Abstract
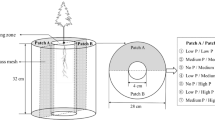
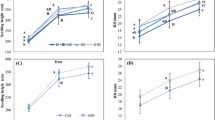
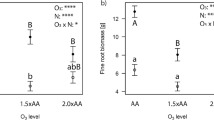
This study was carried out to test ex situ growth and soil nutrient removal efficiency of 1-year-old potted willow and poplar plants. Plants were grown under two different water regimes: low irrigation—around soil field capacity (W)—and high irrigation—five times higher than field capacity (W 5). Results showed that plant productivity and water use efficiency were greater when trees were grown in the appropriate level of soil water content rather than at excessive moisture levels. Nutrient leaching was also affected by the high irrigation treatment. However, the poplar and willow clones used in this experiment showed different nutrient allocation patterns in the plant–soil–water system. The poplar clone accumulated the highest quantities of N and P in the soil. Willow accumulated N and P mainly in the biomass due to better root development under both treatments. This indicates the better performance of the willow clone in removing N and P from contaminated aquaculture wastewaters during the first growing season.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackefors, H., & Enell, M. (1990). Discharge of nutrients from Swedish fish farming to adjacent sea areas. Ambio, 19, 28–35.
Aronsson, P., & Bergstrom, L. (2001). Nitrate leaching from lysimeter-grown short rotation willow coppice in relation to N-application, irrigation and soil type. Biomass and Bioenergy, 21, 155–164.
Aronsson, P., & Perttu, K. (2001). Willow vegetation filters for wastewater treatment and soil remediation combined with biomass production. The Forestry Chronicle, 77, 293–299.
Börjesson, P., & Berndes, G. (2006). The prospects for willow plantations for wastewater treatment in Sweden. Biomass and Bioenergy, 30, 428–438.
Cao, F., & Conner, W. (1999). Selection of flood-tolerant Populus deltoides clones for reforestation projects in China. Forest Ecology and Management, 117, 211–220.
Ceulemans, R., McDonald, A., & Pereira, J. (1996). A comparison among eucalyptus, poplar and willow characteristics with particular reference to a coppice, growth-modelling approach. Biomass and Bioenergy, 11, 215–231.
Christersson, L. (2006). Biomass production of intensively grown poplars in the southernmost part of Sweden: Observations of characters, traits and growth potential. Biomass and Bioenergy, 30, 497–508.
DesRochers, A., van den Driessche, R., & Thomas, B. R. (2006). NPK fertilization at planting of three hybrid poplar clones in the boreal region of Alberta. Forest Ecology and Management, 232, 216–225.
Dickmann, D., Nguyen, P., & Pregitzer, K. (1996). Effects of irrigation and coppicing on above-ground growth, physiology, and fine-root dynamics of two field-grown hybrid poplar clones. Forest Ecology and Management, 80, 163–174.
Dimitriou, I., Aronsson, P., & Weih, M. (2006). Stress tolerance of five willow clones after irrigation with different amounts of landfill leachate. Bioresource Technology, 97, 150–157.
Du, K., Shen, B., Xu, L., & Tu, B. (2008). Estimation of genetic variances in flood tolerance of poplar and selection of resistant F1 generations. Agroforestry Systems, 74, 243–257.
Dumas, A., Laliberté, G., Lessard, P., & de la Noüe, J. (1998). Biotreatment of fish farm effluents using the cyanobacterium Phormidium bohneri. Aquacultural Engineering, 17, 57–68.
Gambrell, R., DeLaune, R., & Patrick, W., Jr. (1991). Redox processes in soils following oxygen depletion. In M. Jackson, D. Davies & H. Lambers (Eds.), Plant life under oxygen stress (pp. 101–117). The Hague: Academic.
Gong, J., Zhang, X., Huang, Y., & Zhang, C. L. (2007). The effects of flooding on several hybrid poplar clones in Northern China. Agroforestry Systems, 69, 77–88.
Guidi, W., Piccioni, E., & Bonari, E. (2008). Evapotranspiration and crop coefficient of poplar and willow short-rotation coppice used as vegetation filter. Bioresource Technology, 99, 4832–4840.
Harvey, H., & Van den Driessche, R. (1999). Nitrogen and potassium effects on xylem cavitation and water-use efficiency in poplars. Tree Physiology, 19, 943–950.
Hassegren, K. (1998). Use of municipal waste products in energy forestry: Highlights from 15 years of experience. Biomass and Bioenergy, 15, 71–74.
Jackson, M., & Attwood, P. (1996). Roots of willow (Salix viminalis L) show marked tolerance to oxygen shortage in flooded soils and in solution culture. Plant and Soil, 187, 37–45.
Jackson, M., & Colmer, T. D. (2005). Response and adaptation by plants to flooding stress. Annals of Botany, 96, 501–505.
