Abstract
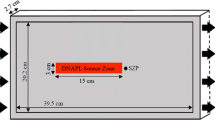
The use of enhanced-flushing technologies has emerged as a promising technique for the remediation of sites contaminated with immiscible liquids. An important aspect for the effective remediation of these sites depends on the physical heterogeneity of the subsurface and the related distribution of immiscible liquid present within porous media. Recent interest has developed in using mass flux-based approaches to evaluate remediation success and performance for immiscible liquid-contaminated sites. The unique focus of these experiments was to evaluate trichloroethene (TCE) mass flux behavior and mass removal effectiveness for various solubilization agents when the distribution of immiscible liquid is uniform. In order to accurately compare the performance of each enhanced-solubilization agent, the distribution of immiscible liquid must be consistent and uniform. Previous dissolution experiments have typically relied upon injecting immiscible liquid into the porous media which can result in nonuniform immiscible liquid distribution causing nonideal dissolution and mass flux behavior (i.e., immiscible liquid fingering and bypass flow). Homogeneous 20/30 quartz sand was thoroughly mixed with a predetermined amount of immiscible liquid TCE and packed into columns to ensure that uniform distributions of residually saturated TCE (S N = 8–11%) were created. These columns were then flushed with a specific enhanced-solubilization flushing agent to initiate dissolution. Of the four enhanced-solubilization used, the lower solubilization power flushing agents (i.e., cyclodextrins) resulted in more ideal TCE mass flux behavior in which mass flux is maximized and maintained during the majority of the flushing experiment. A strong positive correlation (R 2 = 0.92) exists between enhancement factor and mass flux ideality which may suggest that these systems were in fact uniformly distributed with immiscible liquid. In order to appropriately evaluate and compare the effectiveness of specific solubilization agents, it is important to consider mass flux behavior in conjunction with elution behavior and mass removal efficiency.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul, A. S., & Gibson, T. L. (1991). Laboratory study of surfactant-enhanced washing of polychlorinated biphenyl from sandy material. Environmental Science & Technology, 25, 665. doi:10.1021/es00016a009.
Abdul, A. S., Gibson, T. L., & Rai, D. N. (1990). Selection of surfactant for the removal of petroleum products from shallow sandy aquifers. Ground Water, 28(6), 920–926. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.1990.tb01728.x.
Adeel, Z., & Luthy, R. G. (1995). Sorption and transport kinetics of a nonionic surfactant through an aquifer sediment. Environmental Science & Technology, 29(4), 1032–1042. doi:10.1021/es00004a025.
Augustijn, D. C. M., Jessup, R. E., Rao, S. C., & Wood, L. (1994). Remediation of contaminated soils by solvents flushing. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 120(1), 42–56. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1994)120:1(42).
Basu, N. B., Rao, P. S. C., Falta, R. W., Annable, M. D., Jawitz, J. W., & Hatfield, K. (2008). Temporal evolution of DNAPL source and contaminant flux distribution: Impacts of source mass depletion. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 95, 93–109. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2007.08.001.
Bizzigotti, G. O., Reynolds, D., & Kueper, B. H. (1997). Enhanced solubilization and destruction of tetrachloroethylene by hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin and iron. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(2), 472–478. doi:10.1021/es960324g.
Blanford, W. J., Barackman, M. L., Boving, T. B., Klingel, E. J., Johnson, G. R., & Brusseau, M. L. (2001). Cyclodextrin-enhanced vertical flushing of a trichloroethene contaminated aquifer. Ground Water Monitoring & Remediation, 21(1), 58–66. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6592.2001.tb00631.x.
Blue, J. E., Brusseau, M. L., & Srivastava, R. (1998). Simulating tracer and resident contaminant transport to investigate the reduced efficiency of a pump-and-treat operation. In M. Herbert & K. Kovar (Eds.), Groundwater quality: Remediation and protection, vol. 250, pp. 537–543. Wallingford: IAHS.
Boving, T. B., & Brusseau, M. L. (2000). Solubilization and removal of residual trichloroethene from porous media: Comparison of several solubilization agents. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 42, 51–67. doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(99) 00077-7.
Boving, T. B., Wang, X., Ji, W., & Brusseau, M. L. (1999). Cyclodextrin-enhanced solubilization and removal of residual chlorinated solvents from porous media. Environmental Science & Technology, 33(5), 764–770. doi:10.1021/es980505d.
