Abstract
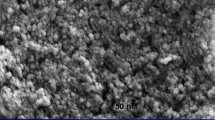
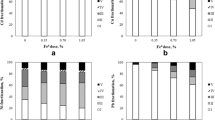
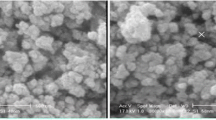
Nanoparticles derived from natural materials are promising compounds in the field of environmental remediation. The present study produces and characterizes Na-zeolitic tuff in the nanorange, stabilizes the nanotuff in suspension, and investigates the effect of Na-zeolitic nanotuff on sorption of Cd. Breakdown of raw zeolitic tuff with a mean particle size of 109 μm to the nanorange was achieved by attrition milling. In the first stage of grinding, a mixture of Al-oxide beads of 1 to 2.6 mm diameter was used. The milling process lasted 4 h. In the second stage, the dried powder was milled again using a mixture of a fine zirconia beads (0.1 mm) and Al-oxide beads (1.0 mm). The powder was treated with 1 M NaCl solution. Finally, the powder was sonicated in water. After this procedure, the mean and median particle diameters were 47.6 and 41.8 nm, respectively. The nanoparticulate zeolitic tuff had a surface area of 82 m2 g−1. The estimated zero charge point of the nanoparticle suspension was 3.2. The surface zeta potential was pH dependent. The Na-zeolitic nanotuff increased Cd sorption by a factor of up to 3 compared to the raw zeolitic tuff. Our results indicate that zeolitic nanoparticles can be produced by grinding using a mixture of fine beads in an attrition mill and that this procedure increases their metal immobilizing potential.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al, T. A., Martin, C. J., & Blowes, D. W. (2000). Carbonate-mineral/water interactions in sulfide-rich mine tailings. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(23), 3933–3948. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00483-X.
Alloway, B. J. (1995). Heavy metals in soils (2nd ed.). London: Chapman and Hall.
Ameyama, K., Hiromitsu, M., & Imai, N. (1998). Room temperature recrystallization and ultra fine grain refinement of an SUS316l stainless steel by high strain powder metallurgy process. Tetsu-To-Hagane/Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute (Japan), 84(5), 37–42.
Athanasiadis, K., & Helmreich, B. (2005). Influence of chemical conditioning on the ion exchange capacity and on kinetic of zinc uptake by clinoptilolite. Water Research, 39, 1527–1532. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.01.024.
Barrer, R. M. (1978). Zeolite s and clay minerals as sorbents and molecular sieves (pp. 65–70). London: Academic.
Baydina, N. L. (1996). Inactivation of heavy metals by humus and zeolites in industrially contaminated soils. Eurasain Soil Science, 28, 96–105.
Bhogal, A., Nicholson, F. A., Chambers, B. J., & Shepherd, M. A. (2003). Effects of past sewage sludge additions on heavy metal availability in light textured soils: Implications for crop yields and metal uptakes. Environmental Pollution, 121, 413–423. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00230-0.
Bilgili, E., Hamey, R., & Scarlett, B. (2004). Production of pigment nanoparticles using a wet stirred mill with polymeric media. China Particuology, 2(3), 93–100. doi:10.1016/S1672-2515(07)60032-3.
Brannvall, E. (2006). An experimental study on the use of natural zeolite for Cu, Pb and Zn immobilization in soil. Geologija, 56, 1–4.
Brar, T. (2000). Novel ways of synthesizing zeolite A. Master thesis, The University of Cincinnati, Kharagpur.
Bremmer, P. R., & Schultze, L. E. (1995). Ability of clinoptilolite rich tuffs to remove metal cations commonly found in acidic drainage. In D. W. Ming & F.A. Mumpton (Eds.), Natural zeolites’93: Occurrence, properties, use (pp. 397–403). New York: Brockport.
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H., & Teller, E. (1938). Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 60(2), 309–319. doi:10.1021/ja01269a023.
Carland, R. M., & Aplan, F. F. (1995). Improving the ion exchange capacity and elution of Cu2+ from natural sedimentary zeolites. Minerals & Metallurgical Processing, 12(4), 210–218.