Janiesch, P. (1991). Ecophysiological adaptations of higher plants to waterlogging. In J. Rozema & J. A. C. Verkleij (Eds.), Ecological responses to environmental stresses (pp. 50–60). Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Karačić, A., & Weih, M. (2006). Variation in growth and resource utilization among eight poplar clones grown under different irrigation and fertilization regimes in Sweden. Biomass and Bioenergy, 30, 115–124.
Kopinga, J., & Van den Burg, J. (1995). Using soil and foliar analysis to diagnose the nutritional status of urban trees. Journal Arboriculture, 21, 17–24.
Kozlowski, T. (1984). Responses of woody plants to flooding (pp. 129–163). Orlando: Academic.
Kozlowski, T. (1997). Responses of woody plants to flooding and salinity. Hernon: Victoria.
Kozlowski, T., & Pallardy, S. (1984). Effects of flooding on water, carbohydrate, and mineral relations (pp 165–193). Orlando: Academic.
Kozlowski, T., & Pallardy, S. (1997). Growth control in woody plants. San Diego: Academic.
Krasny, M., Zasada, J., & Vogt, K. (1988). Adventitious rooting of four Salicaceae species in response to a flooding event. Canadian Journal of Botany, 6, 2597–2598.
Kreuzwieser, J., Fürniss, S., & Rennenberg, H. (2002). Impact of waterlogging on the N-metabolism of flood tolerant and non-tolerant tree species. Plant, Cell and Environment, 25, 1039–1049.
Labrecque, M., & Teodorescu, T. (2001). Influence of plantation site and wastewater sludge fertilization on the performance and foliar nutrient status of two willow species grown under SRIC in southern Quebec (Canada). Forest Ecology and Management, 150, 223–239.
Labrecque, M., & Teodorescu, T. (2003). High biomass yields achieved by Salix clones in SRIC following two 3-years coppice rotations on abandoned farmland in southern Quebec, Canada. Biomass and Bioenergy, 25, 135–146.
Labrecque, M., & Teodorescu, T. (2005). Field performances and biomass production of 12 willow and poplar clones in short-rotation coppice in southern Quebec (Canada). Biomass and Bioenergy, 29, 1–9.
Labrecque, M., Teodorescu, T., & Daigle, S. (1995). Effect of wastewater sludge on growth and heavy metal bioaccumulation on two Salix species. Plant and Soil, 171, 303–316.
Labrecque, M., Teodorescu, T., & Daigle, S. (1997). Biomass productivity and wood energy of Salix species after 2 years growth in SRIC fertilized with wastewater sludge. Biomass and Bioenergy, 12, 409–417.
Labrecque, M., Teodorescu, T., & Daigle, S. (1998). Early performances and nutrition of two willow species in short-rotation intensive culture fertilized with wastewater sludge and impact on the soil characteristics. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 28, 1621–1635.
Li, S., Pezeshki, S., Goodwin, S., & Shields, F. (2004). Physiological responses of black willow (Salix nigra) cuttings to a range of soil moisture regimes. Photosynthetica, 42, 585–590.
Licht, L. (1990). Poplar-tree buffer strips grown in Riparian Zones for biomass production and non-point source pollution control. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Iowa.
Licht, L. A., & Isebrands, J. G. (2005). Linking phytoremediated pollutant removal to biomass economic opportunities. Biomass and Bioenergy, 28, 203–218.
Linderson, M., Iritz, Z., & Lindroth, A. (2007). The effect of water availability on stand-level productivity, transpiration, water use efficiency and radiation use efficiency of field-grown willow clones. Biomass and Bioenergy, 31, 460–468.
Lindroth, A., & Cenciala, E. (1996). Water use efficiency of short-rotation Salix viminalis at leaf, tree and stand level. Tree Physiology, 16, 257–262.
Liu, Z., & Dickmann, D. (1992a). Responses of two hybrid Populus clones to flooding, drought, and nitrogen availability, I. Morphology and growth. Canadian Journal of Botany, 70, 2265–2270.
Liu, Z., & Dickmann, D. (1992b). Responses of two hybrid Populus clones to flooding, drought, and nitrogen availability. II. Gas exchanges and water relations. Canadian Journal of Botany, 71, 927–938.
Martin, P., & Stephens, W. (2006). Willow growth in response to nutrients and moisture on a clay landfill cap soil. II: Water use. Bioresource Technology, 97, 449–458.
Maynard, D. G., & Kalra, Y. P. (1993). Nitrate and exchangeable ammonium nitrogen. In M. R. Carter (Ed.), Soil sampling and methods of analysis (pp. 25–32). Pinawa: Canadian Society of Soil Science.
McGee, A., Schmierbach, M., & Bazzaz, F. (1981). Photosynthesis and growth of populations of Populus deltoides from contrasting habitats. The American Midland Naturalist, 105, 305–311.
Naylor, S., Brisson, J., Labelle, M., Drizo, A., & Comeau, Y. (2003). Treatment of freshwater fish farm effluent using constructed wetlands: The role of plants and substrate. Water Science and Technology, 48, 215–222.
Ohmann, L. F., Knighton, M. D., & McRoberts, R. (1990). Influence of flooding duration on the biomass growth of alder and willow. Research paper NC-292 (pp. 1–5). St. Paul: U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Forest Service, North Central Forest Experiment Station.
