Abstract
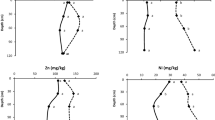
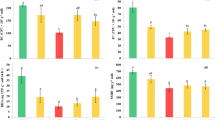
Wastewater land application is a cost-effective method to treat and dispose wastewater; however, it may cause soil salinization. Salt mass balance and the potential soil salinization caused by the wastewater land application were investigated in the crop root zone in a wastewater land application system at the City of Littlefield, TX, USA from October 7, 2005 to September 28, 2007 using a lysimeter system. This study showed that, after 2 years of wastewater land application, the ranges of soil salinity were still lower than the threshold (8,500 μS/cm) for Bermuda grass assuming a 10% yield reduction. The leached salt mass showed large spatial and temporal variation. The average values of electrical conductivity of the saturated paste extract of the soil samples increased from 1,433 μS/cm in June 2006 to 1,840 μS/cm in June 2007. The average values of the soil sodium adsorption ratio between June 2006 and June 2007 increased from 11 to 14 resulting in a potential risk of soil dispersion and decreasing the soil infiltration rate. Although the measured leaching fractions in nearly all sampling periods, except one, were higher than the leaching requirement, salt accumulations in the root zone were still found with only two exceptions. Since the time required for reaching equilibrium between cumulative salt mass input and cumulative salt mass output varies from 1 year to a few years, or even longer, the long-term investigation is recommended for the study of salt mass balance in the root zone of this wastewater land application system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrhein, C., Crowley, D., Holdren, G. C., Kharaka, Y.K., Parkhurst, D., Pyles, J., Schroeder, R. A., Tostrud, M. B., & Weghorst, P. A. (2001). Effect of salt precipitation on historical and projected salinities of the Salton sea: summary comments from workshop at the University of California, Riverside. January 30–31, 2001
Ayers, R. S., & Westcot, D. W. (1976). Water quality for agriculture. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 29, FAO. Rome: United Nations.
Bernstein, L., & Francis, L. E. (1973). Leaching requirement studies: sensitivity of alfalfa to salinity of irrigation and drainage waters. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 37, 931–943.
Bower, C. A., Ogata, G., & Tucker, J. M. (1969). Growth of Sudan and tall fescue grasses as influenced by irrigation water salinity and leaching fraction. Agronomy Journal, 61, 783–785.
Camobreco, V. J., Richards, B. K., Steenhuis, T. S., Peverly, J. H., & Mcbride, M. B. (1996). Movement of heavy metals through undisturbed and homogenized soil columns. Soil Science, 161, 740–750.
Corwin, D. L., Rhoades, J. D., & Simunek, J. (2007). Leaching requirement for soil salinity control: steady-state versus transient models. Agricultural Water Management, 90, 165–180.
Duan, R., & Fedler, C. B. (2007). Quality and quantity of leachate in land application systems. 2007 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Minneapolis Convention Center, Minneapolis, MN, June 17-20, 2007. Paper Number: 074079. ASABE, 2950 Niles Road, St. Joseph, MI 49085-9659. USA.
Duan, R., & Fedler, C. B. (2009). Field study of water mass balance in a wastewater land application system. Irrigation Science, 27(5), 409–416.
Duan, R., Sheppard, C. D., & Fedler, C. B. (2009). Short-term effects of wastewater land application on soil chemical properties. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution. Online published on 12 December 2009, doi:10.1007/s11270-009-0290-7.
Fedler, C. B. (2000). Impact of long-term application of wastewater. Presented at the 2000 ASAE Annual International Meeting, Milwaukee, Wisconsin, July 9–12, 2000. Paper No. 002055. ASAE, 2950 Niles Road, St. Joseph, MI 49085-9659. USA.
Fedler, C. B., & Borrelli, J. (2001). Re-evaluating surface application rates for Texas OSSF systems. Final report to the Texas On-Site Wastewater Treatment Research Council Conference. Contract No. 582-1-83219. Austin, TX 78711-3087: Texas Natural Resource Conservation Commission.
Fedler, C. B. & Borrelli, J. 1995. Designing for optimum land application systems. Presented at the International Summer Meeting of the ASAE. Chicago, IL. June 18–23. Paper No. 952407. ASAE, 2950 Niles Road, St. Joseph, MI 49085-9659. USA.
Gilfedder, M., Connell, L. D., & Mein, R. G. (1999). Implications of irrigation bay management for salt export—a study of irrigation bay processes in the Barr Creek Catchment. Melbourne: Cooperative Research Center for Catchment Hydrology.
