Abstract
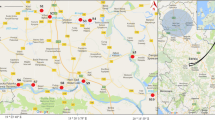
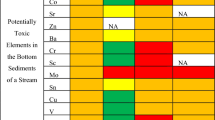
Lipophilic anthropogenic contaminants enter the environment from different kinds of human activities and corresponding emission sources. In the hydrosphere, they accumulate frequently in specific sedimentary zones, among others, and at coastal areas, forming reservoirs of pollutants. Marine and freshwater sediment samples as well as soil samples from a highly industrialized coastal area in Northern Greece have been analyzed in order to have a detailed view on the state of the particle-associated pollution. Noteworthy, based on extended GC/MS non-target screening analyses, interesting, so far unknown, or rarely documented contaminants have been identified and quantified comprising, e.g., mono- and dichlorocarbazoles, bromocarbazole, 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-nitrophenol, etc. However, all relevant contaminants are discussed with respect to their spatial concentration profiles, their emission sources, and their pathway. In addition, numerous pollutants are suggested to become selected for environmental monitoring programs. Hence, this study can act as an example for adapting individual monitoring programs to the individual contamination in coastal areas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, W. K., Briggs, G. B., Still, K. R., Jederberg, W. W., MacMahon, K., Baker, W. H., et al. (2001). Toxicity of 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-4-nitrophenol (DBNP). Applied Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, 16, 487–495.
Apitz, S. E., & Power, E. A. (2002). From risk assessment to sediment management: an international perspective. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2, 61–66.
Barth, J. A. C., Grathwohl, P., & Jones, K. C. (2007). Introduction to AquaTerra special Issue “AquaTerra: pollutant behavior in the soil, sediment, ground, and surface water system”. Environmental Pollution, 148, 693–694.
Bester, K., Gatermann, R., Huehnerfuss, H., Lange, W., & Theobald, N. (1998). Results of non target screening of lipophilic organic pollutants in the German Bight. IV: identification and quantification of chloronitrobenzenes and dichloronitrobenzenes. Environmental Pollution, 102, 163–169.
Bester, K., & Theobald, N. (2000). Results of non-target screening of lipophilic organic pollutants in the German Bight V: xanthen-9-one. Water Research, 34, 2277–2282.
Chen, G., & White, P. A. (2004). The mutagenic hazards of aquatic sediments: a review. Mutation Research, 567, 151–225.
Dsikowitzky, L., Schwarzbauer, J., Kronimus, A., & Littke, R. (2004). The anthropogenic contribution to the organic load of the Lipper River (Germany). Part I: qualitative characterisation of low-molecular organic compounds. Chemosphere, 57, 1275–1288.
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). (1996). The national sediment quality survey: a report to congress on the extent and severity of sediment contamination in surface waters of the united states. Draft. Washington, D.C.: US Environmental Protection Agency.
Galassi, S., Guzzella, L., & Croce, V. (2004). Screening organic micropollutants in surface waters by SPE extraction and ecotoxicological testing. Chemosphere, 54, 1619–1624.
Gerzabek, M. H., Barceló, D., Bellin, A., Rijnaarts, H. H. M., Slob, A., Darmendrail, D., et al. (2007). The integrated project AquaTerra of the EU sixth framework lays foundations for better understanding of river–sediment–soil–groundwater systems. Journal of Environmental Management, 84, 237–243.
Ginzburg, B., Chalifa, I., Zohary, T., Hadas, O., Dor, I., & Lev, O. (1998). Identification of oligosulphide odorous compounds and their source in the Lake of Galilee. Water Research, 32, 1789–1800.
Gocht, T., & Grathwohl, P. (2004). Diffuse input of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: atmospheric deposition and enrichment in soils of rural areas. Umweltwissenschaften und schadstoff-forschung, 4, 245–254.
Grigoriadou, A., Schwarzbauer, J., & Georgakopoulos, A. (2007). Molecular indicators for pollution source identification in marine and terrestrial water of the industrial area of Kavala city, North Greece. Environmental Pollution, 151, 231–242.
Hassenkloever, T., & Bickmeyer, U. (2006). The marine secondary metabolites 2, 4-dibromophenol and 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol differentially modulate voltage dependent ion currents in neuroendocrine (PC12) cells. Aquatic Toxicology, 79, 384–390.
Heim, S., Schwarzbauer, J., Kronimus, A., Littke, R., Woda, C., & Mangini, A. (2004). Geochronology of anthropogenic pollutants in riparian wetland sediments of the Lippe River (Germany). Organic Geochemistry, 35, 1409–1425.
