Abstract
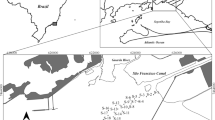
Heavy metals and some major element concentrations were investigated in overbank sediments and stream bed sediments of the ephemeral Beal wadi creek in the Cartagena-La Union mining district (SE Spain). Two vertical sediment profiles were extracted and the chemical and mineralogical compositions were both investigated by X-ray fluorescence and X-ray diffraction. Geochemical variations in vertical profiles of these two kinds of sediments allow observing noticeable heavy metals pollution (especially Fe, Pb, and Zn) in both kind of sediments but especially in the overbank sediments (reaching values of approximately 13% Fe, 6% Pb, and 6% Zn). A single extraction (DIN 38414-S4 leaching test) was made to observe the transfer of metals from solids to liquid phase. Pb, Zn, Cu, and Cd contents surpass the leaching values established by the DIN 38414-S4 limits established by Spanish legislation to consider these wastes as hazardous wastes. Geochemical comparison between leaching behavior of the two types of sediments reveals a major ability of overbank sediments in transferring heavy metals to the water flow.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U., & Helios-Rybicka, E. (2009). Contaminated sediments as a potential source of Zn, Pb, and Cd for a river system in the historical metalliferous ore mining and smelting industry area of South Poland. Journal of Soils & Sediments, 9, 13–22.
Cappuyns, V., & Swennen, R. (2004). Secondary mobilisation of heavy metals in overbank sediments. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 6, 434–440.
Cappuyns, V., & Swennen, R. (2007). Classification of alluvial soils according to their potential environmental risk: A case study for Belgian catchments. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 9, 319–328.
Cappuyns, V., Swennen, R., Vandamme, A., & Niclaes, M. (2006). Environmental impact of the former Pb-Zn mining and smelting in East Belgium. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 88, 6–9.
Ciszewski, D. (2002). Heavy metals in vertical profiles of the middle odra river overbank sediments: evidence for pollution sediments. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 143, 81–98.
DIN 38414-S4. (1984). Schlamm und Sedimente, Bestimmung der Eluierbarkeit mit Wasser. Berlin: DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung.
Elderling, B., Asmund, G., Kunzendorf, H., & Krogstad, E. J. (2002). Geochemical trends in metal-contaminated fiord sediments near a former lead-zinc mine in West Greenland. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 493–502.
Fic, M., & Isenbeck-Schröter, M. (1989). Batch studies for the investigation of the mobility of the heavy metals Cd, Cr, Cu and Zn. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 4, 69–78.
Field, S. (2003). The earth’s open wounds: Abandoned and orphaned mine. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111, A-154–A-161.
Förstner, U. (2008). Sediments—Resource or waste? Journal of Soils & Sediments, 4(1), 3.
Gäbler, H. E. (1997). Mobility of heavy metals as a function of pH of samples from an overbank sediment profile contaminated by mining activities. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 58, 185–194.
García, C. (2004). Impacto y riesgo ambiental de los residuos minero-metalúrgicos de la sierra minera de Cartagena-La Unión. PhD Thesis. Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena. 424pp.
Garcia, G., Peñas, J. M., & Manteca, J. I. (2008). Zn mobility and geochemistry in surface sulfide mining soils from SE Spain. Environmental Research, 106, 333–339.
Gonzalez-Fernandez, O., Queralt, I., Carvalho, M. L., & Garcia, G. (2007). Elemental analysis of mining wastes by energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF). Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 262(1), 81–86.
Herms, U., & Brümmer, G. (1984). Einflussgröβen der Schwermetallöslichkeit und–bindung in Böden. Z Pflanzenernaehr Bodenk, 147, 400–424.
Langedal, M., & Ottesen, R. T. (1998). Airborne pollution in five drainage basins in eastern Finnmark, Norway: An evaluation of overbank sediments as sampling medium for environmental studies and geochemical mapping. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 101(1–4), 377–398.
Linares Martínez, F. (2005). Juegos de estrategia y consecuencias inintencionadas: Un modelo con resultados perversos de la crisis de la minería de Cartagena-La Unión. Papers Journal, 75, 36–61.
Macklin, M. G. (1992). Metal pollution of soils and sediments: A geographical perspective. In M. D. Newson (Ed.), Managing the human impact on the natural environment: Patterns and processes (pp. 172–195). London: Belhaven Press.
Margui, E., Queralt, I., Van Grieken, R. (2009). X-ray fluorescence analysis, sample preparation for. In: R. A. Meyers (Ed.) Encyclopedia of analytical chemistry: Applications, theory, and instrumentation. New York: Wiley Interscience 20pp.
