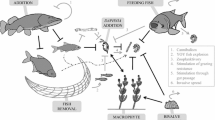
Abstract
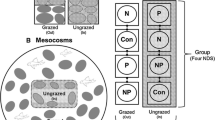
The objectives of this study were algal control and health assessments in a temperate eutrophic reservoir. Laboratory and mesocosm-scale in situ top-down biomanipulation experiments using planktivorous fishes and filter-feeding macroinvertebrates were conducted along with identification of the limiting nutrient using nutrient enrichment bioassays (NEBs), and ecosystem health evaluation based on the modified index of biological integrity model (Reservoir Ecosystem Health Assessment; REHA). Nutrients and N/P ratio analyses during 5 years revealed that the reservoir was in a eutrophic–hypertrophic state and that the key limiting nutrients, based on the NEBs, varied among seasons. Reservoir trophic guilds indicated declines in sensitive and endemic fish species and dominance of tolerant omnivores. Model values from multimetric REHAs averaged 25.8, indicating that the ecological health was in “fair to poor” condition. Overall microcosm biomanipulation tests suggested that macroinvertebrates, specifically Palaemon paucidens and Caridina denticulata, were effective candidates for phytoplankton control, compared to fishes. In situ mesocosm experiments revealed the highest removal rates with bluegreen algae and a phytoplankton size fraction of 2–19 μm (R e > 90%, Mann–Whitney U = 64.5–74.0, p < 0.01), the dominant fractions in the reservoir. Our biomanipulation technique may provide a key tool for efficient management and restoration of eutrophied reservoirs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright, M. F., Harman, W. N., Tibbits, W. T., Gray, M. S., Warner, D. M., & Hamway, R. J. (2004). Biomanipulation: A classic example in a shallow eutrophic pond. Lake and Reservoir Management, 20(3), 181–187.
An, K.-G. (2001). Hydrological significance on interannual variability of cations, anions, and conductivity in a large reservoir ecosystem. Korean Journal of Limnology, 34, 1–8.
An, K.-G. (2002a). An influence of point source and flow events on inorganic nitrogen fractions in a large artificial reservoir. Korean Journal of Limnology, 34, 350–357.
An, K.-G. (2002b). The impact of monsoon on seasonal variability of basin morphology and hydrology. Korean Journal of Limnology, 33, 342–349.
An, K.-G., & Han, J.-H. (2007). A development of multi-metric approach for ecological health assessments in lentic ecosystems. Korean Journal of Limnology, 40(1), 72–81.
An, K.-G., Jung, S.-H., & Choi, S.-S. (2001). An evaluation on health conditions of Pyong-Chang River using the index of biological integrity (IBI) and qualitative habitat evaluation index (QHEI). Korean Journal of Limnology, 34, 153–165.
An, K.-G., Ahn, K.-H., Urchin, C. G., & Park, S. S. (2003). Dynamics of nitrogen, phosphorus, algal biomass, and suspended solids in an artificial lentic ecosystem and significant implications of regional hydrology. Journal of Environmental Biology, 24(1), 29–38.
Annadotter, H., Cronberg, G., Aagren, R., Lundstedt, B., Nilsson, P. A., & Ströbäck, S. (1999). Multiple techniques for lake restoration. Hydrobiologia, 395/396, 77–85. doi:10.1023/A:1017011132649.
APHA. (1995). Standard methods (19th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Attayde, J. L., & Hansson, L.-A. (2001). The relative importance of fish predation and excretion effects on planktonic communities. Limnology and Oceanography, 46, 1001–1012.
Barbour, M.T., Gerritsen, J., Snyder, B.D., & Stribling, J.B.(1999). Rapid bioassessment protocols for use in streams and wadeable rivers: periphyton, benthic macroinvertebrates, and fish. Second Edition. EPA 841-B-99-002. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; Office of Water; Washington, D.C. xiv, 11 chapters, 4 appendices.
Beveridge, M. C. M., Baird, D. J., Rahmatullah, S. M., Lawton, L. A., Beattie, K. A., & Codd, G. A. (1993). Grazing rates on toxic and non-toxic strains of cyanobacteria by Hypophthalmichthys molitrix and Oreochromis niloticus. Journal of Fish Biology, 43, 901–907. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1993.tb01164.x.
Blanco, S., Romo, S., & Fernandez-Alaez, M. (2008). Response of epiphytic algae to nutrient loading and fish density in a shallow lake: A mesocosm experiment. Hydrobiologia, 600, 65–76. doi:10.1007/s10750-007-9176-0.
