Abstract
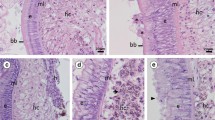
The use of sewage mud in agriculture has generated several discussions due to the risks of soil contamination mainly by metals. Due to the intimate contact of the diplopods with soil, they have been successfully used in ecotoxicological analyses. The impact of the external environment in the physiological changes in organs and tissues of different organisms can be reflected by the ultrastructural changes of their cells. Using the transmission electron microscopy, this study aimed to analyze the ultrastructural alterations in the midgut of the diplopod Rhinocricus padbergi exposed to substrate containing sewage mud from a Sewage Treatment Station of São Paulo State, Brazil. Therefore, it was sought to identify cellular alterations resulting from the subchronic exposure (90 days of exposure) of the animals to complex and potentially toxic mixtures such as sewage mud at different concentrations (1%, 10%, and 50%). The control group presented integrity in the cells and tissues that constitute the midgut. The animals exposed to sewage mud at 10% and 50% died before the 90 days of exposure. The analysis of the midgut of the animals exposed to 1% of sewage mud showed alterations in the epithelial cells, cells of the fat body layer, and hepatic cells. The main alterations observed were cytoplasmatic vacuolization, loss of the plasmatic membrane, and nuclear envelope integrity. We conclude that the mud sample presents a mixture of complex substances of cytotoxic and genotoxic action to the diplopod, causing cell death, since both the nucleus and other cellular compartments were damaged.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araújo, A. S. F., & Monteiro, R. T. R. (2007). Indicadores biológicos de qualidade do solo. Bioscience Journal, 23(3), 66–75.
Bettiol, W., & De Camargo, O. A. A. (2006). A Disposição de Lodo de Esgoto em Solo Agrícola. In W. Bettiol & O. A. De Camargo (Eds.), Lodo de Esgoto: Impactos Ambientais na Agricultura (pp. 25–35). Jaguariúna: Embrapa Meio Ambiente.
Camargo, O. A., Pires, A. M. M., & Bettiol, W. (2008). Lodo na agricultura. Revista Ciência Hoje, 42, 68–70.
Camargo-Mathias, M. I., Fantazzini, E. R., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2004). Ultrastructural features of the midgut of Rhinocricus padbergi (Diplopoda: Spirobolida). Braz. J. morphol. Sci., 21(2), 65–71.
Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental-Cetesb. (1999). Aplicação de biossólidos de sistemas de tratamento biológico em áreas agrícolas: critérios para projeto e operação. São Paulo: Norma P4230.
Chesters, J. K. (1992). Trace element-gene interactions. Nutrition Review, 50, 217–223.
Departamento de Águas e Energia Elétrica do Estado de São Paulo—DAEE. (2006). Plano Estadual de Recursos Hídricos: 2004/2007. São Paulo: Resumo. DAEE.
Edinger, A. L., & Thompson, C. B. (2004). Death by design: apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 16, 663–669.
Epstein, E. (2003). Land application of sewage sludge and biosolids. Londres, Nova York, Washington: Lewis Publishers.
Fantazzini, E. R., Fontanetti, C. S., & Camargo-Mathias, M. I. (2002). Midgut of the millipede “Rhinocricus padbergi” Verhoeff, 1938 (Diplopoda: Spirobolida): histology and histochemistry. Arthropoda Selecta, 11, 135–142.
Fontanetti, C. S., Tiritan, B., & Camargo-Mathias, M. I. (2006). Mineralized bodies in the fat body of Rhinocricus padbergi (Diplopoda). Braz. J. morphol. Sci., 23(3/4), 487–493.
Godoy, J. A. P., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2010). Diplopods as bioindicators of soils: analysis of midgut of individuals maintained in substract containing sewage sludge. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 210, 389–398.
Grivicich, I., Regner, A., & Rocha, A. B. (2007). Apoptosis: programmed cell death. Revista Brasileira de Cancerologia, 53(3), 335–343.
Ha, H. C., & Snyder, S. H. (1999). Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase is a mediator of necrotic cell death by ATP depletion. PNAS, 96(24), 13978–13982.
Hartwig, A., Schlepegrell, R., & Beyersmann, D. (1990). Indirect mechanism of lead-induced genotoxicity in cultured mammalian cells. Mutation Research, 241, 75–82.
Hespanhol, I. (2003). Potencial de reuso de água no Brasil: agricultura, indústria, municípios, recarga de aqüíferos. Bahia Análise & Dados, 13, 411–437.
Hopkin, S. P. (1990). Critical concentrations, pathways of detoxification and cellular ecotoxicology of metals in terrestrial arthropods. Functional Ecology, 4, 321–327.
