Abstract
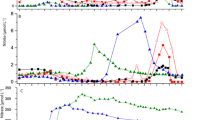
Nitrification is a process in which ammonia is oxidized to nitrite (NO −2 ) that is further oxidized to nitrate (NO −3 ). The relations between these two steps and ambient ammonia concentrations were studied in surface water of Chinese shallow lakes with different trophic status. For the oxidations of both ammonia and NO −2 , more eutrophic lakes generally showed significantly higher potential and actual rates, which was linked with excessive ammonia concentrations. Additionally, both potential and actual rates for ammonia oxidation were higher than those for NO −2 oxidation in the more eutrophic lakes, while in the lakes with lower trophic status, both potential and actual rates for ammonia oxidation were almost equivalent to those for NO −2 oxidation. This can be explained by the excessive unionized ammonia (NH3) concentration that inhibits nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in the more eutrophic lakes. The laboratory experiment with different ammonia concentrations, using the surface water in a eutrophic lake, showed that ammonia oxidation rates were proportional to the ammonia concentrations, but NO −2 oxidation rates did not increase in parallel. Furthermore, NO −2 oxidation was less associated with particles in natural water of the studied lakes. Without effective protection, it would be selectively inhibited by the excessive ammonia in hypereutrophic lakes, resulting in NO −2 accumulation. Shortly, the increased concentrations of ammonia cause a misbalance between the NO −2 -producing and the NO −2 -consuming processes, thereby exacerbating the lake eutrophication.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleem, M. I. H. (1970). Oxidation of inorganic nitrogen compounds. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 21, 67–90.
Anthonisen, A. C., Loehr, R. C., Prakasam, T. B. S., & Srinarh, E. G. (1976). Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation, 48(5), 835–852.
APHA, AWWA, WEF (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington, DC: APHA, AWWA, WEF.
Balmelle, B., Nguyen, K. M., Capdeville, B., Cornier, J. C., & Deguin, A. (1992). Study of factors controlling nitrite build-up in biological processes for water nitrification. Water Science and Technology, 26, 1017–1025.
Barnabe, G. (1990). Aquaculture. London: Horwood.
Bartosch, S., Hartwig, C., Spieck, E., & Bock, E. (2002). Immunological detection of Nitrospira-like bacteria in various soils. Microbial Ecology, 43, 26–33.
Belser, L. W. (1979). Population ecology of nitrifying bacteria. Annual Review of Microbiology, 33, 309–333.
Blackburne, R., Vadivelua, V. M., Yuan, Z. G., & Keller, J. (2007). Kinetic characterisation of an enriched Nitrospira culture with comparison to Nitrobacter. Water Research, 41, 3033–3042.
Butturini, A., Battin, T. J., & Sabeter, F. (2000). Nitrification in stream sediment biofilms: The role of ammonium concentration and DOC quality. Water Research, 34, 629–639.
Cébron, A., & Garnier, J. (2005). Nitrobacter and Nitrospira genera as representatives of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria: Detection, quantification and growth along the lower Seine River (France). Water Research, 39, 4979–4992.
Cébron, A., Berthe, T., & Garnier, J. (2003). Nitrification and nitrifying bacteria in the lower Seine river and estuary (France). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69(12), 7091–7100.
Chen, S., Ling, J., & Jean-Paul, B. (2006). Nitrification kinetics of biofilm as affected by water quality factors. Aquacultural Engineering, 34, 179–197.
Chen, Y., Tang, L., Zhang, D., Li, S., & Zeng, Y. (2007a). The spatially and temporally dynamic variation of total phosphorus in sediment of Dianchi Lake. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 26(1), 51–57.
Chen, Y., Tang, L., Zhang, D., Li, J., Zhou, J., & Guan, X. (2007b). Spatial and temporal dynamic variation of nitrogen in sediment of Dianchi Lake. Soils, 39(6), 879–883.
Chen, F., Xia, Z. Y., Song, C. L., Li, J. Q., & Zhou, Y. Y. (2007c). Relationship between organic matter in sediments and internal nutrient loadings in shallow lakes in Hubei province of China. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 31, 467–472.
Ciudad, G., Werner, A., Bornhardt, C., Muňoz, C., & Antileo, C. (2006). Differential kinetics of ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria: A simple kinetic study based on oxygen affinity and proton release during nitrification. Process Biochemistry, 41, 1764–1772.
Daims, H., Ramsing, N. B., Schleifer, K. H., & Wagner, M. (2001). Cultivation-independent, semiautomatic determination of absolute bacterial cell numbers in environmental samples by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 5810–5818.