Brooks, J. L., & Dodson, S. I. (1965). Predation, body size and composition of plankton. Science, 150, 28–35. doi:10.1126/science.150.3692.28.
Cairns, J,. Jr, McCormick, P. V., & Niedrlehner, B. R. (1993). A proposed framework for developing indicators of ecological health. Hydrobiologia, 263, 1–44. doi:10.1007/BF00006084.
Cammen, L. M. (1980). Ingestion rate: An empirical model for aquatic deposit feeders and detritivores. Oecologia, 44, 303–310. doi:10.1007/BF00545232.
Carlson, R. E. (1977). A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 22(2), 361–369.
Carpenter, S. R., & Kitchell, J. F. (1993). The trophic cascade in lakes. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Carpenter, S. R., Kitchell, J. F., Hodgson, J. R., Cochran, P. A., Elser, J. J., Elser, M. M., et al. (1987). Regulation of lake primary productivity by food web structure. Ecology, 68, 1863–1876. doi:10.2307/1939878.
Carpenter, S. R., Cole, J. J., Kitchell, J. F., & Pace, M. L. (1998). Impact of dissolved organic carbon, phosphorus and grazing on phytoplankton biomass and production in experimental lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 43, 73–80.
Carpenter, S. R., Brock, W. A., Cole, J. J., Kitchell, J. F., & Pace, M. L. (2008). Leading indicators of trophic cascades. Ecology Letters, 11, 128–138.
Collins, S. L., & Glenn, S. M. (1991). Importance of spatial and temporal dynamics in species regional abundance and distribution. Ecology, 73(2), 654–664. doi:10.2307/2937205.
Coveney, M. F., Stites, D. L., Lowe, E. F., Battoe, L. E., & Conrow, R. (2002). Nutrient removal from eutrophic lake water by wetland filtration. Ecological Engineering, 19, 141–159. doi:10.1016/S0925-8574(02)00037-X.
Crumpton, W. G., Isenhart, T. M., & Mitchell, P. D. (1992). Nitrate and organic N analyses with second-derivative spectroscopy. Limnological Oceanography, 37, 907–913.
deBernardi, R., & Giussani, G. (1990). Are blue-green algae a suitable food for zooplankton? An overview. Hydrobiologia, 200/201, 29–41.
Downing, J. A., & McCauley, E. (1992). The nitrogen: Phosphorus relationship in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 37, 936–945.
Drake, M. T., & Pereira, D. L. (2002). Development of a fish-based index of biotic integrity for small inland lakes in Central Minnesota. North American Journal of Fisheries Management, 22, 1105–1123.
Drenner, R. W., & Hambright, K. D. (2002). Piscivores, trophic cascades, and lake management. The Scientific World Journal, 2, 284–307.
Elser, J. J., Marzolf, E. R., & Goldman, C. R. (1990). Phosphorus and nitrogen limitation of phytoplankton growth in the fresh waters of North America: A review and critique of experimental enrichments. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 47, 1468–1477.
Fleeger, J. W., Carman, K. R., Webb, S., Hilbun, N., & Pace, M. C. (1999). Consumption of microalgae by the grass shrimp Palaemonetes pugio. Journal of Crustacean Biology, 19(2), 324–336.
Forsberg, G., & Ryding, S. O. (1980). Eutrophication parameters and tropic state indices in 30 waste receiving Swedish lakes. Archiv fur Hydrobiology, 89, 189–207.
Gulati, R. D., & van Donk, E. (2002). Lakes in The Netherlands, their origin, eutrophication and restoration: State-of-the-art review. Hydrobiologia, 478(1–3), 73–106.
Hansson, L. A., Annadoter, H., Bergman, E., Hamrin, S. F., Jeppesen, E., Kairesalo, T., et al. (1998). Biomanipulation as an application of food chain theory: Constraints, synthesis and recommendations for temperate lakes. Ecosystems, 1, 558–574.
Hansson, L. A., Gyllström, M., Ståhl-Delbanco, A., & Senssson, M. (2004). Responses to fish predation and nutrients by plankton at different levels of taxonomic resolution. Freshwater Biology, 49, 1538–1550.
Hecky, R. E., & Kilham, P. (1988). Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: A review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography, 33, 796–822.
Hilden, M., & Rapport, D. (1993). Four centuries of cumulative impacts on a Finnish river and its estuary: An ecosystem health approach. Journal of Aquatic Ecosystem Stress and Recovery, 2(4), 261–275.
Hunt, R., & Matveev, V. F. (2005). The effects of nutrients and zooplankton community structure on phytoplankton growth in a subtropical Australian reservoir: An enclosure study. Limnologica, 35, 90–101.
