Abstract
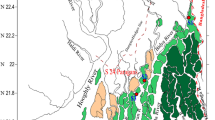
Sediment pollution by metals is of high interest considering that it can affect marine life. The estuaries' quality may be reflected by the environmental intertidal zone condition. Subsurface sediments collected at the nude tidal flats from three sampling stations in the Bahía Blanca Estuary were analyzed for total metals concentrations (Hg, Cd, Pb, and Cr), distribution, and geochemical partitioning. Most of the elements (Hg, Cd, and Cr) have shown highest concentration values in the industrial-influenced area. Maximum value of Pb was obtained where the main freshwater input discharges. Intertidal sediments have presented higher values of Cr than the subtidal ones. Cd and Pb contents near the industrial area were strongly higher in the subtidal zones. The distribution of Cd and Pb demonstrated the occurrence of a diffusion pattern from the land toward the sea, showing a dependence on both the metal itself and/or the source. Not all studied metals have shown the highest content in the fine fraction. The chemical partitioning in the fine fractions offered evidence that the tidal flats were an important source as well as sink of metals to the adjacent coastal area. The studies of intertidal sediments provide an integrative knowledge on the potential effects of different trace metals in the environment and they must be used in the contamination studies within coastal areas.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamo, P., Arienzo, M., Imperato, M., Naimo, D., Nardi, G., & Stanzione, D. (2005). Distribution and partition of heavy metals in surface and sub-surface sediments of Naples city port. Chemosphere, 61, 800–809.
Amín, O., Ferrer, L., & Marcovecchio, J. (1996). Heavy metal concentrations in littoral sediments from the Beagle Channel, Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 41, 219–231.
Andrade, S., Pucci, A., & Marcovecchio, J. E. (2000). Cadmium concentrations in the Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Potential effects of dissolved cadmium on the diatom Thalassiosira curviseriata. Oceanologia, 42, 505–520.
Andrade, S., Poblet, A., Scagliola, M., Vodopivez, C., Curtosi, A., Pucci, A., et al. (2001). Distribution of heavy metals in surface sediments from an Antarctic marine ecosystem. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 66, 147–158.
Baptista Neto, J. A., Smith, B. J., & McAllister, J. J. (2000). Heavy metal concentrations in surface sediments in a nearshore environment, Jurujuba Sound, Southest Brazil. Environmental Pollution, 109, 1–9.
Bilos, C., Colombo, J. C., & Rodríguez Presa, M. J. (1998). Trace metals in suspended particles, sediments and Asiatic clams (Corbicula fluminea) of the Río de la Plata Estuary, Argentina. Environmental Pollution, 99, 1–11.
Bokuniewicz, H. (1995). Sedimentary systems of coastal plain estuaries. In G. M. E. Perillo (Ed.), Geomorphology and sedimentology of estuaries. Developments in sedimentology (Vol. 53, pp. 49–67). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Botté, S. E., Freije, R. H., & Marcovecchio, J. E. (2007). Dissolved heavy metal (Cd, Pb, Cr, Ni) concentrations in surface water and porewater from Bahía Blanca estuary tidal flats. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 79, 415–421.
Buggy, C. J. & Tobin, J. M. (2008). Seasonal and spatial distribution of metals in surface sediment of an urban estuary. Environmental Pollution, 155, 308–319.
Caccia, V. G., Millero, F. J., & Palanques, A. (2003). The distribution of trace metals in Florida Bay sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 46, 1420–1433.
CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers of the environment) (1999). Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: Cadmium. In Canadian environmental quality guidelines, 1999, Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg.
Conaway, C. H., Squire, S., Mason, R. P. & Flegal, A. R. (2003). Mercury speciation in the San Francisco Bay estuary. Marine Chemistry, 80, 199–225.
Dalziel, J. & Baker, C. (1983). Métodos analíticos para medir la presencia de metales mediante espectrofotometría de absorción atómica. FAO, Documento Técnico de Pesca, 212, 15–22.
De Marco, S., Botté, S. E., & Marcovecchio, J. (2006). Mercury distribution in abiotic and biological compartments within several estuarine systems from Argentina: 1980–2005 period. Chemosphere, 65, 213–223.
Emmerson, R. H. C., O'Reilly-Weise, S. B., Macleod, C. L., & Lester, J. N. (1997). A multivariate assessment of metal distribution in inert-tidal sediments of the Blackwater Estuary, UK. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34, 960–968.
Federal Register (1984). Definition and procedure for determination of the method detection limit, EPA, 40 CFR Part 136, Appendix B, Revision 1.11, pp. 198–199.
Fernández Severini, M. D., Botté, S. E., Hoffmeyer, M., & Marcovecchio, J. E. (2009). Spatial and temporal distribution of cadmium and copper in water and zooplankton in the Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 85, 57–66. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2009.03.019.
Ferrer, L. D. (2001). Estudio de diversos metales pesados en sedimentos del estuario de Bahía blanca y sus efectos tóxicos sobre el cangrejo Chasmagnathus granulata. Doctoral Thesis, Univerisidad Nacional del Sur, Argentina, 213 pp.
