Abstract
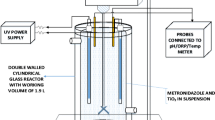
Mature landfill leachate contains some macromolecular organic substances that are resistant to biodegradation. The photocatalytic process helps to enhance biodegradability of landfill leachate. Batch experiments were employed to determine the optimum conditions for removal of organic matter by UV-TiO2 photocatalysis. Under optimum conditions, the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD), dissolved organic carbon (DOC), biological oxygen demand (BOD), and color was determined. Moreover, gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC/MS) was used to analyze the organic matter in the treated leachate before and after treatment by the photocatalysis. The experimental results indicated that the removal of COD, DOC, and color by UV-TiO2 photocatalysis could reach above 60%, 70% and 97%, respectively. Under optimal conditions, the ratio of biological oxygen demand (BOD)/chemical oxygen demand (COD) was elevated from 0.09 to 0.39, representing substantial improvement in biodegradability. GC/MS analysis revealed that 37 out of 72 kinds of organic pollutants in the leachate remained after 72 h treatment. Esters were produced during photocatalytic process and ketones, hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, hydroxybenzenes, and acids were easier to be degraded during photocatalytic oxidation processes. The UV-TiO2 photocatalysis systems proposed may be a cost-effective approach for pre-treatment of landfill leachate.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhakimi, G., Studnicki, L. H., & Al-ghazali, M. (2003). Photocatalytic destruction of potassium hydrogen phthalate using TiO2 and sunlight. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 154, 219–228.
Benfenati, E., Porazzi, E., Bagnati, R., Former, F., Martinex, M. P., Mariani, G., et al. (2003). Organic tracers identification as a convenient strategy in industrial landfills monitoring. Chemosphere, 51, 667–683.
Bila, D. M., Montalvǎo, F., Silva, A. C., & Dezotti, M. (2005). Ozonation of a landfill leachate: evaluation of toxicity removal and biodegradability improvement. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 117, 235–242.
Carcia, J. C., & Tankashima, K. (2003). Photocatalylic degradation of imazaquin in an aqueous suspension of titanium dioxide. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 155, 215–222.
Castillo, E., Vergara, M., & Moreno, Y. (2007). Landfill leachate treatment using a rotating biological contactor and an upward-flow anaerobic sludge bed reactor. Waste Management, 27, 720–726.
Chen, C. Y. (2009). Photocatalytic degradation of Azo Dye Reactive Orange 16 by TiO2. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 202, 335–342.
Chen, D. W., & Ray, A. K. (1999). Photocatalytic kinetics of phenol and its derivatives over UV irradiated TiO2. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 23, 143–157.
Cho, S. P., Hong, S. C., & Hong, S. I. (2002). Photocatalytic degradation of the landfill leachate containing refractory matters and nitrogen compounds. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 39, 125–133.
Cho, S. P., Hong, S. C., & Hong, S. I. (2004). Study of the end point of photocatalytic degradation of landfill leachate containing refractory matter. Chemical Engineering Journal, 98, 245–253.
de Morais, J. L., & Zamora, P. P. (2005). Use of advanced oxidation processes to improve the biodegradability of mature landfill leachates. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 123, 181–186.
Doong, R. A., & Chang, W. H. (1998). Photodegradation of parathion in aqueous titanium dioxide and zero valent iron solutions in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 116, 221–228.
Durmusoglu, E., & Yilmaz, C. (2006). Evaluation and temporal variation of raw and pre-treated leachate quality from an active solid waste landfill. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 171, 359–382.
Esplugas, S., Contreras, S., & Ollis, D. F. (2004). Engineering aspects of the integration of chemical and biological oxidation: simple mechanistic models for the oxidation treatment. Journal of Environmental Engineering-Asce, 130, 967–974.
Farre, M. J., Franch, M. I., Ayllon, J. A., Peral, J., & Domenech, X. (2007). Biodegradability of treated aqueous solutions of bio-recalcitrant pesticides by means of photocatalytic ozonation. Desalination, 211, 22–33.
Herrmann, J. M. (1999). Heterogeneous photocatalysis: fundamentals and applications to the removal of various types of aqueous pollutants. Catalysis Today, 53, 115–129.