Hutchinson, G. E. (1957). A treatise on limnology. Introduction to lake biology and limnoplankton, vol II. New York: Wiley.
Hwang, S. J., Kim, H. S., & Shin, J. K. (2001). Filter-feeding effect of a freshwater bivalve (Corbicula leana PRIME) on phytoplankton. Korean Journal of Limnology, 34(4), 298–309.
Jeppesen, E., Jensen, J. P., Kristensen, P., Søndergaard, M., Mortensen, M., Sortkjaer, O., et al. (1990). Fish manipulation as a lake restoration tool in shallow, eutrophic, temperate lakes. II. Threshold levels, long-term stability and conclusions. Hydrobiologia, 200/201, 219–227.
Jones, J. R., An, K.-G., & Knowlton, M. F. (2003). Trophic state, seasonal patterns and empirical models in South Korean reservoirs. Lake and Reservoir Management, 19(1), 64–78.
KARICO (2001). Report of water monitoring in Agricultureal reservoirs, S. Korea. Korea Agriculture and Rural Infrastructure Cooperation (in Korean)
Karr, J. R. (1981). Assessment of biotic integrity using fish communities. Fisheries, 6(6), 21–27.
Karr, J. R., & Chu, E. W. (1997) Biological monitoring and assessment: Using multimetric indexes effectively. EPA 235-R97-001. Seattle: University of Washington.
Karr, J. R., Fausch, K. D., Angermeier, P. L., Yant, P. R., & Schlosser, I. J. (1986). Assessing biological integrity of running waters: A method and its rationale. Special Publication 5. Champaign: Illinois Natural History Survey.
Kasai, F., Takamura, N., & Hatakeyama, S. (1993). Effects of symetrine on growth of various freshwater algal taxa. Environmental Pollution, 76, 77–83.
Kim, I. S. (1995). The conservation and status of threatened freshwater fishes in Korea. In H.-J. Lee & I. S. Kim (Eds.), Proceedings of ichthyofauna and characteristics of freshwater ecosystems in Korea, pp. 31–50. Seoul: The Ecological Society of Korea and The Korean Society of Ichthyology.
Kim, H.-S., & Hwang, S.-J. (2004). Effects of nutrients and N/P ratio stoichiometry on phytoplankton growth in an eutrophic reservoir. Korean Journal of Limnology, 37(1), 36–46.
Kim, I. S., & Park, J. Y. (2002). Freshwater fish of korea. Seoul: Kyo-Hak.
Kim, H.-S., Hwang, S.-J., Shin, J.-K., An, K.-G., & Yoon, C.-G. (2007). Effects of limiting nutrients and N:P ratios on the phytoplankton growth in a shallow hypertrophic reservoir. Hydrobiologia, 581, 255–267.
Kratzer, C. R., & Brezonik, P. L. (1981). A Carlson-type trophic state index for nitrogen in Florida lakes. Water Research Bulletin, 17, 713–715.
Lammens, E. M. R. R. (1988). Trophic interactions in the hypertrophic Lake Tjenke Meere: Top-down and bottom-up effects in relation to hydrology, predation and bioturbation during the period 1974 to 1985. Limnologica, 19, 81–87.
Lammens, E. H. R. R. (1999). The central role of fish in lake restoration and management. Hydrobiologia, 395/396, 191–198.
Lieberman, D. M. (1996). Use of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molotrix) and bighead carp (Aristichthys nobillis) for algae control in a small pond: Changes in water quality. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 11(4), 391–393.
Marker, A. F. H., Crowther, C. A., & Gunn, R. J. M. (1980). Methanol and acetone as solvents for estimating chlorophyll and pheopigments by spectrophotometry. Ergebnisse der Limnologie, 14, 52–69.
Meijer, M. L., Jeppesen, E., van Donk, E., Moss, B., Sceffer, N., Lammens, E., et al. (1994). Long term responses to fish reduction in small shallow lakes: interpretation five year results of four biomanipulation cases in the Netherlands and Denmark. Hydrobiologia, 275/276, 457–464.
Meijer, M.-L., DeBoos, I., Scheffer, M., Portielje, R., & Hosper, H. (1999). Biomanipulation in shallow lakes in the Netherlands: An evaluation of 18 case studies. Hydrobiologia, 408/409, 13–30.
Miura, T. (1990). The effects of planktivorous fishes on the plankton community in a eutrophic lake. In R. D. Gulati, E. H. R. R. Lammens, M. L. Meijer & E. van Donk (Eds.), Biomanipulation-tool for water management, pp. 567–579. Dordrecht, Belgium: Kluwer Academic.