Ferrer, L., Contardi, E., Andrade, S. J., Asteasuain, R., Pucci, A. E., & Marcovecchio, J. E. (2000). Environmental cadmium and lead concentrations in the Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Potential toxic effects of Cd and Pb on crab larvae. Oceanologia, 42, 493–504.
Freije, R. H. & Marcovecchio, J. E. (2004). Oceanografía química. In M. C. Piccolo & M. Hoffmeyer (Eds.), Ecosistema del estuario de bahía blanca (pp. 69–78). Argentina: Bahía Blanca.
Gelós, E. M., Marcos, A. O., Spagnuolo, J. O., & Schillizzi, R. A. (2004). Textura y mineralogía de sedimentos. In M. C. Piccolo & M. Hoffmeyer (Eds.), Ecosistema del estuario de bahía blanca (pp. 43–50). Argentina: Bahía Blanca.
Giordano, R., Musmeci, L., Ciaralli, I., Vernillo, M., Chirico, A., Piccioni, A., et al. (1992). Total contents and sequential extractions of mercury, cadmium, and lead in coastal sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 24, 350–357.
Grecco, L. E., Marcos, A. O., Gómez, E. A., Botté, S. E., & Marcovecchio, J. E. (2006). Natural and anthropogenic input of heavy metals in sediments from Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Journal of Coastal Research, SI 39 (Proceedings of the 8th International Coastal Symposium), 1021–1025.
Hempel, M., Botté, S. E., Negrin, V. L., Chiarello, M. N., & Marcovecchio, J. E. (2008) The role of the smooth cordgrass Spartina alterniflora and associated sediments in the heavy metal biogeochemical cycle within Bahía Blanca estuary salt marshes. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 8, 289–297.
Hylander, L. D., Maili, M., Oliveira, L. J., de Castro e Silva, E., Guimarães, J. R. D., Araujo, D. M., et al. (2000). Relationship of mercury with aluminum, iron and manganese oxy-hydroxides in sediments from the Alto Pantanal, Brazil. Science of the Total Environment, 260, 97–107.
Ip, C. C. M., Li, X.-D., Zhang, G., Wai, O. W. H., & Li, Y.-S. (2007). Trace metal distribution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the surrounding coastal area, South China. Environmental Pollution, 147, 311–323.
Jones, R. P., & Clarke, J. U. (2005). Analytical chemistry detection limits and the evaluation of dredged sediment. ERDC/TN EEDP-04-36, U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center, Vicksburg, MS.
Krumbein, W. C. & Pettijohn, F. J. (1938). Manual of sedimentary petrography. New York: Appleton–Century–Crofts.
Lacerda, L. D., Souza, C. M. M., & Pestana, M. H. D. (1988). Geochemical distribution of Cd, Cu, Cr, and Pb in sediment of estuarine areas along the Southeastern Brazilian coast. In U. Seeliger, L. D. Lacerda & S. R. Patchineelam (Eds.), Metals in coastal environments of Latin America (pp. 86–99). Berlin: Springer.
Maddock, J. E. L. & Lopes, C. E. A. (1988). Behavior of pollutant metals in aquatic sediments. In U. Seeliger, L. D. Lacerda & S. R. Patchineelam (Eds.), Metals in coastal environments of Latin America (pp. 100–105). Berlin: Springer.
Marcovecchio, J. E. & Ferrer, L. D. (2005). Distribution and geochemical partitioning of heavy metals in sediments of the Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Journal of Coastal Research, 21, 826–834.
Marcovecchio, J. E., Lara, R. J., & Gómez, E. (1986). Total mercury in marine sediments near a sewage outfall. Relation with organic matter. Environmtal Technology Letters, 7, 501–507.
Marcovecchio, J. E., Moreno, V. J., & Perez, A. (1988). Determination of heavy metal concentrations in biota of Bahía Blanca, Argentina. Science of the Total Environment, 75, 181–190.
Marcovecchio, J. E., Asteasuain, R., Rusansky, C., Ferrer, L., Andrade, S., & Asteasuain, A. (1997). Estudio de la calidad de agua en la ria de Bahía Blanca. Capítulo 1: Quimica Marina. Technical Report. Instituto Argentino de Oceanografía (IADO), Bahía Blanca, Argentina, 48 pp.
Marcovecchio, J. E., Andrade, S., Ferrer, L. D., Asteasuain, R. O., De Marco, S. G., Gavio, M. A., et al. (2001). Mercury distribution in estuarine environments from Argentina: The detoxification and recovery of salt marshes after 15 years. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 9, 317–322.
Marcovecchio, J. E., Botté, S. E., Delucchi, F., Arias, A. H., Fernández Severini, M. D., De Marco, S. G., et al. (2008). Pollution processes in Bahía Blanca estuarine environment. In R. Neves, J. Baretta & M. Mateus (Eds.), Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America (pp. 301–314). Lisbon: IST.
