aquatic organisms. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Lodeiro, P., Cordero, B., Grille, Z., Herrero, R., & Sastre de Vicente, M. E. (2004). Physicochemical studies of cadmium (II) biosorption by the invasive alga in Europe, Sargassum muticum. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 88, 237–247.
Malea, P., & Haritonidis, S. (1999). Seasonal accumulation of metals by red alga Gracilaria verrucosa (Huds.) Papens, from Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Journal of Applied Phycology, 11, 503–509.
Mann, S. S., & Ritchie, G. S. P. (1995). Forms of cadmium in sandy soils after amendment with soils of higher fixing capacity. Environmental Pollution, 87, 23–29.
Mata, Y. N., Blázquez, M. L., Ballester, A., González, F., & Muñoz, J. A. (2009). Biosorption of cadmium, lead and copper with calcium alginate xerogels and immobilized Fucus vesiculus. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 555–562.
Méndez, L., Acosta, B., Álvarez-Castañeda, S. T., & Lechuga-Devéze, C. H. (1998). Trace metal distribution along the southern coast of Bahía de La Paz (Gulf of California), Mexico. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 61, 616–622.
Méndez, L., Palacios, E., Acosta, B., Monsalvo-Spencer, P., & Alvarez-Castañeda, T. (2006). Heavy metals in the clam Megapitaria squalida collected from wild and phosphorite mine-impacted sites in Baja California, Mexico. Biological Trace Element Research, 110, 275–287.
Murillo-Álvarez, I., & Hernández-Carmona, G. (2007). Monomer composition and sequence of sodium alginate extracted at pilot plant scale from three commercially important seaweeds from Mexico. Journal of Applied Phycology, 19, 545–548.
Pacheco-Ruíz, I., Zertuche-González, J. A., Chee-Barragán, A., & Blanco-Betancourt, R. (1998). Distribution and quantification of Sargassum beds along the west coast of the Gulf of California, Mexico. Botanica Marina, 14, 203–208.
Páez-Osuna, F., Ochoa-Izaguirre, M. J., Bojórquez-Leyva, H., & Michel-Reynoso, I. L. (2000). Macroalgae as biomonitors of heavy metal availability in coastal lagoons from the subtropical Pacific of Mexico. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 64, 846–851.
Patrón-Prado, M., Acosta-Vargas, B., Serviere-Zaragoza, E., & Méndez-Rodríguez, L. C. (2010). Copper and cadmium biosorption by dried seaweed Sargassum sinicola in saline wastewater. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2010, 197–202.
Paul-Chávez, L. (2005). Taxonomía y dinámica poblacional del complejo sinicola (Fucales: Phaeophyta) para el suroeste del Golfo de California. Tesis Doctoral. La Paz, Baja California Sur, México: CICIMAR. 194 pp.
Pérez-Reyes, C. (1997). Composición química de Sargassum spp. Colectado en la Bahía de La Paz, B.C.S., y la factibilidad de su aprovechamiento en forma directa o como fuente de alginato. Masters’Thesis. La Paz, B.C.S., Mexico: CICIMAR.
Riley, J. P. (1989). Los elementos más abundantes y menores en el agua de mar. In J. P. Riley & R. Chester (Eds.), Introducción a la química marina. Mexico City: AGT SA.
Riosmena-Rodríguez, R., Talavera-Sáenz, A., Acosta-Vargas, B., & Gardner, S. C. (2010). Heavy metals dynamics in seaweeds and seagrasses in Bahía Magdalena, B.C.S., Mexico. Journal of Applied Phycology, 22, 283–291.
Rodríguez-Figueroa, G. M., Shumilin, E., & Sánchez-Rodríguez, I. (2009). Heavy metal pollution monitoring using the brown seaweed Padina durviallaei in the coastal zone of the Santa Rosalía mining region, Baja California Peninsula, Mexico. Journal of Applied Phycology, 21, 19–26.
Romera, E., González, F., Ballester, A., Blázquez, M. L., & Muñoz, J. A. (2007). Comparative study of biosoption of heavy metals using different types of algae. Bioresource Technology, 98, 3344–3353.
Rule, K. L., Comber, S. D., Ross, D., Thornton, A., Makropoulos, C. K., & Rautiu, R. (2006). Diffuse sources of heavy metals entering an urban wastewater catchment. Chemosphere, 63, 64–72.
Sánchez-Rodríguez, I., Huerta-Diaz, M. A., Choumiline, E., Holguín-Quiñones, O., & Zertuche-González, J. A. (2001). Elemental concentrations in different species of seaweed from Loreto Bay (Baja California del Sur). Mexico. Implications for the geochemical control of metals in algal tissues. Environmental Pollution, 114, 145–160.
Schiewer, S., & Volesky, B. (1999). Advances in biosorption of heavy metals. In M. C. Flickinger & S. W. Drew (Eds.), Encyclopedia of bioprocess engineering. New York: Wiley.
Sheng, P. S., Ting, Y. P., Chen, J. P., & Hong, L. (2004). Sorption of lead, copper, cadmium, zinc, and nickel by marine algal biomass: characterization of biosorptive capacity and investigation of mechanisms. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 275, 131–141.
Smidsrod, O., & Haug, A. (1968). Dependence upon uronic acid and composition of some ion-exchange properties of alginates. Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 22, 1989–1997.
Stirk, W. A., & Van Staden, J. (2000). Removal of heavy metals from solution using dried brown seaweed material. Botanica Marina, 43, 467–473.
Vieira, R., & Volesky, B. (2000). Biosorption: a solution to pollution? International Microbiology, 3, 17–24.
Wilde, E. W., & Benemann, J. R. (1993). Bioremoval of heavy metals by the use of microalgae. Biotechnology Advances, 11, 781–812.
Williams, C. J., Aderhold, D., & Edyvean, G. J. (1998). Comparison between biosorbents for the removal of metal ions from aqueous solutions. Water Research, 32, 216–224.
Yabur, R., Basham, Y., & Hernández-Carmona, G. (2007). Alginate from the macroalgae Sargassum sinicola as a novel source for microbial immobilization material in wastewater treatment and plant growth promotion. Journal of Applied Phycology, 19, 43–53.
Acknowledgments
We thank to Dora L. Arvizu Higuera and Sonia Rodriguez Astudillo of the laboratory of CICIMAR-IPN and Baudilio Acosta, Alejandra Mazariegos, and Orlando Lugo of CIBNOR. Ira Fogel of CIBNOR provided editorial improvements. Funding was provided by Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas del Noroeste (grants EP 3.3, PC 2.0, and PC 2.1). M.P.P. is a recipient of a CONACYT doctoral fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patrón-Prado, M., Casas-Valdez, M., Serviere-Zaragoza, E. et al. Biosorption Capacity for Cadmium of Brown Seaweed Sargassum sinicola and Sargassum lapazeanum in the Gulf of California. Water Air Soil Pollut 221, 137–144 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0776-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0776-y