Abstract
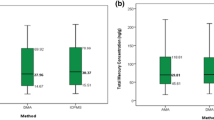
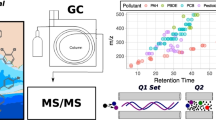
The use of purge and trap gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) technique for the determination of methylmercury in biological and sediment samples was described. The GC-MS detection system was combined with the dithizone extraction method for biological samples and the distillation method for sediment samples to alleviate matrix interference problems. The method was validated by analysis of CRMs such as SRM 966 (human blood), BCR 463 (tuna fish), IAEA 407 (fish), ERM CC580 (estuarine sediment), and IAEA 405 (sediment). The performance of the purge and trap GC-MS method was also tested on field samples of freshwater fish and sediment. The results were compared with those of the GC-ECD and the GC-CVAFS, which were used widely for methylmercury analysis. Additionally, total mercury and methylmercury levels in freshwater fish and sediments from various reservoirs and streams in Korea were measured to understand mercury contamination status in Korean peninsula. Methylmercury concentrations in freshwater fish were found to correlate with body weight, diet habit, and food availability. In sediment, total mercury concentrations correlated with methylmercury concentrations and organic matter such as %C and %S. However, no significant relationships between methylmercury and sediment organic matter have been found.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi, H., & Ikingura, J. R. (1999). Methylmercury production and distribution in aquatic systems. Science of the Total Environment, 234, 109–118.
Akagi, H., & Naganuma, A. (2000). Human exposure to mercury and the accumulation of methylmercury that is associated with gold mining in the Amazon basin, Brazil. Journal of Health Science, 46(50), 323–328.
Akagi, H., & Nishimura, H. (1991). Advances in Mercury Toxicology. New York: Plenum Press.
Baxter, D. C., Rodushkin, I., Engstrom, E., Klockare, D., & Waara, H. (2007). Methylmercury measurement in whole blood by isotope-dilution GC-ICPMS with 2 sample preparation methods. Clinical Chemistry, 53(1), 111–116.
Benoit, J. M., Gilmour, C. C., Mason, P. R., Riedel, G. S., Reidel, G. F., & Sullivan, K. A. (1998). Sources and cycling of mercury in the Patuxent estuary. Biogeochemistry, 40, 249–265.
Benoit, J. M., Gilmour, C. C., Heyes, A., Mason, P. R., & Miller, C. (2003). Geochemical and biological controls over methylmercury production and degradation in aquatic systems. In Y. Chai & O. C. Braids (Eds.), Biochemistry of environmental important trace elements (pp. 262–297). Washington, DC: American Chemical Society.
Blanco, R. M., Villanueva, M. T., Uria, J. E. S., & Sanz-Medel, A. (2000). Field sampling, preconcentration and determination of mercury species in river waters. Analytica Chimica Acta, 419, 137–144.
Bloom, N. S. (1989). Determination of picogram levels of methylmercury by aqueous phase ethylation, followed by cryogenic gas chromatography with cold vapor atomic fluorescence detection. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 46, 1131–1140.
Bloom, N. S. (1992). On the chemical form of mercury in edible fish and marine invertebrate tissue. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 49, 1010–1017.
Boening, D. W. (2000). Ecological effects, transport, and fate of mercury: A general review. Chemosphere, 40, 1335–1351.
Caricchia, A. M., Minervini, G., Soldati, P., Chiavarini, S., Ubaldi, C., & Morabito, R. (1997). GC-ECD determination of methylmercury in sediment samples using a SPB-608 capillary column after alkaline digestion. Microchemical Journal, 55, 44–55.
Choi, E. M., Kim, S. H., Holsen, T. M., & Yi, S. M. (2009). Total gaseous concentrations in mercury in Seoul, Korea: Local sources compared to long-range transport from China and Japan. Environmental Pollution, 157(3), 816–822.
Hammerschmidt, C. R., & Fitzgerald, W. F. (2001). Formation of Artifact Methylmercury during extraction from a sediment reference material. Analytical Chemistry, 73, 5930–5936.
Han, J. S., Hong, Y. D., Ahn, J. Y., Chung, I. R. (2008). Acid deposition monitoring and impact assessment. National Institute of Environmental Research Report, NIER NO. 2008-78-1028.
Henny, C. J., Hill, E. F., Hoffman, D. J., Spalding, M. G., & Grove, R. A. (2002). Nineteenth Century mercury: Hazard to wading birds and cormorants of the Carson River, Nevada. Ecotoxicology, 11, 213–231.
Hong, Y. D., Han, J. S., Lee, Y. K., Ahn, J. Y., Chung, I. R. (2007). Study on the atmospheric distribution characteristics and test method of mercury. National Institute of Environmental Research Report, NIER NO. 2007-81-997.