Dang, H., Zhang, X., Sun, J., Li, T., Zhang, Z., & Yang, G. (2008). Diversity and spatial distribution of sediment ammonia-oxidizing crenarchaeota in response to estuarine and environmental gradients in the Changjiang Estuary and East China Sea. Microbiology, 154, 2084–2209.
de Bie, J. M., Starink, M., Boschker, H. T. S., Peene, J. J., & Laanbroek, H. J. (2002). Nitrification in the Schelde estuary: Methodological aspects and factors influencing its activity. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 42, 99–107.
Deng, P., Ma, J., Wu, X., Gao, Y., Cheng, S., & He, F. (2007). Dynamics of phytoplankton in the process of the aquatic macrophyte rehabilitation in Lake Yuehu (Wuhan). Journal of Lake Sciences, 19, 552–557.
Effler, S. W., Hassett, J. P., Auer, M. T., & Johnson, N. A. (1988). Depletion of epilimnetic oxygen, and accumulation of hydrogen sulfide in the hypolimnion of Onondaga Lake, NY, USA. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 39, 59–74.
Effler, S. W., Brooks, C. M., & Whitehead, K. A. (1996). Domestic waste inputs of nitrogen and phosphorus to Onondaga Lake, and water quality implications. Lake and Reservoir Management, 12, 127–140.
Fang, T., Ao, H., Liu, J., Cai, Q., & Liu, Y. (2004). The spatial–temporal distribution of water environmental status in Dianchi Lake. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 28, 124–130.
Féray, C., & Montuelle, B. (2003). Chemical and microbial hypotheses explaining the effect of wastewater treatment plant discharges on the nitrifying communities in freshwater sediment. Chemosphere, 50, 919–928.
Gernaey, K., Bogaert, H., Vanrolleghem, P., Massone, A., Rozzi, A., & Verstraete, W. (1998). A titration technique for on-line nitrification monitoring in activated sludge. Water Science and Technology, 37, 103–110.
Gießen, R. (1994). Modellhafte erarbeitung eines ökologisch begründeten sanierungskonzeptes für kleine fließgewässer am beispiel der Lahn. Endbericht: BMFT-Projekt.
Hagopian, D. S., & Riley, J. G. (1998). A closer look at the bacteriology of nitrification. Aquacultural Engineering, 18, 223–244.
Harris, G. P. (1986). Phytoplankton ecology, structure, function and fluctuation. New York: Chapman and Hall.
Hatzenpichler, R., Lebedeva, E. V., Spieck, E., Stoecker, K., Richter, A., Daims, H., et al. (2008). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(6), 2134–2139.
He, J., Shen, J., Zhang, L., Zhu, Y., Zheng, Y., Xu, M., et al. (2007). Quantitative analyses of the abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea of a Chinese upland red soil under long term fertilization practices. Environmental Microbiology, 9, 2364–2374.
Herrmann, M., Saunders, A. M., & Schramm, A. (2008). Archaea dominate the ammonia-oxidizing community in the rhizosphere of the freshwater macrophyte Littorella uniflora. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74(10), 3279–3283.
Herrmann, M., Saunders, A. M., & Schramm, A. (2009). Effect of lake trophic status and rooted macrophytes on community composition and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in freshwater sediments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 3127–3136.
Iriarte, A., Madariaga, I., de Diez-Garagarza, F., Revilla, M., & Orive, E. (1996). Primary plankton production, respiration and nitrification in a shallow temperate estuary during summer. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 208, 127–151.
James, J. P., & Martin, T. A. (2000). Nitrification in the water column and sediment of a hypereutrophic lake and adjoining river system. Water Research, 34(4), 1247–1254.
Kim, D. J., Lee, D. I., & Keller, J. (2006). Effect of temperature and free ammonia on nitrification and nitrite accumulation in landfill leachate and analysis of its nitrifying bacterial community by FISH. Bioresource Technology, 97, 459–468.
Klapwijk, A., & Snodgrass, W. J. (1982). Experimental measurement of sediment nitrification and denitrification in Hamilton Harbor, Canada. Hydrobiologia, 91, 207–216.
Lam, P., Cowen, J. P., & Jones, R. D. (2004). Autotrophic ammonia oxidation in a deep-sea hydrothermal plume. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 47, 191–206.
Leininger, S., Urich, T., Schloter, M., Schwark, L., Qi, J., Nicol, G. W., et al. (2006). Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature, 442, 806.
Liu, Y. M., Chen, W., Li, D. H., Shen, Y. W., Li, G. B., & Liu, Y. D. (2006). First report of aphantoxins in China-waterblooms of toxigenic Aphanizomenon flos-aquae in Lake Dianchi. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 65, 84–92.