Megalatti, N., Robbe, O., Marchandise, P., & Astruk, M. (1983). A new chemical extraction procedure in the fractionation of heavy metals in sediments. In U. Förstner (Ed.), Proceeding of international conference heavy metals in the environment (Vol. 4, pp. 1090–1093). Edinburgh: CEP Consultants.
Melo, W. D. & Limbozzi, F. (2008). Geomorphology, hydrological systems and land use of Bahía Blanca estuarine region. In R. Neves, J. Baretta & M. Mateus (Eds.), Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America (pp. 317–331). Lisbon: IST.
Perillo, G. M. E., Piccolo, C., Parodi, E., & Freije, R. H. (2001). Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. In U. Seeliger & B. Kjerfve (Eds.), Coastal marine ecosystems of Latin America, ecological studies (Vol. 144, pp. 205–217). Berlin: Springer.
Piccolo, M. C. & Perillo, M. E. G. (1990). Physical characteristics of the Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 31, 303–317.
Ponce-Velez, G. & Botello, A. V. (1991). Aspectos geoquímicos y de contaminación por metales pesados en la Laguna de Términos, Campeche. Hidrobiológica, 1, 1–10.
Pucci, A. E. (1988). Heavy metals in water and sediments of the Blanca Bay, Argentina. In U. Seeliger, L. D. de Lacerd & S. R. Patchineelam (Eds.), Metals in coastal environments of Latin America (pp. 9–15). Berlin: Springer.
Pucci, A. E., Freije, R. H., Asteasuain, R. O., Zavatti, J. R., & Sericano, J. L. (1979). Evaluación de la contaminación de las aguas y sedimentos de la Bahía Blanca. Contribución Científica I.A.D.O. (52), Bahía Blanca, Argentina.
Pucci, A. E., Freije, R. H., Asteasuain, R. O., Zavatti, J. R., & Sericano, J. L. (1980). Evaluación de la contaminación de las aguas y sedimentos de la Bahía Blanca. Contribución Científica I.A.D.O. (56), Bahía Blanca, Argentina.
Ram, A., Rokade, M. A., Borole, D. V., & Zingde, M. D. (2003). Mercury in sediments of Ulhas estuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 46, 846–857.
Ramirez, M., Massolo, S., Frache, R., & Correa, J. A. (2005). Metal speciation and environmental impact on sandy beaches due to El Salvador copper mine, Chile. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 62–72.
Rosales-Hoz, L., Cundy, A. B., & Bahena-Manjarrez, J. L. (2003). Heavy metals in sediments cores from a tropical estuary affected by anthropogenic discharges: Coatzacoalcos estuary, Mexico. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 58, 117–126.
Ruiz, F. (2001). Trace metals in estuarine sediments from the southwestern Spanish coast. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42, 482–490.
Salomons, W. & Fösrtner, U. (1984). Metals in the hydrocycle. 3. Sediments and the transport of metals. Berlin: Springer.
Sericano, J. L. & Pucci, A. E. (1982). Cu, Cd and Zn in Blanca Bay surface sediments, Argentina. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 13, 429–431.
Spencer, K. L., Cundy, A. B., & Croudace, I. W. (2003). Heavy metal distribution and early-diagenesis in salt marsh sediments from the Medway, Kent, UK. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 57, 43–54.
StatSoft, Inc. (2004). STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 7. Retrieved from http://www.statsoft.com.
Turner, A. & Millward, G. E. (2002). Suspended particles: Their role in estuarine biogeochemical cycles. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 55, 857–883.
Villa, N. (1988). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in seawater and sediments from coastal areas of the southeastern Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. In U. Seeliger, L. D. de Lacerda & S. R. Patchineelam (Eds.), Metals in coastal environments of Latin America (pp. 33–44). Berlin: Springer.
Villaescusa-Celaya, J. A., Gutiérrez-Galindo, E. A., & Flores-Muñoz, G. (2000). Heavy metals in the fine fraction of coastal sediments from Baja California (Mexico) and California (USA). Environmental Pollution, 108, 453–462.
Acknowledgements
The authors are greatly indebted to Lic. Federico Delucchi (IADO) for his help in samples processing and chemical analysis; Dr. Laura E. Grecco and Dr. Angel O. Marcos (UNS) for their assistance with the geochemical partitioning analysis. Thanks to Raul Asteasuain and M. Nedda Chiarello (IADO) for their assistance during sampling and laboratory work. Mrs. Mariela Gherbi has kindly reviewed the English version of this manuscript. Thanks also to the anonymous referee who greatly contributed with a critical reading and valuable corrections to the improvement of the original manuscript. This research was funded through grants by ANPCyT (PICT No. 07-11636/02 and PICT 0945/06) from Argentina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Botté, S.E., Freije, R.H. & Marcovecchio, J.E. Distribution of Several Heavy Metals in Tidal Flats Sediments within Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Water Air Soil Pollut 210, 371–388 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0260-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0260-0