Jolly, I. D., Narayan, K. A., Armstrong, D., & Walker, G. R. (1998). Impact of flooding on modeling salt transport processes to streams. Environmental Modelling and Software, 13, 87–104.
Jury, W. A., Frenkel, H., & Stolzy, L. H. (1978). Transient changes in the soil-water system from irrigation with saline water: I. Theory. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42, 579–585.
Karmeli, D., Salazar, L. L., & Walker, W. R. (1978). Assessing the spatial variability of irrigation water applications. US Environmental Protection Agency. Ada, OK: Robert S. Kerr Environmental Research Laboratory.
Munshower, F. F. (1994). Practical handbook of disturbed land revegetation. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
O’Connor, G. A. (1975). Calcium carbonate equilibria in soils. Technical completion report. Project 3109-144. New Mexico water resources research institute in cooperation with department of agronomy New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, New Mexico, June 1975.
O’Connor, G. A., Elliott, H. A., Basta, N. T., Bastian, R. K., Pierzynski, G. M., Sims, R. C., et al. (2005). Sustainable land application: an overview. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 7–17.
Pair, C. H., Hinz, W. H., Frost, K. R., Sneed, R. E., & Schiltz, T. J. (1983). Irrigation (p. 686). Silver Spring, MD: The Irrigation Association.
Peck, A. J., & Hurle, D. H. (1973). Chloride balance of some farmed and forested catchments in south Western Australia. Water Resources Research, 9, 648–657.
Rhoades, J. D., Lesch, S. M., LeMert, R. D., & Alves, W. J. (1997). Assessing irrigation, drainage, salinity management using spatially referenced salinity measurements. Agricultural Water Management, 35(35), 147–165.
Rhoades, J. D., & Loveday, J. (1990). Salinity in irrigated agriculture. Chapter 36. In B. A. Stewart et al. (Eds.), Irrigation of agricultural crops. Agronomy, vol. 30 (pp. 1089–1042). Madison, WI: American Society of Agronomy.
Scofield, C. S. (1940). Salt balance in irrigated areas. Journal of Agricultural Research, 61, 17–39.
Shainberg, I. (1990). Soil Response to saline and sodic conditions. In K. K. Tanji (Ed.), Agricultural salinity assessment and management. Am. Soc. Civil Eng. ASCE New York: Manuals and Reports on Engineering Practice.
Sheng, F., & Xiuling, C. (1997). Using shallow saline groundwater for irrigation and regulating for soil salt regime. Irrigation and Drainage Systems, 11, 1–14.
Sparks, D. L. (1996). Methods of soil analysis. Part 3. Chemical methods. Madison, Wisconsin: Soil Science Society of America, Inc.
Systat Software. (2004). SigmaStat 3.1. Users manual. Point Richmond: Systat Software.
Thayalakumaran, T., Bethune, M. G., & McMahon, T. A. (2007). Achieving a salt balance—should it be a management objective? Agricultural Water Management, 92, 1–12.
Tyagi, N. K. (2003). Managing saline and alkaline water for higher productivity. In J. W., Kijne, R., Barker, D., Molden (eds.). Water productivity in agriculture: limits and opportunities for improvement. CAB International, pp. 69–87.
US Salinity Laboratory Staff. (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. United States Department of Agriculture, Handbook 60 (p. 160). Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office.
Wichelns, D., & Oster, J. D. (2006). Sustainable irrigation is necessary and achievable, but direct costs and environmental impacts can be substantial. Agricultural Water Management, 86, 114–127.
Wilcox, L. V. (1963). Salt balance and leaching requirement in irrigated lands. Technical Bulletin No. 1290.
Williams, C. (2005). Is irrigated agriculture sustainable? The battle to counteract salinity. Southwest Hydrology, 4(4), 22–23.
Williamson, D. R., Gates, G. W. B., Robinson, G., Linke, G. K., Seker, M. P., & Evans, W. R. (1997). Salt trends: historic trend in salt concentration and salt load of stream flow in the Murray-Darling Drainage Division. Canberra: Murray Darling Basin Ministerial Committee.
Acknowledgments
We thank Texas Onsite Wastewater Treatment Research Council of the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, Austin, TX, USA for providing the funding support. We also thank the staff of the wastewater treatment plant and officials with the City of Littlefield, TX, USA for the help, land, and facility used to conduct this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, R., Fedler, C.B. & Sheppard, C.D. Field Study of Salt Balance of a Land Application System. Water Air Soil Pollut 215, 43–54 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0455-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0455-4