Morris, D. P., & Lewis, W. M. (1988). Phytoplankton nutrient limitation in Colorado mountain lakes. Freshwater Biology, 20(3), 315–327.
Moss, B. (1999). Ecological challenges for lake management. Hydrobiologia, 395/396, 3–11.
Nurnberg, G. K. (1996). Trophic state of clear and colored, soft- and hard-water lakes with special consideration of nutrients, anoxia, phytoplankton and fish. Lake Reservoir Management, 12, 432–447.
Onkal-Engin, G., Demir, I., & Engin, S. N. (2005). Determination of the relationship between sewage odour and BOD by neural networks. Environmental Modelling & Software, 20, 843–850.
Persson, L., Andersson, G., Hamrin, S. F., & Johansson, L. (1988). Predator regulation and primary production along the productivity gradient of temperate lake ecosystems. In S. R. Carpenter (Ed.), Complex interactions in lake communities, pp. 45–65. New York: Springer.
Phillips, N. W. (1984). Compensatory intake can be consistent with an optimal foraging model. The American Naturalist, 123(6), 867–872.
Pick, F. R., & Lean, D. R. S. (1987). The role of macronutrients (C, N, P) in controlling cyanobacterial dominance in temperate lakes. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater research, 21, 425–434.
Pitois, S., Jackson, M. H., & Wood, B. J. B. (2001). Sources of the eutrophication problems associated with toxic algae: An overview. Journal of Environmental Health, 64, 25–32.
Prokopkin, I. G., Gubanov, V. G., & Gladyshev, M. I. (2006). Modelling the effect of planktivorous fish removal in a reservoir on the biomass of cyanobacteria. Ecological Modelling, 190(3–4), 419–431.
Quirós, R. (2002). The nitrogen to phosphorus ratio for lakes: A cause or a consequence of aquatic biology? In Cirelli Fernandez & G. Chalar Marquisa (Eds.), El Agua en Iberoamerica: De la Limnologia a la Gestion en Sudamerica, pp. 11–26. Buenos Aires, Argentina: CYTED XVII, Centro de Estudios Transdiciplinarios del Agua, Facultad de Veterinaria, Universidad de Buenos Aires.
Rabergh, C. M. I., Bylund, G., & Eriksson, J. E. (1991). Histopathological effects of microcystin-LR, a cyclic peptide toxin from the cyanobacterium (blue-green alga) Microcystis aeruginosa, on common carp. Aquatic Toxicology, 20, 131–146.
Rankin, E. T., & Yoder, C. O. (1999). Adjustments to the index of biotic integrity: A summary of Ohio experiences and some suggested modifications. In T. P. Simon (Ed.), Assessing the sustainability and biological integrity of water resources using fish communities. Boca Raton, FL: CRC.
Reynolds, C. S. (1984). The ecology of freshwater phytoplankton. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Romare, P., & Bergman, E. (1999). Juvenile fish expansion following biomanipulation and resulting effect on the predation pressure on zooplankton. Hydrobiologia, 404, 89–97.
Romo, S., Miracle, M. R., Villens, M.-J., Rueda, J., Ferriol, C., & Vicente, E. (2004). Mesocosm experiments on nutrient and fish effects on shallow lake food webs in a Mediterranean climate. Freshwater Biology, 49, 1593–1607.
Sanders, R. E., Miltner, R. J., Yoder, C. O., & Rankin, E. T. (1999). The use of external deformities, erosion, lesions, tumors (DELT anomalies) in fish assemblages for characterizing aquatic resources: A case study of seven Ohio streams. In T. P. Simon (Ed.), Assessing the sustainability and biological integrity of water resources using fish communities. Boca Raton, FL: CRC.
Schauser, I., Chorus, I., & Heinzmann, B. (2006). Strategy and current status of combating eutrophication in two Berlin Lakes for safeguarding drinking water resources. Water Science & Technology, 54(11–12), 93–100.
Schindler, D. W. (1974). Eutrophication and recovery in experimental lakes: Implications for lake management. Science, 184, 897–899.
Schindler, D. W. (1977). Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science, 195, 260–262.
Schindler, D. E., Carpenter, S. R., Cole, J. J., Kitchell, J. F., & Pace, M. L. (1997). Food web structure alters carbon exchange between lakes and the atmosphere. Science, 277, 248–251.
Schwarz, D., Grosch, R., & Gross, W. (2004). Water quality for hydroponics: Nutrients, bacteria and algae in rainwater ponds. Acta Horticulturae, 644, 533–539.
Shapiro, J., & Wright, D. I. (1984). Lake restoration by biomanipulation: Round Lake, Minnesota, the first two years. Freshwater biology, 14, 371–383.