Carmichael, W. (1994). The toxins of cyanobacteria. Scientific American, 170, 78–86.
Chlopecka, A., & Adriano, D. C. (1996). Mimicked in-situ stabilization of metals in a cropped soil: Bioavailability and chemical form of zinc. Environmental Science & Technology, 30, 3294–3303. doi:10.1021/es960072j.
Chlopecka, A., & Adriano, D. C. (1997). Influence of zeolite, apatite and Fe-oxide on Cd and Pb uptake by crops. The Science of the Total Environment, 207, 195–206. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(97)00268-4.
Choi, J. (2006). Geochemical modeling of cadmium sorption to soil as a function of soil properties. Chemosphere, 63, 1824–1834. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.10.035.
Cmielewska, H. E., & Lensy, J. (1995). Study of sorption equilibrium in the systems: water solutions of inorganic ions-clinoptilolite. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 201, 293–301. doi:10.1007/BF02164048.
De Castro, C. L., & Mitchell, B. S. (2003). Nanoparticles from mechanical attrition. In M. I. Baraton (Ed.), Synthesis, functionalization and surface treatment of nanoparticles (pp. 1–15). France: University of Limoges.
Decker, D. L., Papelis, C., Hershey, R. L., Harris, R., & Schmett, G. (2003). Temperature dependence of sorption behavior of lead and cesium metal ions on western Pahute Mesa and Reiner Mesa aquifer rocks. Report, Nevada Site Office National Nuclear Security Administration, U.S. Department of Energy, Las Vegas, Nevada, publication no. 45193.
Dutta, M. K., Pabi, S. K., & Murty, B. S. (2000). Thermal stability of nanocrystalline Ni silicides synthesised by mechanical alloying. Materials Science and Engineering A, 284, 219–225. doi:10.1016/S0921-5093(00)00774-7.
Eckert, J., Schultz, L., & Urban, K. (1989). Formation of quasicrystals by mechanical alloying. Applied Physics Letters, 55(2), 117–119. doi:10.1063/1.102394.
Eckert, J., Holzer, J. C., Krill, I. C. E., & Johnson, W. L. (1992). Structural and thermodynamic properties of nanocrystalline fcc metals prepared by mechanical attrition. Journal of Materials Research, 7(7), 1751–1761. doi:10.1557/JMR.1992.1751.
Edelstein, A. S., & Cammarata, R. C. (1996). Nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties and applications (p. 596). Bristol: Institute of Physics.
Fenn, M. E., Perea-Estrada, V. M., De Bauer, L. I., Perez-Suarez, M., Parker, D. R., & Centina-Alcala, V. M. (2006). Nutrient status and plant growth effects of forest soils in the basin of Mexico. Environmental Pollution, 140, 187–199. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.07.017.
Fernandez-Nieves, A., & de las Nieves, F. J. (1999). The role of ζ potential in the colloidal stability of different TiO2/electrolyte solution interfaces. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 148(3), 231–243. doi:10.1016/S0927-7757(98)00763-8.
Gabas, N., Hiquily, N., & Laguerie, C. (1994). Response of laser diffraction particle sizer to anisometric particles. Particle and Particle Systems Characterization, 11(2), 121–126. doi:10.1002/ppsc.19940110203.
Gao, S., Walker, W. J., Dahlgren, R. A., & Bold, J. (1997). Simultaneous sorption of Cd, Cu, Ni, Zn, Pb, and Cr on soils treated with sewage sludge supernatant. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 93(1–4), 331–345. doi:10.1007/BF02404765.
Garau, G., Castaldi, P., Santona, L., Deiana, P., & Melis, P. (2007). Influence of red mud, zeolite and lime on heavy metal immobilization, culturable heterotrophic microbial populations and enzyme activities in a contaminated soil. Geoderma, 142, 47–57. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.07.011.
Gatti, A. M., & Montanari, S. (2008). Nanopollution: The invisible fog of future wars. The Futurist, 42(3), 32–34.
Gessinger, G. H. (1984). Powder metallurgy of superalloys (1st ed., pp. 213–294). London: Butterworth.