Higashio, Y., & Shoji, T. (2004). Heterocyclic compounds such as pyrrole, pyridines, pyrrolidine, piperidine, indole, imidazol and pyrazines. Applied Catalysis A, 260, 251–259.
Hoenicke, R., Oros, D. R., Oram, J. J., & Taberski, K. M. (2007). Adapting an ambient monitoring program to the challenge of managing emerging pollutants in the San Francisco Estuary. Environmental Research, 105, 132–144.
Horn, O., Nalli, S., Cooper, D., & Nicell, J. (2004). Plasticizer metabolites in the environment. Water Research, 38, 3693–3698.
Kronimus, A., Schwarzbauer, J., Dsikowitzky, L., Heim, S., & Littke, R. (2004). Anthropogenic organic contaminants in sediments of the Lippe river, Germany. Water Research, 38, 3473–3484.
Larsson, P., Thuren, A., & Gahnstroem, G. (1986). Phthalate esters inhibit microbial activity in aquatic sediments. Environmental Pollution Series A, Ecological and Biological, 42, 223–231.
Long, E. R., MacDonal, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects with ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19, 81–97.
Martinez-Carballo, E., González-Barreiro, C., Sitka, A., Scharf, S., & Gans, O. (2007). Determination of selected organophosphate esters in the aquatic environment of Austria. Science of the Total Environment, 388, 209–299.
Olsen, C. R., Cutshall, N. H., & Larsen, I. L. (1982). Pollutant-particle associations and dynamics in coastal marine environments: a review. Marine Chemistry, 11, 501–533.
Parks, G. A. (1975). Adsorption in the marine environment. Chemical oceanography I (pp. 241–308). New York: Academic.
Peré-Trepat, E., Olivella, L., Ginebreda, A., Caixach, J., & Tauler, R. (2006). Chemometrics modelling of organic contaminants in fish and sediment river samples. Science of the Total Environment, 371, 223–237.
Petty, J. D., Huckins, J. N., Alvarez, D. A., Brumbaugh, W. G., Cranor, W. L., Gale, R. W., et al. (2004). A holistic passive integrative sampling approach for assessing the presence and potential impacts of waterborne environmental contaminants. Chemosphere, 54, 695–705.
Pinsky, C., & Bose, R. (1988). Pyridine and other coal tar constituents as free radical-generating environmental neurotoxicants. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 84, 217–222.
Reischl, A., Joneck, M., & Dumler-Gradl, R. (2005). Chlorocarbazoles in soils. Umweltwissenschaften and Schadstoff-Forschung, 4, 197–200.
Ricking, M., Schwarzbauer, J., & Franke, S. (2003). Molecular markers of anthropogenic activity in sediments of the Havel and Spree rivers (Germany). Water Research, 37, 2607–2617.
Scheffer, F., & Schachtschabel, P. (1998). Lehrbuch der Bodenkunde (14th Edition). Stuttgart: Enke Verlag.
Schwarzbauer, J., Littke, R., & Weigelt, V. (2000). Identification of specific organic contaminants for estimating the contribution of the Elber river to the pollution of the German Bight. Organic Geochemistry, 31, 1713–1731.
Schwarzbauer, J., & Littke, R. (2004). Quantitative evaluation of Elbe river-derived organic marker compounds in sediment samples of the German Bight. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 4, 177–183.
Schwarzbauer, J., & Heim, S. (2005). Lipophilic organic contaminants in the Rhine River, Germany. Water Research, 39, 4735–4748.
Wang, H., Wang, C., Wu, W., Mo, Z., & Wang, Z. (2003). Persistent organic pollutants in water and surface sediments of Taihu Lake, China and risk assessment. Chemosphere, 50, 557–562.
Warren, N., Allan, I. J., Carter, J. E., House, W. A., & Parker, A. (2003). Pesticides and other micro-organic contaminants in freshwater sedimentary environments—a review. Apllied Geochemistry, 18, 159–194.
Weigel, S., Bester, K., & Hühnerfuss, H. (2005). Identification and quantification of pesticides, industrial chemicals, and organobromine compounds of medium to high polarity in the North Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 252–263.
Witter, A. E., & Jones, A. D. (1999). Chemical characterization of organic constituents from sulfide-rich produced water using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18, 1920–1926.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude for the financial support provided by the Greek State Scholarships Foundation (I.K.Y.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grigoriadou, A., Schwarzbauer, J. Non-target Screening of Organic Contaminants in Sediments from the Industrial Coastal Area of Kavala City (NE Greece). Water Air Soil Pollut 214, 623–643 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0451-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0451-8