Abstract
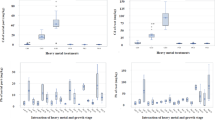
Two varieties of Bechmeria nivea (L.) Gaud. (Ramie), namely, triploid Tri-2 and diploid Xiangzhu-3, were potted with soils from Guangdong for 15 weeks and treated with 10 mmol kg−1 EDTA or EGTA before harvest at 17th week. Lead, Zn, and Cd in plant and soil materials were analyzed, and their potential ecological risk in soils was simultaneously evaluated. These three metals in soils was found to be above 14.4, 3.0, and 29.9 times higher than the national (China) background value, 10.9, 6.19, and 96.7 times higher than the local (Guangdong) background value, and 1.25, 1.20, and 9.67 times higher than the maximum permissible concentration for soils, respectively. An ecological risk analysis of metals using Häkanson's method indicated an extremely high contamination and a significantly high potential ecological risk by these three metals in soils. The both ramie varieties contained respective concentration exceeding the concentration of <10, <80, and <0.27 mg kg−1, respectively, for Pb, Zn, and Cd in normal plants, suggesting they were multimetal tolerant. Tri-2 generally contained higher Pb, Zn, and Cd than Xiangzhu-3. Treatment with EDTA or EGTA applied at 10 mmol kg−1 generally promoted Pb or Cd concentration in both plants while the uptake of Zn was depressed. The ramie variety of Tri-2 and Xiangzhu-3 could extract 0.161 and 0.147 t ha−1 of Cd, respectively, equaling to the 0.17 t Cd per hectare by Cd-hyperaccumulating species Viola baoshanensis. Therefore, two ramie varieties in this study had a higher extracting potential for removal of Cd from contaminated soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adesodun, J. K., Atayese, M. O., Agbaje, T. A., Osadiaye, B. A., Mafe, O. F., & Soretire, A. A. (2009). Phytoremediation potentials of sunflowers (Tithonia diversifolia and Helianthus annuus) for metals in soils contaminated with zinc and lead nitrates. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution. doi:10.1007/s11270-009-0128-3.
Allen, S. E. (1989). Chemical analysis of ecological materials. Oxford: Blackwell.
Baker, A. J. M., McGrath, S. P., Sidoli, C. M. D., & Reeves, R. D. (1994). The possibility of in situ heavy metal decontamination of polluted soils using crops of metal-accumulating plants. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 11, 41–49.
Brown, S. L., Chaney, R. L., Angle, J. S., & Baker, A. J. M. (1995). Zinc and cadmium uptake by hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens grown in nutrient solution. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 59, 125–133.
Cambra, K., Martinez, T., Urzelai, A., & Alonso, E. (1999). Risk analysis of area near a lead-and cadmium-contaminated industrial site. Journal of Environmental Health, 8, 527–540.
Cao, D. J., Zhou, S. B., & Xiang, J. (2004). Ramie tolerance to Cd in soil and its accumulation effect. Plan Fibers and Product, 26, 272–274.
CEPA (Chinese Environmental Protection Administration). (1990). Elemental background values of soils in China (pp. 2–3). Beijing: Environmental Science Press of China.
CEPA (Chinese Environmental Protection Administration). (1995). Environmental Quality Standard for Soils (GB 15618–1995).
Chen, H., & Cutright, T. (2001). EDTA and HEDTA effects on Cd, Cr, and Ni uptake by Helianthus annuus. Chemosphere, 45, 21–28.
Chen, H. M., Zheng, C. R., Tu, C., & Zhu, Y. G. (1999). Heavy metal pollution in soils in China: status and countermeasures. Ambio, 28, 130–134.
Cooper, E. M., Sims, J. T., Cunningham, S. D., Huang, J. W., & Berti, W. R. (1999). Chelate-assisted phytoextraction of lead from contaminated soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 28, 1709–1719.
Dudka, S., & Adriano, D. C. (1997). Environmental impacts of metal ore mining and processing: a review. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26, 590–602.
Epstein, A. L., Gussman, C. D., Blaylock, M. J., Yermiyahu, U., Huang, J. W., Kapulnik, Y., et al. (1999). EDTA and Pb-EDTA accumulation in Brassica juncea grown in Pb-amended soil. Plant and Soil, 208, 87–94.
Gupta, U. C., & Gupta, S. C. (1998). Trace element toxicity relationships to crop production and livestock and human health: implications for management. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 29, 1491–1522.
Häkanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
Hammer, D., & Keller, C. (2003). Phytoextraction of Cd and Zn with Thlaspi caerulescens in field trials. Soil Use and Management, 19, 144–149.