Ilisz, I., Dombi, A., Mogyorósi, K., Farkas, A., & Dékány, I. (2002). Removal of 2-chlorophenol from water by adsorption combined with TiO2 photocatalysis. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 39, 247–256.
Koh, I. O., Chen, H. X., Hicke, K., & Thiemann, W. (2004). Leachate treatment by the combination of photochemical oxidation with biological process. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 162, 261–271.
Konstantinou, I. K., & Albanis, T. A. (2004). TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations—A review. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 49, 1–14.
Lin, S. H., & Kiang, C. D. (2003). Combined physical, chemical and biological treatments of wastewater containing organics from a semiconductor plant. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 97, 159–17.
Lopez, A., Pagano, M., Volpe, A., & Di Pinto, A. C. (2004). Fenton’s pretreatment of mature landfill leachate. Chemosphere, 54, 1005–1010.
Marco, A., Esplugas, S., & Saum, G. (1997). How and why to combine and biological processes for wastewater treatment. Water Science and Technology, 35, 321–327.
Merabet, S., Bouzaza, A., & Wolbert, D. (2009). Photocatalytic degradation of indole in a circulating upflow reactor by UV/TiO2 process—influence of some operating parameters. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 1244–1249.
Ntampou, X., Zouboulis, A. I., & Samaras, P. (2006). Appropriate combination of physicochemical methods (coagulation/flocculation and ozonation) for the efficient treatment of landfill leachates. Chemosphere, 63, 722–730.
Rajeswari, R., & Kanmani, S. (2009). A study on synergistic effect of photocatalytic ozonation for carbaryl degradation. Desalination, 242, 277–285.
Sang, Y. M., Gu, Q. B., Sun, T. C., Li, F. S., & Pan, Y. T. (2008). Analysis and removal of organic pollutants in biologically treated landfill leachate by an inorganic flocculent composite of Al (III)-Mg (II). Environmental Challenges in the Pacific Basin, 1140, 412–419.
Sarria, V., Péringer, P., Cáceres, J., Blanco, J., Malato, S., & Pulgarin, C. (2004). Solar degradation of 5-amino-6-methyl-2-benzimidazolone by TiO2 and iron (III) catalyst with H2O2 and O2 as electron acceptors. Energy, 29, 853–860.
Seo, D. J., Kim, Y. J., Ham, S. Y., & Lee, D. H. (2007). Characterization of dissolved organic matter in leachate discharged from final disposal sites which contained municipal solid waste incineration residues. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 148, 679–692.
State Environmental Protection Administration of China (2002). Monitoring and Analysis Methods of Water and Waste Water (Fourth revised version). Beijing: China Environmental Science Press.
Wang, K. H., Hsieh, Y. H., & Chen, L. J. (1998). The heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation, intermediates and mineralization for the aqueous solution of cresols and nitrophenols. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 59, 251–260.
Wang, F., Smith, D. W., & El-Din, M. G. (2003). Application of advanced oxidation methods for landfill leachate treatment—A review. Journal of Environmental Engineering and Science, 2, 413–427.
Wiszniowski, J., Robert, D., Surmacz-Gorska, J., Miksch, K., Malato, S., & Weber, J. V. (2004). Solar photocatalytic degradation of humic acids as a model of organic compounds of landfill leachate in pilot-plant experiments: Influence of inorganic salts. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 53, 127–137.
Wiszniowski, J., Robert, D., Surmacz-Gorska, J., Miksch, K., & Weber, J. V. (2006). Landfill leachate treatment methods: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 4, 51–61.
Zhang, C. X., Wang, Y. X., & Qi, S. H. (2008). Identification and significance of sterols in MSW landfill leachate. Journal of Chromatography B, 874, 1–6.
Zheng, H. L., Pan, Y. X., Li, D. D., & Wu, Y. Q. (2009). Degradation of organic contaminant in landfill leachate by photo-fenton process. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 29, 1661–1664.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40972156 and No. 40830748), Wuhan Science and Technology Department (No. 200860423203), and Open Research Program of Key Lab of Biogeology and Environmental Geology of Ministry of Education of China University of Geosciences (BGEGF200820).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, C., Wang, Y., Zhang, C. et al. UV-TiO2 Photocatalytic Degradation of Landfill Leachate. Water Air Soil Pollut 217, 375–385 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0594-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0594-7