Abstract
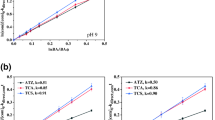
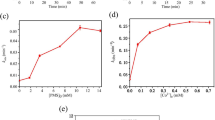
The efficiency of UV- and VUV-based processes (UV, VUV, UV/H2O2, and VUV/H2O2) for removal of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) in Milli-Q water and sewage treatment plant (STP) effluent was investigated at 20°C. The investigated factors included initial pH, variety of inorganic anions (NO −3 and HCO −3 ), and humic acid (HA). The results showed that the degradation of SMX in Milli-Q water at both two pH (5.5 and 7.0) followed the order of VUV/H2O2 > VUV > UV/H2O2 > UV. All the experimental data well fitted the pseudo-first order kinetic model and the rate constant (k) and half-life time (t 1/2) were determined accordingly. Indirect oxidation of SMX by generated •OH was the main degradation mechanism in UV/H2O2 and VUV/H2O2, while direct photolysis predominated in UV processes. The quenching tests showed that some other reactive species along with •OH radicals were responsible to the SMX degradation under VUV process. The addition of 20 mg L−1 HA significantly inhibited SMX degradation, whereas, the inhibitive effects of NO −3 and HCO −3 (0.1 mol L−1) were observed as well in all processes except in UV irradiation for NO −3 . The removal rate decreased 1.7–3.6 times when applying these processes to STP effluent due to the complex constituents, suggesting that from the application point of view the constituents of these complexes in real STP effluent should be considered carefully prior to the use of UV-based processes for SMX degradation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexy, R., Kümpel, T., & Kümmerer, K. (2004). Assessment of degradation of 18 antibiotics in the Closed Bottle Test. Chemosphere, 57, 505–512.
Andreozzi, R., Marotta, R., & Paxéus, N. (2003). Pharmaceuticals in STP effluents and their solar photodegradation in aquatic environment. Chemosphere, 50, 1319–1330.
Boreen, A. L., Arnold, W. A., & McNeill, K. (2004). Photochemical fate of sulfa drugs in the aquatic environment: sulfa drugs containing five-membered heterocyclic groups. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 3933–3940.
Bueno, M. J. M., Agüera, A., Gómez, M. J., Hernando, M. D., García-Reyes, J. F., & Fernández-Alba, A. R. (2007). Application of liquid chromatography/quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry and time-of-flight mass spectrometry to the determination of pharmaceuticals and related contaminants in wastewater. Analytical Chemistry, 79, 9372–9384.
Chin, Y.-P., Miller, P., Zeng, L., Cawley, K., & Weavers, L. (2004). Photosensitized degradation of Bisphenol A by dissolved organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 5888–5894.
Daughton, C. G., & Ternes, T. A. (1999). Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: agents of subtle change. Environmental Health Perspectives, 107, 907–938.
Davidson, J. (1999). Genetic exchange between bacteria in the environment. Plasmid, 42, 73–91.
Gao, N-y, Deng, Y., & Zhao, D. (2009). Ametryn degradation in the ultraviolet (UV) irradiation/hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) treatment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 640–645.
Gonzalez, M. G., Oliveros, E., Wörner, M., & Braun, A. M. (2004). Vacuum-ultraviolet photolysis of aqueous reaction systems. J Photochem Photobiol C, 5, 225–246.
Halling-Sørensen, B., Nors Nielsen, S., Lanzky, P. F., Ingerslev, F., Holten Lützhøft, H. C., & Jørgensen, S. E. (1998). Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment- A review. Chemosphere, 36, 357–393.
Han, W., Zhu, W., Zhang, P., Zhang, Y., & Li, L. (2004). Photocatalytic degradation of phenols in aqueous solution under irradiation of 254 and 185 nm UV light. Catalysis Today, 90, 319–324.
Heit, G., Neuner, A., & Saugy, P. Y. (1998). Vacuum-UV (172 nm) actinometry. The quantum yield of the photolysis of water [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 102, 5551–5561.
Hirsch, R., Ternes, T., Haberer, K., & Kratz, K.-L. (1999). Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. The Science of the Total Environment, 225, 109–118.
Ingerslev, F., & Halling-Sorensen, B. (2000). Biodegradability properties of sulfonamides in activated sludge. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 19, 2467–2473.