Horvat, M. (1996). Mercury analysis and speciation in environment samples. In W. Beayens (Ed.), Global and regional mercury cycles: Sources (fluxes and mass balances, pp. 1–31). The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic.
Horvat, M., Liang, L., & Bloom, N. S. (1993). Comparison of distillation with other current isolation methods for the determination of methylmercury compounds in low level environmental samples. Analytica Chimica Acta, 282, 153–168.
Hutchson, M. S., Smith, C. M., Wallace, G. T., Rose, J., Eddy, B., Sullivan, J., et al. (2008). Freshwater fish mercury concentrations in a regionally high mercury deposition area. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 191, 15–31.
Ignacio, J., Alone, G., & Sanz-mede, A. (2000). Comparison of different derivatization approach for mercury speciation in biological tissues by gas chromatography/inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 35, 639–646.
Krabbenhoft, D., Engstrom, D., Gilmour, C., Harris, H., Hurley, J., & Mason, R. (2006). Monitoring and evaluation trends in sediment and water indicators. In R. Harris, et al. (Eds.), Ecosystem responses to mercury contamination (pp. 47–86). NY: CRC Press.
Liang, L., Evens, C., Lazoff, S., Woods, J. S., Cernichiari, E., Horvat, M., et al. (2000). Determination of methyl mercury in whole blood by ethylation-GC-CVAFS after alkaline digestion—solvent extraction. Journal of Analytical Toxicology, 24, 328–332.
Lindberg, A., Björnberg, A., Vahter, M., & Berglund, M. (2004). Exposure to methylmercury in non-fish-eating people in Sweden. Environmental Research, 96, 28–33.
Logar, M., Horvat, M., Akagi, H., & Pihlar, B. (2002). Simultaneous determination of inorganic mercury and methylmercury compounds in natural waters. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 374, 1015–1021.
Mason, P. R., & Lawrence, A. L. (1999). Concentration, distribution, and bioavailability of mercury and methylmercury in sediments of Baltimore Harbor and Chesapeake Bay, Maryland, USA. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18(11), 2438–2447.
Mason, R. P., Lawson, N. N., Lawrence, A. L., Leaner, J. J., Lee, J. G., & Sheu, G.-R. (1999). Mercury in the Chesapeake Bay. Marine Chemistry, 65, 77–96.
Mergler, D., Anderson, H. A., Chan, L. H. M., Mahaffey, K. R., Murray, M., & Sakamoto, M. (2007). Methylmercury exposure and health effects in humans: A worldwide concern. Ambio, 36, 3–11.
Quevauviller, Ph., Fortunati, G. U., Filippelli, M., & Muntau, H. (1997). The certification of the contents (mass fractions) of total mercury and methylmercury in estuarine sediment CRM 580. EUR 17658 EN.
Rice, D. C. (2004). The US EPA reference dose fir methylmercury: Sources of uncertainty. Environmental Research, 95, 406–413.
Stephenson, M., Landing, M., Foe, C., Gill, G. A., & Coale, K. H. (2008). Transport, Cycling, and Fate of Mercury and Monomethyl Mercury in the San Francisco Delta and Tributaries: An Integrated Mass Balance Assessment Approach, CALFED Mercury Project Final Report.
Sveinsdottir, A. Y., & Mason, R. P. (2005). Factors controlling mercury and. methylmercury concentrations in largemouth bass (Micropterus. salmoides) and other fish from Maryland reservoirs. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 49, 528–545.
Ullrich, S. M., Tanton, T. W., & Abdrashitova, S. W. (2001). Mercury in the aquatic environment: A review factors affecting methylation. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 31(3), 241–293.
USEPA (2001). EPA method 1630. Methylmercury in water by distillation, aqueous ethylation, purge and trap, and CVAFS.
Vidler, D., Jenkins, R., Hall, J., & Harrington, C. (2007). The determination of methylmercury in biological samples by HPLC coupled to ICP-MS detection. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 21, 303–310.
Wagemann, R. E., Trebacz, R., & Hunt, R. (1997). Percent methylmercury and organic mercury in tissues of marine mammals and fish by different experimental and calculation methods. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 16(9), 1859–1866.
Westöö, G. (1966). Determination of methylmercury compounds in food stuffs. I. Methylmercury compounds in fish, identification and determination. Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 21, 2131–2137.
Young, C., & Josep, M. B. (1995). Determination of methylmercury in fish and river water samples using in situ sodium tetraethylborate derivatization following by solid-sample microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 113-112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JS., Lee, JS., Kim, GB. et al. Mercury and Methylmercury in Freshwater Fish and Sediments in South Korea Using Newly Adopted Purge and Trap GC-MS Detection Method. Water Air Soil Pollut 207, 391–401 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0144-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0144-3