Abstract
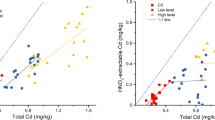
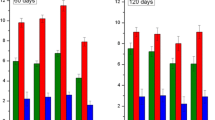
About 170 million tons of phosphogypsum (PG) are annually generated worldwide as a by-product of phosphoric acid factories. Agricultural uses of PG could become the main sink for this waste, which usually contains significant radionuclide (from the 238U-series) and toxic metals concentrations. To study PG effects on pollutant uptake by crops, a completely randomised greenhouse experiment was carried out growing Lycopersicum esculentum Mill L. on a reclaimed marsh soil amended with three PG rates (treatments), corresponding to zero (control without PG application), one, three and ten times the typical PG rates used in SW Spain (20 Mg ha−1). The concentrations of Cd, Pb, U (by inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy) and 226Ra and 210Po (by γ-spectrometry and α-counting, respectively) were determined in soil, vegetal tissue and draining water. Cadmium concentrations in fruit increased with PG rates, reaching 44 ± 7 μg kg−1 formula weight with ten PG rates (being 50 μg kg−1 the maximum allowed concentration by EC 1881/2006 regulation). Cd transfer factors in non-edible parts were as high as 4.8 ± 0.5 (dry weight (d.w.)), two orders of magnitude higher than values found for lead, lead, uranium and radium concentrations in fruit remained below the corresponding detection limits—0.5 and 0.25 mg kg−1 and 0.6 mBq kg−1, respectively (in a d.w. basis). 238U (up to 7 μg kg−1 d.w.) and 210Po (up to 0.74 Bq kg−1 d.w.) could be measured in some fruit samples by α-spectrometry. Overall, the concentrations of these metals and radionuclides in the draining water accounted for less than 1% of the amount applied with PG.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abril, J. M., García-Tenorio, R., Enamorado, S. M., Hurtado, M. D., Andreu, L., & Delgado, A. (2008). The cumulative effect of three decades of phosphogypsum amendments in reclaimed marsh soils from SW Spain: 226Ra, 128U and Cd contents in soils and tomato fruit. The Science of the Total Environment, 403, 80–88.
Barnett, M. O., Jardine, P. M., Brooks, S. C., & Selim, H. M. (2000). Absorption and transport of U(VI) in subsurface media. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 64, 908–917.
Bolivar, J. P., Garcia-Tenorio, R., & Garcia-Leon, M. (1995). Enhancement of natural radioactivity in soils and salt-marshes surrounding a non-nuclear industrial complex. The Science of the Total Environment, 173/174, 125–136. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)04735-2.
Bostick, B. C., Fendorf, S., Barnett, M. O., Jardine, P. M., & Brooks, S. C. (2002). Uranyl surface complexes formed on subsurface media from DOE facilities. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 66, 99–108.
Campbell, C. G., Garrido, F., Illera, V., & García-González, M. T. (2005). Transport of Cd, Cu and Pb in an acid soil amended with phosphogypsum, sugar foam and phosphoric rock. Applied Geochemistry, 21, 1030–1043. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.02.023.
Chen, F., Wu, F., Dong, J., Vincze, E., Zhang, G., Wang, F., et al. (2007). Cadmium translocation and accumulation in developing barley grains. Planta, 227, 223–232. doi:10.1007/s00425-007-0610–3.
Choi, J. (2006). Geochemical modelling of cadmium sorption to soil as a function of soil properties. Chemosphere, 63, 1824–1834. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.10.035.
De Haro, J. (2006). Efectos de la aplicación de enmiendas de fosfoyeso en los contenidos de radionúclidos y metales pesados en suelos agrícolas de las marismas de Lebrija. Seville: Escuela de Ingeniería Técnica Agrícola, University of Seville (in Spanish).
Delgado, A., Hurtado, M. D., & Andreu, L. (2006). Phosphorus loss in tile drains from a reclaimed marsh soil amended with manure and phosphogypsum. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 74, 191–202. doi:10.1007/s10705-005-6240-x.