Jorgensen, S. E., & Halling-Sorensen, B. (2000). Drugs in the environment. Chemosphere, 40, 691–699.
Kim, I., & Tanaka, H. (2009). Photodegradation characteristics of PPCPs in water with UV treatment. Environment International, 35, 793–802.
Kim, I., Yamashita, N., & Tanaka, H. (2009a). Performance of UV and UV/H2O2 processes for the removal of pharmaceuticals detected in secondary effluent of a sewage treatment plant in Japan. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 1134–1140.
Kim, I., Yamashita, N., & Tanaka, H. (2009b). Photodegradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products during UV and UV/H2O2 treatments. Chemosphere, 77, 518–525.
Kümmerer, K. (2001). Drugs in the environment: emission of drugs, diagnostic aids and disinfectants into wastewater by hospitals in relation to other sources–a review. Chemosphere, 45, 957–969.
Lam, M. W., Tantuco, K., & Mabury, S. A. (2003). PhotoFate: a new approach in accounting for the contribution of indirect photolysis of pesticides and pharmaceuticals in surface waters. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 899–907.
Li, W., Lu, S., Qiu, Z., & Lin, K. (2010). Clofabric acid degradation in UV254/H2O2: effect of temperature. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 176, 1051–1057.
Lopez, A., Bozzi, A., Mascolo, G., & Kiwi, J. (2003). Kinetic investigation on UV and UV/H2O2 degradations of pharmaceutical intermediates in aqueous solution. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology. A, 156, 121–126.
Lu, C.-S., Chen, C.-C., Mai, F.-D., & Li, H.-K. (2009). Identification of the degradation pathways of alkanolamines with TiO2 photocatalysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165, 306–316.
Mouamfon, M. V. N., Li, W., Lu, S., Qiu, Z., Chen, N., & Lin, K. (2010). Photodegradation of sulphamethoxazole under UV-light irradiation at 254 nm. Environmental Technology, 31, 489–494.
Neamtu, M., & Frimmel, F. H. (2006). Photodegradation of endocrine disrupting chemical nonylphenol by simulated solar UV-irradiation. The Science of the Total Environment, 369, 295–306.
Oppenlander, T., & Gliese, S. (2000). Mineralization of organic micropollutants (homologous alcohols and phenols) in water by vacuum-UV-oxidation (H2O2-VUV) with an incoherent xenon-excimer lamp at 172 nm [J]. Chemosphere, 40, 15–21.
Perez, S., Eichhorn, P., & Aga, D. S. (2005). Evaluating the biodegradability of sulfamethazine, sulfamethoxazole, sulfathiazole and trimethroprim at different stages of sewage treatment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 1361–1367.
Sacher, F., Lange, F. T., Brauch, H. J., & Blankenhorn, I. (2001). Pharmaceuticals in groundwaters. Analitycal methods and results of a monotoring program in Baden-Württember, Germany. Journal of Chromatography A, 938, 199–210.
Stefan, M. I., Mack, J., & Bolton, J. R. (2000). Degradation pathways during the treatment of methyl tert-butyl ether by the UV/H2O2 process. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 650–658.
Trovo’ Alam, G., Nogueira, R. F. P., Agüera, A., Fernandez-Alba, A. R., Sirtori, C., & Malato, S. (2009). Degradation of sulfamethoxazole in water by solar photo-Fenton. Chemical and toxicological evaluation. Water Research, 43, 3922–3931.
Vogna, D., Marotta, R., Andreozzi, R., Napolitano, A., & d’Ischia, M. (2004). Kinetic and chemical assessment of the UV/H2O2 treatment of antiepileptic drug carbamazepine. Chemosphere, 54, 497–505.
Zhang, P. Y., Liu, J., & Zhang, Z. L. (2004). VUV photocatalytic degradation of toluen in the gas phase [J]. Chemistry Letters, 33, 1242–1243.
Zhou, W., & Moore, D. E. (1994). Photochemical decomposition of sulfamethoxazole. International Journal of Pharmaceutics (Amst), 110, 55–63.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20677015, No. 40871223), and the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 program) of China (2007AA06Z331), and Chinese Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (B506).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ngouyap Mouamfon, M.V., Li, W., Lu, S. et al. Photodegradation of Sulfamethoxazole Applying UV- and VUV-Based Processes. Water Air Soil Pollut 218, 265–274 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0639-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0639-y