Huang, J. W., Chen, J., Berti, W. B., & Cunningham, S. D. (1997). Phytoremediation of lead-contaminated soils: role of synthetic chelates in lead phytoextraction. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 800–805.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Pendias, H. (1992). Trace elements in soils and plants. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Kumar, N. P. B. A., Dushenkov, V., Motto, H., & Raskin, I. (1995). Phytoextraction: the use of plants to remove heavy metals from soils. Environmental Science and Technology, 29, 1232–1238.
Li, X. Y., Zuo, C. S., Tschirley, J. B., Webb, S. E., & Morton, A. (1997). Sustainable agriculture and rural development in China, Part 1: the agro-ecosystem and China's rural economy. In Promotion of Sustainable Agriculture and Rural Development in China: Elements for a Policy Framework and a Notional Agenda 21 Action Programme, FAO/UNDP/Ministry of Agriculture, China.
Liphadzi, M. S., Kirkham, M. B., Mankin, K. R., & Paulsen, G. M. (2003). EDTA-assisted heavy-metal uptake by poplar and sunflower grown at a long-term sewage-sludge farm. Plant and Soil, 257, 171–182.
McGrath, S. P., & Zhao, F. J. (2003). Phytoextraction of metals and metalloids from contaminated soils. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 14, 277–282.
Michael, J. B., & Huang, J. W. (2000). Phytoextraction of metals. In I. Raskin & B. D. Ensley (Eds.), Phytoremediation of toxic metals using plants to clean up the environment (pp. 53–70). New York: John Wiley.
Peralta-Videa, J. R., Gardea-Torresdey, J. L., Gomez, E., Tiemann, K. J., Parsons, J. G., & Carrillo, G. (2002). Effect of mixed cadmium, copper, nickel, and zinc at different pHs upon alfalfa growth and heavy metal uptake. Environmental Pollution, 119, 291–301.
Steele, M. C., & Pichtel, J. (1998). Ex-situ remediation of a metal-contaminated Superfund soil using selective extractants. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 124, 639–645.
Turgut, C., Pepe, M. K., & Cutright, T. J. (2004). The effect of EDTA and citric acid on phytoremediation of Cd, Cr, and Ni from soil using Helianthus annuus. Environmental Pollution, 131, 147–154.
Wang, K. R., & Gong, H. Q. (1998). Abstraction and the effect of cleaning up of ramie (Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaud.) on soil cadmium. Acta Sci Cirum Stantiae, 5, 510–518.
Wang, X., Liu, Y. G., Zeng, G. M., Chai, L. Y., Song, X. C., Min, Z. Y., et al. (2008). Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in Bechmeria nivea (L.) Gaud. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 62, 389–395.
Wong, S. C., Li, X. D., Zhang, G., Qi, S. H., & Min, Y. S. (2002). Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environmental Pollution, 119, 33–44.
Xu, L. F., & Liu, T. H. (1996). The zonal differentiation of soil environmental background values and critical concentrations in Guangdong Province China (in Chinese). Journal of South China Agricultural University, 17, 58–62.
Xu, Y., Jie, Y. C., Sun, Z. M., & Leng, J. (2005). A study on ramie adaptability to Cd polluted soil (in Chinese). Plant Fibers and Products, 27, 249–253.
Yang, R. F., Cui, G. X., Guo, Q. Q., & Zheng, S. X. (2007). Breeding reports on new ramie varieties of triploid Tri-1 and Tri-2. Hunan Agricultural Science, 2(29), 30.
Yue, Q. L. (2004). Study on heavy metal of soils and plants in mining in Hu Nan. Master Thesis, Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry, Yangling, PR China.
Zhao, F. J., Lombi, E., & McGrath, S. P. (2003). Assessing the potential for zinc and cadmium phytoremediation with the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant and Soil, 249, 37–43.
Zhou, J. H. (2008). Study on the effect of chelating agents on absorption and accumulation of heavy metal in ramie and its mechanism. Ph D thesis, Zhongshan University, Guangzhou, PR China.
Zhuang, P., Ye, Z. H., Lan, C. Y., Xie, Z. W., & Shu, W. S. (2005). Chemically assisted phytoextraction of heavy metals contaminated soils using three plant species. Plant and Soil, 276, 153–162.
Zhuang, P., Yang, Q. W., Wang, H. B., & Shu, W. S. (2007). Phytoextraction of heavy metals by eight plant species in the field. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 184, 235–242.
Acknowledgments
Supports for this work were provided by the National Natural Science Fund of China (no. 30770417 and 40871222), Natural Science Foundation Project of CQ CSTC (CSTC, 2009BA7029, 2006BB7424), and Science Foundation of Chongqing Educational Committee (KJ050410, KJ060412).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Jh., Yang, Qw., Lan, Cy. et al. Heavy Metal Uptake and Extraction Potential of Two Bechmeria nivea (L.) Gaud. (Ramie) Varieties Associated with Chemical Reagents. Water Air Soil Pollut 211, 359–366 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0305-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0305-4