Domínguez, R., Campillo, M. C., Peña, F. P., & Delgado, A. (2001). Effect of soil properties and reclamation practices on phosphorus dynamics in reclaimed calcareous marsh soils from the Guadalquivir Valley, SW Spain. Arid Land Research and Management, 15, 203–221. doi:10.1080/15324980152119775.
El-Mrabet, R., Abril, J. M., Periáñez, R., Manjón, G., García-Tenorio, R., Delgado, A., et al. (2003). Phosphogypsum amendment effect on radionuclide content in drainage water and marsh soils from southwestern Spain. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 1262–1268.
Florian, D., Barnes, R. M., & Knapp, G. (1998). Comparison of microwave-assisted acid leaching techniques for the determination of heavy metals in sediments, soils, and sludges. Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 362, 558–565. doi:10.1007/s002160051124.
Gelinas, Y., Barnes, R. M., Florian, D., & Schmit, J. P. (1998). Acid leaching of metals from environmental particles: Expressing results as a concentration within the leachable fraction. Environmental Science & Technology, 32, 3622–3627. doi:10.1021/es980092g.
Holland, H. D., & Turekian, K. K. (Eds.) (2005). Environmental geochemistry. In: Treatise on geochemistry, vol. 9. Oxford: Pergamon.
International Union of Radioecologists. (1994). Handbook of parameter values for the prediction of radionuclide transfer in temperate environments. Technical reports series no. 364. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency.
Jones, J. B., & Case, V. W. (1990). Sampling, handling and analyzing plant tissue samples. In R. L. Westerman (Ed.), Soil testing and plant analysis. Madison, U.S.A.: Soil Science Society of America.
Köhler, M., Gleisberg, B., & Niese, S. (2000). Investigation of the soil-plant transfer of primordial radionuclides in tomatoes by low-level γ-ray spectrometry. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 53, 203–208. doi:10.1016/S0969-8043(00)00134-2.
Link, D. D., Walter, P. J., & Kingston, H. M. (1998). Development and validation of the new IPA microwave-assisted beach method 3051A. Environmental Science & Technology, 32, 3628–3632. doi:10.1021/es980559n.
Martínez-Aguirre, A., & Periáñez, R. (1998). Soil to plant transfer of 226Ra in a marsh area: modelling application. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 39, 199–213. doi:10.1016/S0265-931X(97)00048-9.
Mas, J. L., San Miguel, E. G., Bolívar, J. P., Vaca, F., & Pérez-Moreno, J. P. (2006). An assay on the effect of preliminary restoration tasks applied to a large TENORM wastes disposal in the south-west of Spain. The Science of the Total Environment, 364, 55–66. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.11.006.
May, D. A., & Mortvedt, J. E. (1986). Crop response to soil applications of phosphogypsum. Journal of Environmental Quality, 15, 78–81.
Miretzky, P., & Fernández-Cirelli, A. (2008). Phosphate for Pb immobilization in soils: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 6, 121–133. doi:10.1007/s10311-007-0133-y.
Mullins, G. L., Mitchell, C. C. (1990). Use of phosphogypsum to increase yield and quality of annual forages. Publication no 01-048-084. Bartow: Florida Institute of Phosphate Research.
Oster, J. D., Shainberg, I., & Abrol, I. P. (1999). Reclamation of salt-affected soils. In R. W. Skaggs, & J. van Schilfgaarde (Eds.), Agricultural drainage (pp. 659–691). Madison, Wisconsin: Soil Science Society of America.
Pérez-López, R., Álvarez-Valero, A. M., & Nieto, J. M. (2007). Changes in mobility of toxic elements during the production of phosphoric acid in the fertilizer industry of Huelva (SW Spain) and environmental impact of phosphogypsum wastes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 148, 745–750. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.068.