Parkinson, A., & Allen, N. (1975). A wet oxidation procedure suitable for the determination of nitrogen and mineral nutrients in biological material. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 6, 1–11.
Perttu, K. (1999). Environmental and hygienic aspects of willow coppice in Sweden. Biomass and Bioenergy, 16, 291–297.
Perttu, K., & Kowalik, P. (1997). Salix vegetation filters for purification of waters and soils. Biomass and Bioenergy, 12, 9–19.
Ponnamperuma, F. (1984). Effects of flooding on soils. In T. Kozlowski (Ed.), Flooding and plant growth (pp. 9–45). Orlando: Academic.
Porrello, S., Lenzi, M., Ferrari, G., Persia, E., Savelli, F., & Tomassetti, P. (2005). Loading of nutrient from a land-based fish farm (Orbetello, Italy) at different times. Aquaculture International, 13, 97–108.
Ripullone, F., Lauteri, M., Grassi, G., Amato, M., & Borghetti, M. (2004). Variation in nitrogen supply changes water-use efficiency of Pseudotsuga menziesii and Populus × euroamericana; a comparison of three approaches to determine water-use efficiency. Tree Physiology, 24, 671–679.
Rosenqvist, H., & Ness, B. (2004). An economic analysis of leachate purification through willow-coppice vegetation filters. Bioresource Technology, 94, 321–329.
Rosenqvist, H., Aronsson, P., Hasselgren, K., & Perttu, K. (1997). Economics of using municipal wastewaters irrigation of willow coppice crops. Biomass and Bioenergy, 12, 1–8.
Roy, S., Labelle, S., Mehta, P., Mihoc, A., Fortin, N., Masson, C., et al. (2005). Phytoremediation of heavy metal and PAH-contaminated brownfield sites. Plant and Soil, 272, 277–290.
Russell, J., Cooper, N., & Lindsey, S. (1993). Soil denitrification rates at wastewater irrigation sites receiving primary-treated and anaerobically treated meat-processing effluent. Bioresource Techniques, 43, 41–46.
Schmull, M., & Thomas, F. (2000). Morphological and physiological reactions of young deciduous trees (Quercus robur L., Q. petraea [Matt.] Liebl., Fagus sylvatica L.) to waterlogging. Plant and Soil, 225, 227–242.
Šottníková, A., Lunáčková, L., Masarovičová, E., Lux, A., & Streško, V. (2003). Changes in the rooting and growth of willows and poplars induced by cadmium. Biologia Plantarum, 46, 129–131.
Souch, C., & Stephens, W. (1998). Growth, productivity and water use in three hybrid polar clones. Tree Physiology, 18, 829–835.
Tran, S. T., & Simard, R. R. (1993). Mehlich III—extractable elements. In M. R. Carter (Ed.), Soil samplings and methods of analysis. Canadian Society of Soil Science (pp. 43–49). Boca Raton: Lewis.
Vartapetian, B., & Jackson, M. (1997). Plant adaptations to anaerobic stress. Annals of Botany, 79, 3–20.
von Fircks, Y., Ericsson, T., & Sennerby-Forsse, L. (2001). Seasonal variation of macronutrients in leaves, stems and roots of Salix dasyclados Wimm. grown at two nutrient levels. Biomass and Bioenergy, 21, 321–334.
Williams, B., Shand, C., Hill, M., O'Hara, C., Smith, S., & Young, M. (1995). A procedure for the simultaneous oxidation of total soluble nitrogen and phosphorus in extracts of fresh and fumigated soils and litters. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 26, 91–106.
Yamamoto, F., & Kozlowski, T. (1987a). Effects of flooding, tilting of stems, and ethrel application on growth, stem anatomy, and ethylene production of Acer platanoides seedlings. Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 2, 141–156.
Yamamoto, F., & Kozlowski, T. (1987b). Regulation by auxin and ethylene of responses of Acer negundo seedlings to flooding of soil. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 27, 329–340.
Zacchini, M., Pietrini, F., Scarascia Mugnozza, G., Iori, V., Pietrosanti, L., & Massacci, A. (2008). Metal tolerance, accumulation and translocation in poplar and willow clones treated with cadmium in hydroponics. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 197, 23–34.
Acknowledgments
This study received financial support from the Technology and Innovation (T&I) program of the Canadian Biomass Innovation Network and “FQRNT—Actions concertées consolidation de la recherche sur l'environnement rural” of the provincial Government of Quebec. The authors would like to thank Gabriel Teodorescu, horticulturalist at the Montreal Botanical Garden, and Hélène Lalande of the Department of Geography at the University of Montreal for their technical support. We also thank Stéphane Daigle for his help with the statistical analysis and Karen Grislis for her critical review of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guidi, W., Labrecque, M. Effects of High Water Supply on Growth, Water Use, and Nutrient Allocation in Willow and Poplar Grown in a 1-Year Pot Trial. Water Air Soil Pollut 207, 85–101 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0121-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0121-x