Gleiter, H. (1989). Nanocrystalline materials. Progress in Materials Science, 33(4), 223–315. doi:10.1016/0079-6425(89)90001-7.
Gürel, A. (2006). Adsorption characteristics of heavy metals in soil zones developed on spilite. Environmental Geology, 51(3), 333–340.
Han, B. Q., Lavernia, E. J., & Mohamed, F. A. (2005). Mechanical properties of nanostructured materials. Reviews on Advanced Materials Science, 9(1), 1–16.
Hay, L. R., & Sheppard, A. R. (2001). Occurrence of zeolites in sedimentary rocks: an overview. In reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry, natural zeolites, occurrence, properties, applications. In D. L. Bish & D. W. Ming (Eds.), Reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry, vol 45 (pp. 217–234). Washington, DC: Mineralogical Society of America.
He, N., Xie, H.-b., & Ding, Y.-h. (2008). Computational study on IM-5 zeolite: What is its preferential location of Al and proton siting? Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 111(1–3), 551–559.
Hristovski, K. D., Westerhoff, P. K., Crittenden, J. C., & Olson, L. W. (2008). Arsenate removal by nanostructured ZrO2 spheres. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(10), 3786–3790.
Ichinose, N., Ozaki, Y., & Karsu, S. (1992). Superfine particle technology (p. 223). London: Springer.
Inglezakis, V. J., Diamandis, N. A., Loizidou, M. D., & Grigoropoulou, H. P. (1999). Effect of pore clogging on kinetics of lead uptake by clinoptilolite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 215, 54–57.
Ingwersen, J. (2001). The environmental fate of cadmium in the soils of the waste water irrigation area of Braunschweig. Ph.D. dissertation, Braunschweig University, 170p.
Ingwersen, J., & Streck, T. (2005). A regional-scale study on the crop uptake of cadmium from sandy soils: measurement and modeling. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 1026–1035.
Jankovic, A. (2003). Variables affecting the fine grinding of minerals using stirred mills. Minerals Engineering, 16(4), 337–345.
Kalantari, M. R., Shokrzadeh, M., Ebadi, A. G., Mohammadizadeh, C., Choudhary, M. I., & Atta-ur-Rahman, (2006). Soil pollution by heavy metals and remediation (Mazandaran-Iran). Journal of Applied Sciences, 6(9), 2110–2116.
Kimura, Y., Takaki, S., Suejima, S., Uemori, R., & Tamehiro, H. (1999). Ultra grain refining and decomposition of oxide during super-heavy deformation in oxide dispersion ferritic stainless steel powder. ISIJ International, 39(2), 176–182.
Knox, A. S., Kaplan, D. I., Adriano, D. C., Hinton, T. G., & Wilson, M. D. (2003). Apatite and phillipsite as sequestering agents for metals and radionuclide. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 515–525.
Koch, C. C. (1993). The synthesis and structure of nanocrystalline materials produced by mechanical attrition: A rev. Nanostructured Materials, 2(2), 109–129.
Koch, C. C., Cavin, O. B., McKamey, C. G., & Scarbrough, J. O. (1983). Preparation of “amorphous” Ni60Nb40 by mechanical alloying. Applied Physics Letters, 43(11), 1017–1019.
Kockrick, E., Krawiec, P., Petasch, U., Martin, H., Herrmann, M., & Kaskel, S. (2008). Porous CeOx/SiC nanocomposites prepared from reverse polycarbosilane-based microemulsions. Chemistry of Materials, 20(1), 77–83.
Kuhn, E. (1984). Powder metallurgy, ASM handbook, vol. 7 (pp. 56–70) Materials Park, OH: ASM International.
Laborde-Boutet, C., Joly, G., Nicolaos, A., Thomas, M., & Magnoux, P. (2006). Selectivity of thiophene/toluene competitive adsorptions onto zeolites. Influence of the alkali metal cation in FAU(Y). Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 45(24), 8111–8116.
Liang, P., Qin, Y., Hu, B., Li, C., Peng, T., & Jiang, Z. (2000). Study of the adsorption behavior of heavy metal ions on nanometer-size titanium dioxide with ICP-AES. Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 368, 638–640.