Smith, V. H. (1983). Low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios favor dominance by blue-green algae in lake phytoplankton. Science, 221, 669–671.
Smith, D. W. (1989). The feeding selectivity of silver carp Hypophthalmicthys molitrix Val. Journal of Fish Biology, 34, 819–828.
SPSS (2004). SPSS 12.0 KO for Windows. Apache Software Foundation.
Starling, F. L. R. M. (1993). Control of eutrophication by silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) in the tropical Paranoa Reservoir (Brasilia, Brazil): A mesocosm experiment. Hydrobiologia, 257, 143–152.
Starling, F. L. R. M., & Rocha, A. J. A. (1990). Experimental study of the impacts of planktivorous fishes on plankton community and eutrophication of tropical Brazilian reservoir. In R. D. Gulati, E. H. R. R. Lammens, M. L. Meijer & E. van Donk (Eds.), Biomanipulation-tool for water management, pp. 581–591. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Tada, K., Sakai, K., Nakano, Y., Takemura, A., & Montani, S. (2003). Size-fractionated phytoplankton biomass in coral reef waters off Sesoko Island, Okinawa, Japan. Journal of Plankton Research, 25(8), 991–997.
Tong, S. T. Y. (2001). An integrated exploratory approach to examining the relationships of environmental stressors and fish responses. Journal of Aquatic Ecosystem Stress and Recovery, 9, 1–19.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). (1993). Fish field and laboratory methods for evaluating the biological integrity of surface waters. U.S. Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory-Cincinnati, Office of Modelling, Monitoring Systems and Quality Assurance, Cincinnati, Ohio 45268, USA. EPA 600-R-92-111.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). (1994). Environmental monitoring and assessment program: Integrated quality assurance project plan for the surface waters resource group, 1994 activities, Rev. 2.00. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Las Vegas, NV. EPA 600/X-91/080.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). (1998). Lake and reservoir bioassessment and biocriteria technical guidance document. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, Washington, D.C. EPA-841-B-98-007.
van Donk, E., Gulati, R. D., & Grimm, M. P. (1990). Restoration by biomanipulation in a small hepertrophic lake: First-year results. Hydrobiologia, 191, 285–295.
Van Liere, L. (Ed.), (1986). Flushing as a tool to combat eutrophication in L. vuntus (in Dutch). WQL Report 1986-3.
Vanni, M. J. (2002). Nutrient cycling by animals in fresh water ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 33, 341–370.
Vanni, M. J., & Layne, C. D. (1997). Nutrient recycling and herbivory as mechanisms in the ‘top-down’ effect of fish and algae in lakes. Ecology, 78, 21–40.
Vollenweider, A. (1976). Advances in defining critical loading levels for phosphorus in lake eutrophication. Memorie dellIstituto Italino di Idrobiologia (International Journal of Limnology), 33, 53–83.
Wang, H.-J., Liang, X.-M., Jiang, P.-H., Wang, J., Wu, S.-K., & Wang, H.-Z. (2008). TN:TP ratio and planktivorous fish do not affect nutrient-chlorophyll relationships in shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology, 53, 935–944.
Weithman, A. S., & Anderson, R. O. (1976). Angling vulnerability of Esocidae. Proceedings of the Annual Conference of South East Association of Game Fish Commissioners, 30, 99–102.
Winemiller, K. O. (1990). Spatial and temporal variation in tropical fish trophic networks. Ecological Monographs, 60, 331–367.
Xu, F.-L., Tao, S., & Xu, Z.-R. (1999). The restoration of riparian wetlands and macrophytes in Lake Chao, an eutrophic Chinese lake: Possibilities and effects. Hydrobiologia, 405, 169–178.
Zhang, X., Xie, P., Hao, L., Guo, N., Gong, Y., Hu, X., et al. (2006). Effects of the phytoplanktivorous silver carp (Hypophthalmicthys molitrixon) on plankton and the hepatotoxic microcystins in an enclosure experiment in a eutrophic lake, Lake Shichahai in Beijing. Aquaculture, 257, 173–186.
Acknowledgment
This research was funded by the project (no. 306009-03-2-CG000) of the Agricultural Technology Development Center, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, Korea (Project Title: Development of Water Quality Management Techniques in Agricultural Reservoirs Using Fish Trophic Structure Analysis and Top-down Biomanipulations).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, KG., Lee, JY., Kumar, H.K. et al. Control of Algal Scum Using Top-Down Biomanipulation Approaches and Ecosystem Health Assessments for Efficient Reservoir Management. Water Air Soil Pollut 205, 3–24 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0053-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0053-5