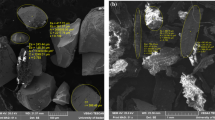
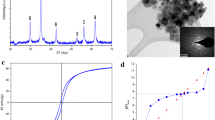
Abstract
Increasing release of organic pollutants to the environment has caused one of the largest world crises for water resources. Volatile organic compounds are toxic monoaromatic pollutants of soil and water. In this research, natural zeolite nanoparticles were produced mechanically by means of a milling technique, modified using two cationic surfactants of hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride and n-cetyl pyridinium bromide and formed as granules using a novel technique already developed by our group. The granulated adsorbents were used to uptake benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes (BTEX) from contaminated water. Two intra-particle diffusion models (i.e., Weber and Morris and Vermeulen models) and three surface reaction models (i.e., pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, and Elovich) were applied to evaluate the kinetics of adsorption and the best fitted model was chosen. Results of the adsorption kinetic evaluations were shown that uptake of granulated nanozeolites are higher than natural zeolites (in the order of four). Kinetic results revealed that the adsorption follows a pseudo-second order indicating existence of chemisorption in the studied conditions. It was noticed that the intra-particle diffusion is prevailing in the first stage of adsorption for a relatively short time (i.e., first 25 min).













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramian, L., & El-Rassy, H. (2009). Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics of azo-dye Orange II onto highly porous titania aerogel. Chemical Engineering Journal, 150, 403–410.
Accay, K., Sirkecioglu, A., Tather, M., Savasci, O. T., & Erdem-Senatalar, A. (2004). Wet ball milling of zeolite HY. Powder Technology, 142, 121.
Azizian, S. (2004). Kinetic models of sorption: A theoretical analysis. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 276, 47–52.
Bowman, R. S., et al. (2001). In J. A. Smith & S. Burns (Eds.), Physical and Chemical Remediation of Contaminated Aquifers (p. 161). New York: Kluwer Academic.
Breck, D. W. (1974). Zeolite Molecular Sieves. New York: Wiley.
Charkhi, A., Kazemeini, M., Kazemian, H., & Ahmadi, S. J. (2010a). Granulation of nano zeolites utilizing sodium alginate as an external template, Iran international zeolite conference, IIZC2010, April 29–30, Tehran, Iran.
Charkhi, A., Kazemian, H., & Kazemeini, M. (2010). Experimental design optimized ball milling of natural clinoptilolite zeolite for production of nano powders. Powder Technology, 203, 389–396.
Cook, D., Newcombe, G., & Sztajnbok, P. (2001). The application of PAC for MIB and Geosmin removal: Predicting PAC doses in four raw waters. Water Research, 35, 1325–1333.
Farhad, N., et al. (2000). Detection and remediation of soil and aquifer systems contaminated with petroleum products: An overview. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 26, 169–178.
Ghiaci, M., Abbaspour, A., Kia, R., & Seyedeyn-Azad, F. (2004). Equilibrium isotherm studies for the sorption of benzene, toluene, and phenol onto organo-zeolites and as-synthesized MCM-41. Separation and Purification Technology, 40, 217–229.
Haggerty, G. M., & Bowman, R. S. (1994). Sorption of chromate and other inorganic anions by organo-zeolite. Environmental Science & Technology, 28, 452–458.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1998). The kinetics of sorption of basic dyes from aqueous solutions by sphagnum moss peat. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 76, 822–826.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34, 451–465.
Hornig, G., Northcott, K., Snape, I., & Stevens, G. (2008). Assessment of sorbent materials for treatment of hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater in cold regions. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 53, 83–91.
Karapanagioti, H. K., Sabatini, D. A., & Bowman, R. S. (2005). Partitioning of hydrophobic organic chemicals (HOC) into anionic and cationic surfactant-modified sorbents. Water Research, 39, 699–709.
Kharitonov, A. S., Fenelonov, V. B., Voskresenskaya, T. P., Rudina, N. A., Molchanov, V. V., Plyasova, L. M., et al. (1995). Mechanism of FeZSM-5 milling and its effect on the catalytic performance in benzene to phenol oxidation. Zeolites, 15, 253.