Madrid, F., Diaz-Barrientos, E., & Florido, M. C. (2008). Inorganic amendments to decrease metal availability in soil of recreational urban areas: limitations to their efficiency and possible drawbacks. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 192, 117–125.
Marconi, A. (2006). Fine, ultrafine particles and nanoparticles in ambient and work environments: Possible health effects and measure of inhaled exposure [Particelle fini, ultrafini e nanoparticelle in ambiente di vita e di lavoro: Possibili effetti sanitari e misura dell’esposizione inalatoria]. Giornale Italiano di Medicina del Lavoro ed Ergonomia, 28(3), 258–265.
McBirde, M. B. (1994). Environmental chemistry of soils (p. 406). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Morais, W. A., Fernandes, A. L. P., Dantas, T. N. C., Pereira, M. R., & Fonseca, J. L. C. (2007). Sorption studies of a model anionic dye on crosslinked chitosan. Colloids Surf., A, 310(1–3), 20–31.
Mumpton, F. A. (1977). Mineralogy and geology of natural zeolites, vol. 4 (pp. 1–15). Washington: Mineralogical Society of America.
Naidu, R., Bolan, N. S., Kookana, R. S., & Tiller, K. G. (1994). Ionic-strength and effects on the sorption of cadmium and the surface charge of soils. European Journal of Soil Science, 45, 419–429.
Nichols, W. T., Kodaira, T., Sasaki, Y., Shimizu, Y., Sasaki, T., & Koshizaki, N. (2006). Zeolite LTA nanoparticles prepared by laser-induced fracture of zeolite microcrystals. Journal of Physical Chemistry, B, 110(1), 83–89.
Nissen, L. R., Leppy, N. W., & Edwards, R. (2000). Synthetic zeolites as amendments for sewage sludge-based compost. Chemosphere, 41, 265–269.
Oste, L. A., Lexmond, T. M., & Van Riemsdijk, W. H. (2002). Metal immobilization in soils using synthetic zeolites. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 813–821.
Perez, J., Bax, L., & Escolano, C. (2004). Roadmaps at 2015 on nanotechnology application in the sectors of: materials, health and medical systems, energy. Report prepared by Willems &van den Wildenberg.
Purves, D. (1985). Trace-element contamination of the environment. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Puschenreiter, M., Horak, O., Friesl, W., & Hartl, W. (2005). Low-cost agricultural measures to reduce heavy metal transfer into the food chain—a review. Plant, Soil Environ, 51(1), 1–11.
Querol, X., Alastuey, A., Moreno, N., Alvarez-ayuso, E., Garacia-Sanchez, A., Cama, J., Ayora, C., & Simon, M. (2006). Immobilization of heavy metals in polluted soils by the addition of zeolitic material synthesized from coal fly ash. Chemoshere, 62, 171–180.
Riddick, T. (1968). Control of colloid stability through zeta potential; with a closing chapter on its relationship to cardiovascular disease. Wynnewood, PA: Livingston. Published for ZETA–METER, INC. 372p.
Rumpf, H. (1962). The strength of granules and agglomerates. In W. Knepper (Ed.), Agglomeration (pp. 281–304). New York: Wiley.
Schultz, L. (1988). Formation of amorphous metals by mechanical alloying. Materials Science and Engineering, 97, 15–23.
Seaton, A. (2007). Nanotoxicology: Hazard and risk. PulPaper 2007 Conference: Innovative and sustainable use of forest resources, 1 p
Sekara, A., Poniedzialek, M., Ciura, J., & Jedrszczyk, E. (2005). Cadmium and lead accumulation and distribution in the organs of nine crops: implications for phytoremediation. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 14(4), 509–516.
Siegel, R. W. (1991). Cluster-assembled nanoparticles materials. Annual Review of Material Science, 21, 559–578.
Singh, B. R., & Oste, L. (2001). In situ immobilization of metals in contaminated or naturally metal-rich soils. Environmental Review, 9, 81–97.
Sposito, G. (1984). The surface chemistry of soil, vol. 231 (pp. 78–106). New York: Oxford University Press.
Sposito, G. (1989). The chemistry of soils. New York: Oxford University Press.