Martínez-Sánchez, M. J., García-Lorenzo, M. L., Pérez-Sirvent, C., & Marimón, J. (2008). Use of marble cutting sludges to immobilize heavy metals and decrease toxicity of contaminated soils. Fresenius' Environmental Bulletin, 17(10B), 1672–1678.
Monna, F., Petit, C., Guillaumet, J. P., Jouffroy-Bapicot, I., Blanchot, C., Dominik, J., et al. (2004). History and environmental impact of mining activity in Celtic aeduan territory recorded in a peat bog (Morvan, France). Environmental Science & Technology, 38(3), 665–673.
Moreno-Grau, S., Cascales-Pujalte, J. A., Martinez-Garcia, M. J., Angosto, J. M., Moreno, J., Bayo, J., et al. (2002). Relationships between levels of lead, cadmium, zinc, and copper in soil and settleable particulate matter in Cartagena (Spain). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 137(1–4), 365–383.
Morse, J. W., & Luther, G. W. (1999). Chemical influences on trace metal–sulfide interactions in anoxic sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimia Acta, 63(19/20), 3373–3378.
NRCS. Natural Resources Conservation Services. (2004). Soil Survey Laboratory Methods Manual. Version 4.0. Soil Survey Investigations report Nº 42. 735pp. <http://soils.usda.gov/technical/lmm/>.
Peh, Z., & Miko, S. (2001). Geochemical comparison of stream and overbank sediments: A case study from the Zumberak Region, Croatia. Geologia Croatica, 54(1), 119–130.
Plumlee, G. S., & Logsdon, M. J. (1999). The environmental geochemistry of mineral deposits, part A: Processes, techniques, and health issues. Society of Economic Geologists, Reviews in Economic Geology, 6A, 371.
Real Decreto (RD) 1310/1990 de 29 de octubre, por el cual se regula la utilización de los lodos de depuración en el sector agrario, 1990, Gobierno de España.
Real Decreto (RD) 1481/2001, de 27 de diciembre, por el que se regula la eliminación de residuos mediante depósito en vertedero, 2001, Gobierno de España.
Robles-Arenas, V. M., Rodríguez, R., García, C., Manteca, J. I., & Pascual, L. (2006). Sulphide-mining impacts in the physical environment: Sierra de Cartagena–La Unión (SE Spain) case study. Environmental Geology, 51(1), 47–64.
Rothwell, J. J., Evans, M. G., & Allott, T. E. H. (2007). Lead contamination of fluvial sediments in an eroding blanket peat cachment. Applied Geochemistry, 22, 446–459.
Rousseau, R. M. (2001). Detection limit and estimate of uncertainty of analytical XRF results. Rigaku Journal, 18(2), 33–47.
Software SPECTRAplus, (1998). Bruker AXS, Oestliche Rheinbrueckenstr. 50, D-76187 Karlsruhe, Germany
Swennen, R., & Van der Sluys, J. (2002). Anthropogenic impact on sediment composition and geochemistry in vertical overbank profiles of river alluvium from Belgium and Luxembourg. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 75, 93–105.
Swennen, R., Van Keer, I., & Vos, D. (1994). Heavy metal contamination in overbank sediments of the Geul river (East Belgium): Its relation to former Pb-Zn mining activities. Environmental Geology, 24, 12–21.
Taylor, M. P., & Kesterton, R. G. H. (2002). Heavy metal contamination of an arid river environment: Gruben River, Namibia. Geomorphology, 42, 311–327.
Wilding, L. P., & Drees, L. R. (1983). Spatial variability and pedology. In L. P. Wilding, N. E. Smeck, & G. F. Hall (Eds.), Pedogenesis and soil Taxonomy: I. Concepts and interactions (pp. 83–116). New York: Elsevier Science.
Acknowledgments
This study was financed by the Spanish National Research Programme (CGL2007-66861-C04) and by CONSOLIDER Research Programme (CSD2006-00044). O. Gonzalez-Fernandez gratefully acknowledges a grant from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Education (Ref. BES2005-6810).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonzalez-Fernandez, O., Jurado-Roldan, A.M. & Queralt, I. Geochemical and Mineralogical Features of Overbank and Stream Sediments of the Beal Wadi (Cartagena-La Union Mining District, SE Spain): Relation to Former Lead–Zinc Mining Activities and Its Environmental Risk. Water Air Soil Pollut 215, 55–65 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0458-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0458-1