Abstract
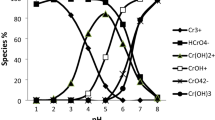
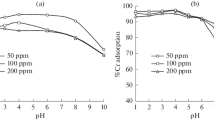
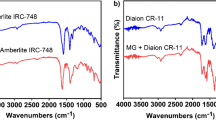
A strong base anion exchange resin Amberlite IRA-400 Cl− and its hybrids with Mn(OH)2 and Cu(OH)2 are used for the removal of chromium from the synthetic spent tannery bath. The recovery is examined by varying the experimental conditions, viz., resin dosage, stirring speed, and temperature. The rate of chromium removal by Amberlite IRA-400 Cl− increased almost four times when the resin dosage was increased from 0.2 to 1.0 g. Furthermore, the rate of chromium sorption almost doubled when the stirring speed was increased from 100 to 1,000 rpm, suggesting that the sorption is a diffusionally controlled process. The chromium removal capacity also increased with the rise of temperature, showing the endothermic nature of the process. The results are explained with the help of film diffusion, particle diffusion, and Lagergren pseudo-first-order kinetic models. The kinetics results of the Amberlite IRA-400 Cl− are compared with its hybrid anion exchange resins IRA-400 Mn(OH)2 and IRA-400 Cu(OH)2. It is found that the hybrid ion exchangers have greater removal ability and fast kinetics as compared to the parent exchanger.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awan, M. A., Baig, M. A., Iqbal, J., Aslam, M. R., & Ijaz, N. (2003). Recovery of chromium (III) from tannery wastewater. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 7, 5–8.
Ayoob, S., Gupta, A. K., Bhakat, P. B., & Bhat, V. T. (2008). Investigations on the kinetics and mechanisms of sorptive removal of fluoride from water using alumina cement granules. Chemical Engineering Journal, 140, 6–14.
Blaney, L. M., Cinar, S., & SenGupta, A. K. (2007). Hybrid anion exchanger for trace phosphate removal from water and wastewater. Water Research, 41, 1603–1613.
Cumbal, L., & SenGupta, A. K. (2005). Arsenic removal using polymer-supported hydrated iron(III) oxide nanoparticles: Role of Donnan membrane effect. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 6508–6515.
Cumbal, L., Greenleaf, J., Leun, D., & SenGupta, A. K. (2003). Polymer supported inorganic nanoparticles: Characterization and environmental applications. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 54, 167–180.
Dabrowski, A., Hubicki, Z., Podkoscielny, P., & Robens, E. (2004). Selective removal of the heavy metal ions from waters and industrial wastewaters by ion-exchange method. Chemosphere, 56, 91–106.
DeMarco, M. J., SenGupta, A. K., & Greenleaf, J. E. (2003). Arsenic removal using a polymeric/inorganic hybrid sorbent. Water Research, 37, 164–176.
Eary, L. E., & Ray, D. (1987). Kinetics of chromium(III) oxidation to chromium(VI) by reaction with manganese dioxide. Environmental Science and Technology, 21, 1187–1193.
Erdem, M., Altundogan, H. S., & Tumen, F. (2004). Removal of hexavalent chromium by using heat-activated bauxite. Mineral Engineering, 17, 1045–1052.
Gode, F., & Pehlivan, E. (2003). A comparative study of two chelating ion-exchange resins for the removal of chromium(III) from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B100, 231–243.
Herrmann, M. S. (1994). Testing the waters for chromium. Journal of Chemical Education, 71, 323–324.
Kocaoba, S., & Akcin, G. (2002). Removal and recovery of chromium and chromium speciation with MINTEQA2. Talata, 57, 23–30.
Kotas, J., & Stasicka, Z. (2000). Commentary: Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation. Environmental Pollution, 107, 263–283.
Mohan, D., & Pittman, C. U., Jr. (2006). Review: Activated carbons and low cost adsorbents for remediation of tri- and hexavalent chromium from water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137, 762–811.
Mustafa, S., Bashir, H., Rehana, N., & Naeem, A. (1997). Selectivity reversal and dimerization of chromate in the exchanger Amberlite IRA-400. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 34, 135–144.
Mustafa, S., Shah, K. H., Naeem, A., Waseem, M., & Tahir, M. (2008). Chromium (III) removal by weak acid exchanger Amberlite IRC-50 (Na). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 160, 1–5.
Nakayama, E., Kuwamoto, T., Tsurubo, G., & Fujinaga, T. (1981). Chemical speciation of chromium in seawater: Part2. Effect of manganese oxides and reducible organic materials on the redox process of chromium. Analytica Chimica Acta, 130, 401–404.
Narin, I., Kars, A., & Soylak, S. (2008). A novel solid phase extraction procedure on Amberlite XAD-1180 for speciation of Cr(III), Cr(VI) and total chromium in environmental and pharmaceutical samples. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 150, 453–458.
Pehlivan, E., & Cetin, S. (2009). Sorption of Cr(VI) ions on two Lewatit-anion exchange resins and their quantitative determination using UV–visible spectrophotometer. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 448–453.
Petruzzelli, D., Santori, M., Passino, R., & Tiravanti, G. (1991). Cr(III) recovery and separation from spent tannery baths by carboxylic ion exchange resins “New Developments in Ion Exchange”. Proceedings of the International Conference on Ion Exchange Resins (pp. 383–388). Kodansha, Tokyo, Japan.
Reichenberg, D. (1953). Properties of ion exchange resins in relation to their structure. III. Kinetics of exchange. Journal of American Chemical Society, 75, 589–597.
Rengaraj, S., Yeon, K. H., & Moon, S. H. (2001). Removal of chromium from water and wastewater by ion exchange resins. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B87, 273–287.
Rengaraj, S., Joo, C. K., Kim, Y., & Yi, J. (2003). Kinetics of removal of chromium from water and electronic process wastewater by ion exchange resins: 1200H, 1500H and IRN97H. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 102, 257–275.
Scheckel, K. G., & Sparks, D. L. (2001). Temperature effects on nickel sorption kinetics at the mineral– water interface. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 719–728.
Sengupta, A. K., & Lim, L. (1988). Modeling chromate ion-exchange processes. AIChE Journal, 34, 2019–2029.
Tadesse, I., Isoaho, S. A., Green, F. B., & Puhakka, J. A. (2006). Lime enhanced chromium removal in advanced integrated wastewater pond system. Bioresource Technology, 97, 529–534.
Tenório, J. A. S., & Espinosa, D. C. R. (2001). Treatment of chromium plating process effluents with ion exchange resins. Waste Management, 21, 637–642.
The Gazette of Pakistan, Extra. (2000). Statutory notification (S.R.O). Government of Pakistan Ministry of Environment, Local Government and Rural Development Notification, Islamabad. S.R.O. 549 (1)/2000.
van Heerden, P. V., Jenkins, I. R., Woods, W. P. D., Rossi, E., & Cameron, P. D. (1994). Death by tanning—A case of fatal basic chromium sulfate poisoning. Intensive Care Medicine, 20, 145–147.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mustafa, S., Ahmad, T., Naeem, A. et al. Kinetics of Chromium Ion Removal from Tannery Wastes Using Amberlite IRA-400 Cl− and its Hybrids. Water Air Soil Pollut 210, 43–50 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0221-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0221-7