Springob, G., & Böttcher, J. (1998). Parameterization and regionalization of Cd sorption characteristics of sandy soils. I. Freundlich type parameters. Zeitschrift fuÉr PflanzenernaÉhrung und Bodenkunde, 161, 681–687.
Sprynskyy, M., Kosobucki, T., Kowalkowski, B., & Buszewski, B. (2007). Influence of clinoptilolite rock on chemical speciation of selected heavy metals in sewage sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 149, 310–316.
Streck, T., Poletika, N. N., Jury, W. A., & Farmer, W. J. (1995). Description of simazine transport with rate-limited, two-stage, linear and nonlinear sorption. Water Resources Research, 31(4), 811–822.
Tellkamp, V. L., Melmed, A., & Lavernia, E. J. (2001). Mechanical behavior and microstructure of a thermally stable bulk nanostructured Al alloy. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions. A, Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 32(9), 2335–2343.
Tjong, S. C., & Chen, H. (2004). Nanocrystalline materials and coatings. Materials Science and Engineering R: reports, 45(1–2), 88.
Tsitsishvili, G. V., Andorikashvili, T. G., Kirov, G. N., & Filizova, L. D. (1992). Natural zeolites. New York: Horwood.
Van Heyden, H., Mintova, S., & Bein, T. (2008). Nanosized SAPO-34 synthesized from colloidal solutions. Chemistry of Materials, 20(9), 2956–2963.
Voegelin, A., & Kretzschmar, R. (2003). Modelling sorption and mobility of cadmium and zinc in soils with scaled exchange coefficients. European Journal of Soil Science, 54(2), 387–400.
Wang, X. K., Chen, C. L., Du, J. Z., Tan, X. L., Xu, D., & Yu, S. M. (2005). Effect of pH and aging time on the kinetic dissociation of 243Am(III) from humic acid coated γ-Al2O3: A chelating resin exchange study. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 7084–7088.
Way, H. W. (2004). Grinding and dispersing nanoparticles. JCT, Journal of Coatings Technology, 1(1), 54–60.
Weber, M. A., Barbarick, K. A., & Westfall, D. G. (1984). Application of clinoptilolite to soil amended with municipal sludge. In W. G. Pond, & F. A. Mumpton (Eds.), Zeo-agriculture, use of natural zeolite in agriculture and aquaculture (1st ed., pp. 263–271). Boulder, CO: Westview.
Wu, W., Fan, Q., Xu, J., Niu, Z., & Lu, S. (2007). Sorption–desorption of Th(IV)on attapulgite: effects of pH, ionic strength and temperature. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 65, 1108–1114.
Zamzow, M. J., Eichbaum, R., Sandgren, K. R., & Shanks, D. E. (1990). Removal of heavy metals and other cations from wastewater using zeolites. Separation Science and Technology, 25, 1555–1569.
Zhang, W. (2003). Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: An overview. Journal Of Nanoparticle Research, 5, 323–332.
Zhang, Y., Yu, X., Wang, X., Shan, W., Yang, P., & Tang, Y. (2004). Zeolite nanoparticles with immobilized metal ions: isolation and MALDI-TOF-MS/MS identification of phosphopeptides. Chemical Communications, 2882–2883.
Zheng, J., Harris, C. C., & Somasundaran, P. (1996). A study on grinding and energy input in stirred media mills. Powder Technology, 86(2), 171–178.
Zorpas, A. A., Arapoglou, D., & Panagiotis, K. (2003). Waste paper and clinoptilolite as a bulking material with dewatered anaerobically stabilized primary sewage sludge (DASPSS) for compost production. Waste Manager, 23, 27–35.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express thanks for the support of Prof. Dr. F. Aldinger and Dr. J. Bill from the Max-Planck Institute for Metal Research (Stuttgart, Germany) during many fruitful discussions and for providing the attrition ball mill and testing the nanoparticle powder. This research was supported by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghrair, A.M., Ingwersen, J. & Streck, T. Nanoparticulate Zeolitic Tuff for Immobilizing Heavy Metals in Soil: Preparation and Characterization. Water Air Soil Pollut 203, 155–168 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-9999-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-9999-6