Hopkin, S. P., & Martin, M. H. (1982). The distribution of zinc, cadmium, lead and copper within the hepatopancreas of a woodlouse. Tissue & Cell, 14, 703–715.
Hopkin, S. P., & Read, H. J. (1992). The biology of millipedes (p. 233). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Hopkin, S. P., Watson, K., Martin, M. H., & Mould, M. L. (1985). The assimilation of heavy metals by Lithobius variegates and Glomeris marginata (Chilopoda; Diplopoda). Bijdr. Dierk, 55(1), 88–94.
Ianella, P., & Itoyama, M. M. (2006). Morte Celular. Rev. Unorp, 5(12), 63–77.
Kerr, J. F., Wyllie, A. H., & Currie, A. R. (1972). Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. British Journal of Cancer, 6, 239–257.
Kocssis, M.A., & De Maria, I.C. (2004). O efeito do lodo de esgoto na recuperação da estrutura física de solos degradados. http://www.cibergeo.org/cigbnacional/VICBG.
Köhler, H. R., & Triebskorn, R. (1998). Assessment of the cytotoxic impact of heavy metals on soil invertebrates using a protocol integrating qualitative and quantitative components. Biomarkers, 3(2), 109–127.
Köhler, H. R., Storch, V., & Alberti, G. (1992). The impact of lead on the assimilation efficiency of laboratory-held Diplopoda (Arthropoda) preconditioned in different environmental situations. Oecologia, 90, 113–119.
Marques, M. O., Nogueira, T. A. R., Fonseca, I. M., & Marques, T. A. (2007). Teores de Cr, Ni, Pb e Zn em Argissolo Vermelho tratado com lodo de esgoto e cultivado com cana-de-açúcar. Revista de Biologia e Ciências da Terra, 7(1), 133–143.
Nogarol, L. R., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2010). Acute and subchronic exposure of diplopods to substrate containing sewage: tissular responses of the midgut. Micron, 41, 239–246.
Parolin, M. B., & Reason, I. J. M. (2001). Apoptose como mecanismo de lesão nas doenças hepatobiliares. Arquivos de Gastroenterologia, 38(2), 138–144.
Petersen, H., & Luxton, M. (1982). A comparative analysis of soil fauna populations and their role in decomposition processes. Oikos, 39(3), 291–357.
Schubart, O. (1942). Os miriápodos e suas relações com a agricultura. Pap. Avul. Dep. Zool., 2(16), 205–234.
Storch, V. (1988). Cell and environment: a link between morphology and ecology. In J. C. Iturrondobeitia (Ed.), Biologia Ambiental I (pp. 179–190). Bilbo: Serv. Ed. Univers. Pais Vasco.
Triebskorn, R., Köhler, H. R., Zanh, T., Vogt, G., Ludwing, M., Rumpf, S., et al. (1991). Invertebrate cells as targets for hazardous substances. Ziet Fur angewandte Zool., 78, 277–287.
Triebskorn, R., Henderson, I. F., Martin, A., & Köhler, H. R. (1996). Slugs as targets or non-target organisms for environmental chemicals. In slug and snail pests in agriculture. BCPC Symposiun Proceedings, 66, 65–71.
Triebskorn, R., Henderson, I. F., & Martin, A. P. (1999). Detection of iron in tissues from slugs (Deroceras reticulatum Müller) after ingestion of iron chelates by means of energy-filtering transmission electron microscopy (EFTEM). Pesticide. Science, 55, 55–61.
Tsutyia, M. T. (2001) Características de biossólidos gerados em estações de tratamento de esgotos. In M. T. Tsutiya, J. B. Comparini, A. P. Sobrinho, I. Hespanhol, P. C. T. Carvalho, & A. J. Melfi (Eds.). Biossólidos na agricultura (pp. 89–131). São Paulo: Sabesp, cap.4.
Tsutyia, M. T. (1999). Metais pesados: o principal fator limitante para o uso agrícola de biossólidos das estações de tratamento de esgoto. In 20°Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental. Anais do 20°Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental ABES, Rio de Janeiro
Acknowledgements
This research has been supported by FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo) Grant n. 08/50309-0, CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) and FUNDUNESP (Fundação para o Desenvolvimento da UNESP). The authors thank Dr. Gisela de Aragão Umbuzeiro, Engineer Samira Issa, and Marcus da Matta for providing the sewage mud; Antonio Teruyoshi Yabuki and Mônika Iamonte for the support during technical procedures; and Raphael Bastão de Souza, Vlamir Bozzatto de Oliveira, and Danielli Giuliano Perez for helping during the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nogarol, L.R., Fontanetti, C.S. Ultrastructural Alterations in the Midgut of Diplopods after Subchronic Exposure to Substrate Containing Sewage Mud. Water Air Soil Pollut 218, 539–547 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0666-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0666-8