Lusby, F. E., Gibbs, M. M., Cooper, A. B., & Thompson, K. (1998). The fate of groundwater ammonium in a lake edge wetland. Journal of Environmental Quality, 27, 459–466.
Ma, K., Cai, Q. H., Xie, Z. C., Li, D. F., & Liu, R. Q. (2003). Influence of submerged macrophytes distribution pattern on nitrogen and phosphorous factors water environment in lakes. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 27(3), 12–17.
Magalhães, C. M., Joye, S. B., Moreira, R. M., Wiebe, W. J., & Bordalo, A. A. (2005). Effect of salinity and inorganic nitrogen concentrations on nitrification and denitrification rates in intertidal sediments and rocky biofilms of the Douro River estuary, Portugal. Water Research, 39, 1783–1794.
Marilley, L., & Aragno, M. (1999). Phylogenetic diversity of bacterial communities differing in degree of proximity of Lolium perenne and Trifolium repens roots. Applied Soil Ecology, 13, 127–136.
Pan, W., & Cai, Q. (2000). The function of the macrophyte in the carbon circulation of Baoan Lake. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 24, 418–425.
Parinet, B., Lhote, A., & Legube, B. (2004). Principal component analysis: An appropriate tool for water quality evaluation and management—application to a tropical lake system. Ecological Modelling, 178, 295–311.
Park, H. D., Wells, G. F., Bae, H., Criddle, C. S., & Francis, C. A. (2006). Occurrence of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in wastewater treatment plant bioreactors. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 5643–5647.
Siripong, S., & Rittmann, B. E. (2007). Diversity study of nitrifying bacteria in fullscale municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Research, 41, 1110–1120.
Soetaert, K., & Herman, P. M. J. (1995). Estimating estuarine residence times in the Westerschelde (The Netherlands) using a box model with fixed dispersion coefficients. Hydrobiologia, 311, 215–224.
Stehr, G., Böttcher, B., Dittberner, P., Rath, G., & Koops, H. P. (1995). The ammonia-oxidizing nitrifying population of the River Elble estuary. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 17, 177–186.
Tanner, C. C., Kadlec, R. H., Gibbs, M. M., Sukias, J. P. S., & Nguyen, M. L. (2002). Nitrogen processing gradients in subsurface-flow treatment wetlands—influence of wastewater characteristics. Ecological Engineering, 18, 499–520.
Turk, O., & Mavinic, D. S. (1989). Maintaining nitrite build-up in a system acclimated to free ammonia. Water Research, 23, 1383–1388.
Vadivelu, V. M., Keller, J., & Yuan, Z. G. (2007). Effect of free ammonia on the respiration and growth processes of an enriched Nitrobacter culture. Water Research, 41, 826–834.
Verdouw, H. C., Van Echteld, J. A., & Dekkers, T. (1978). Ammonia determination based on indophenol formation with sodium salicylate. Water Research, 13, 399–402.
Ward, B. B., & Carlucci, A. F. (1985). Marine ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria: Serological diversity determined by immunofluorescent in culture and in environment. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 50, 194–201.
Wetzel, R. G. (1983). Limnology (2nd ed.). New York: Saunders College.
Wu, A. P., Wu, S. K., & Li, L. Y. (2005). Study of macrophytes nitrogen and phosphorus contents of the shallow lakes in the middle reaches of Changjiang River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 29(4), 406–412.
Wu, S. K., Xie, P., Wang, S. B., & Zhou, Q. (2006). Changes in the patterns of inorganic nitrogen and TN/TP ratio and the associated mechanisms of biological regulation in the shallow lakes along the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Science in China Series D—Earth Sciences, 49(Suppl I), 126–134.
Yoon, H. J., & Kim, D. J. (2003). Nitrification and nitrite accumulation characteristics of high strength ammonia wastewater in a biological aerated filter. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 78, 377–383.
Zhang, T. C., Fu, Y. C., & Bishop, P. L. (1995). Competition for substrate and space in biofilms. Water Environment Research, 67, 992–1003.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2008CB418006) and the grants (KZCX2-YW-426-01 and KZCX1-YW-14-1) from the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Mr. Yunbing Liu, Yingjie Li, Neng Wan, Yu Zeng, Zhi Wang, and Shanlian Qiu are thanked for their assistance throughout the course of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Cao, X., Song, C. et al. Adverse Effects of Ammonia on Nitrification Process: the Case of Chinese Shallow Freshwater Lakes. Water Air Soil Pollut 210, 297–306 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0253-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0253-z