Koh, S. M., & Dixon, J. B. (2001). Preparation and application of organo-minerals as sorbents of phenol, benzene and toluene. Applied Clay Science, 18, 111–122.
Kosanovic, C., Bronic, J., Cizmek, A., Subotic, B., Smit, I., Stubicar, M., et al. (1995). Mechanochemistry of zeolites: Part 2. Change in particulate properties of zeolites during ball milling. Zeolites, 15, 247.
Kosanovic, C., Subotic, B., & Cizmek, A. (1996). Thermal analysis of cation exchanged zeolites before and after their amorphization by ball milling. Thermochimica Acta, 276, 91.
Marcussen, E. (1993). Encapsulation and Controlled Release. Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Mardini, F. A., & Legube, B. (2009). Effect of the adsorbate (Bromacil) equilibrium concentration in water on its adsorption on powdered activated carbon Part 2: Kinetic parameters. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170, 754–762.
McKay, G. (1998). Application of surface diffusion model to the adsorption of dyes on bagasse pith. Adsorpt, 4, 361–372.
Ozacar, M., & Sengil, I. A. (2005). A kinetic study of metal complex dye sorption onto pine sawdust. Process Biochemistry, 40, 565–572.
Schulze-Makuch, D., et al. (2002). Surfactant-modified zeolite can protect drinking water wells from viruses and bacteria. EOS Trans AGU, 83(18), 193.
Seifi, L., Torabian, A., Kazemian, H., Bidhendi, G. N., Azimi, A. A., & Charkhi, A. (2010). Adsorption of petroleum monoaromatics from aqueous solutions using granulated surface modified natural nanozeolites: systematic study of equilibrium isotherms, Water Air Soil Pollution. doi:10.1007/s11270-010-0614-7.
Stankovic, J., & Kazemian, H. (2000). Clinoptilolite from zeolite deposits Semnan, Meyaneh and Firouzkooh in Iran. Mineral, 7, 31–32 (in Slovak).
Tan, I. A. W., Ahmad, A. L., & Hameed, B. H. (2009). Adsorption isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and desorption studies of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol on oil palm empty fruit bunch-based activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 473–482.
Torabian, A., Kazemian, H., Seifi, L., Bidhendi, G. N., Azimi, A. A., & Ghadiri, S. K. (2010). Removal of petroleum aromatics hydrocarbons by surfactant-modified natural zeolite: The effect of surfactant. Clean Soil Air Water, 38, 77–83.
Tseng, R. L. (2006). Mesopore control of high surface area NaOH-activated carbon. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 303, 494–502.
Vimonses, V., Lei, S., Jin, B., Chow, C. W. K., & Saint, C. (2008). Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis of Congo red adsorption by clay materials. Chemical Engineering Journal, 148, 354–364.
Weber, W. J., & Morris, J. C. (1963). Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. Journal of the Sanitary Engineering Division, 89, 31–60.
Wu, F. C., Tseng, R. L., & Juang, R. S. (2005). Comparisons of porous and adsorption properties of carbons activated by steam and KOH. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 283, 49–56.
Xie, J., & Kaliaguine, S. (1997). Zeolite ball milling as a means of enhancing the selectivity for base catalyzed reactions. Applied Catalysis A, 148, 415.
Zielinski, P. A., van Neste, A., & Akolekar, D. B. (1995). Effect of high-energy ball milling on the structural stability, surface and catalytic properties of small-, medium- and large-pore zeolites. Microporous Materials, 5, 123.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the National Iranian Oil Production and Distribution Company (NIOPDC) for financial support of this study. Dr. A. Charkhi from Sharif University of technology and the SPAG zeolite group are also acknowledged for fruitful scientific discussion and technical support. The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seifi, L., Torabian, A., Kazemian, H. et al. Kinetic Study of BTEX Removal Using Granulated Surfactant-Modified Natural Zeolites Nanoparticles. Water Air Soil Pollut 219, 443–457 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0719-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0719-z