Periáñez, R., & García-León, M. (1993). Ra-isotopes around a phosphate fertilizer complex in an estuarine system at the southwest of Spain. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 172, 71–79. doi:10.1007/BF02040663.
Pett-Ridge, J. C., Monastra, V. M., Derry, L. A., & Chadwick, O. A. (2007). Importance of atmospheric inputs and Fe-oxides in controlling soil uranium budgets and behavior along a Hawaiian chronosequence. Chemical Geology, 244, 691–707. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.07.016.
Rutherdord, P. M., Dudas, M. J., & Samek, R. A. (1994). Environmental impacts of phosphogypsum. The Science of the Total Environment, 149, 1–38. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(94)90002-7.
Rios-Arana, J. V., Walsh, J. E., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2004). Assessment of arsenic and heavy metal concentrations in water and sediments of the Rio Grande at El Paso-Juarez metroplex region. Environment International, 29, 957–971. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00080-1.
Soil Survey Staff (1998). Keys to soil taxonomy (8th ed.). Washington: US Government Print Office.
Thakur, S. K., Tomar, N. K., & Pandeya, S. B. (2006). Influence of phosphate on cadmium sorption by calcium carbonate. Geoderma, 130, 130–139. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.01.026.
Tsukada, H., & Nakamura, Y. (1998). Transfer factors of 31 elements in several agricultural plants collected from 150 farm fields in Aomori, Japan. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 236, 123–131. doi:10.1007/BF02386329.
Uchida, S., Tagami, K., & Hirai, I. (2007). Soil-to-plant transfer factors of stable elements and naturally occurring radionuclides (1) Upland field crops collected in Japan. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44, 628–640. doi:10.3327/jnst.44.628.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1994). Method 200.8. Determination of trace elements in waters and wastes by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Revision 5.4. Cincinnati, OH: Office of Research and Development, USEPA 2002.
Vandenhove, H., Eyckmans, T., & van Hees, M. (2005). Can barium and strontium be used as tracers for radium in soil-plant transfer studies? Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 81, 255–267. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2004.01.039.
Vandenhove, H., van Hees, M., Wouters, K., & Wannijn, J. (2007). Can we predict uranium bioavailability based on soil parameters? Part 1: Effect of soil parameters on soil uranium concentration. Environmental Pollution, 145, 587–595. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.04.011.
Voegelin, A., Vulava, V. M., & Kretzschmar, R. (2001). Reaction-based model describing competitive sorption and transport of Cd, Zn, and Ni in an acidic soil. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 1651–1657. doi:10.1021/es0001106.
Wazne, M., Korfiatis, G. P., & Meng, X. G. (2003). Carbonate effects on hexavalent uranium adsorption by iron oxyhydroxide. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 3619–3624. doi:10.1021/es034166m.
Wolterbeek, H. Th., van der Meer, A., & de Bruin, M. (1988). The uptake and distribution of cadmium in tomato plants as affected by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and 2,4-dinitrophenol. Environmental Pollution, 55, 301–315. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(88)90252-7.
Zhang, X. C., Miller, W. P., Nearing, M. A., & Norton, L. D. (1998). Effects of surface treatment on surface sealing, runoff, and interril erosion. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 41(4), 989–994.
Acknowledgments
The authors are deeply grateful to Dr. S. Hurtado and Dr. M. Villa (Service of Radioisotopes, CITIUS, University of Seville) for the radionuclide radiometric analyses. This work was funded by ENRESA (Spanish Public Corporation of Radioactive Residues) and by the IFAPA-C039 project from the regional Andalusia government. Authors wish also to thank to the Agriculture Cooperatives “Las Marismas” and “La Amistad” for making available some facilities and the experimental site.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enamorado, S., Abril, J.M., Mas, J.L. et al. Transfer of Cd, Pb, Ra and U from Phosphogypsum Amended Soils to Tomato Plants. Water Air Soil Pollut 203, 65–77 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-9992-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-9992-0