Boyd, G. R., & Farely, K. J. (1992). NAPL removal from groundwater by alcohol flooding: Laboratory studies and applications. In P. Kostechi, E. Calabrese & C. Bell (Eds.), Hydrocarbon contaminated soils and groundwater: Analysis and fate, environmental and public health effects, and remediation. Ann Arbor, MI: Lewis.
Brandes, D., & Farley, K. J. (1993). Importance of phase behavior on displacement on the removal of residual DNAPLs from porous media by alcohol flooding. Water Environment Research, 65, 869–878.
Broholm, K., Cherry, J.A., & Feenstra, S.(1992). Dissolution of heterogeneously distributed solvent residuals. Proceeding of subsurface restoration conference, third international conference on ground water quality research, June 21–24, 1992, Dallas, TX. National Center for Ground Water Research, Rice University, Environmental Science & Engineering, pp. 96–98.
Brooks, M. C., Annable, M. D., Rao, P. S. C., Hatfield, K., Jawitz, J. W., Wise, W. R., et al. (2004). Controlled release, blind test of DNAPL remediation by ethanol flushing. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 69, 281–297. doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(03)00158-X.
Brown, C. L., Pope, G. A., Abriola, L. M., & Sepehernoori, K. (1994). Simulation of surfactant-enhanced aquifer remediation. Water Resources Research, 30(11), 2959–2977. doi:10.1029/94WR01458.
Brusseau, M. L. (1992). Rate-limited mass transfer and transport of organic solutes in porous media that contain immobile immiscible organic liquid. Water Resources Research, 28, 33–45. doi:10.1029/91WR02498.
Brusseau, M. L., Wang, X., & Hu, Q. (1994). Enhanced transport of low-polarity organic compounds through soil by cyclodextrin. Environmental Science & Technology, 28(5), 952–956. doi:10.1021/es00054a030.
Brusseau, M. L., Wang, X., & Wang, W. (1997). Simultaneous elution of heavy metals and organic compounds from soil by cyclodextrin. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(4), 1087–1092. doi:10.1021/es960612c.
Brusseau, M. L., Rohrer, J. W., Decker, T. M., Nelson, N. T., & Linderfelt, W. R. (1999). Contaminant transport and fate in a source zone of a chlorinated-solvent contaminated superfund site: overview and initial results of an advanced site characterization project. In M. L. Brusseau, D. A. Sabatini, J. S. Gierke & M. D. Annable (Eds.), Innovative subsurface remediation: field testing of physical, chemical, and characterization technologies. American Chemical Society: Washington, DC.
Brusseau, M. L., Nelson, N. T., Oostrom, M., Zhang, Z. H., Johnson, G. R., & Wietsma, T. W. (2000). Influence of heterogeneity and sampling method on aqueous concentrations associated with NAPL dissolution. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 3657–3664. doi:10.1021/es9909677.
Brusseau, M. L., Zhang, Z., Nelson, N. T., Cain, R. B., Tick, G. R., & Oostrom, M. (2002). Dissolution of non-uniformly distributed immiscible liquid: Intermediate-scale experiments and mathematical modeling. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 1033–1041. doi:10.1021/es010609f.
Brusseau, M. L., Nelson, N. T., Zhang, Z., Blue, J. E., Rohrer, J., & Allen, T. (2007). Source-zone characterization of a chlorinated-solvent contaminated Superfund site in Tucson, AZ. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 90, 21–40. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2006.09.004.
Brusseau, M. L., DiFilippo, E. L., Marble, J. C., & Oostrom, M. (2008). Mass-removal and mass-flux-reduction behavior for sources zones with hydraulically-poorly accessible immiscible liquid. Chemosphere, 71(8), 1511–1521. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.064.
Carroll, K.C. and Brusseau, M.L. (2009). Dissolution, cyclodextrin-enhanced solubilization, and mass removal of an ideal multicomponent organic liquid. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology (in press).
Chawla, R.C., Doura, K.F., & McKay, D.(2001). Effect of alcohol cosolvents on the aqueous solubility of trichloroethylene. Proceedings of the 2001 conference on environmental research.
Childs, J., Acosta, E., Annable, M. D., Brooks, M. C., Enfield, C. G., Harwell, J. H., et al. (2006). Field demonstration of sufactant-enhanced solubilization of DNAPL at Dover Air Force Base, Delaware. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 82, 1–22. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2005.08.008.
DiFilippo, E. L., & Brusseau, M. L. (2008). Mass flux reduction as a function of source zone mass removal: Evaluation of field data. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 98(1–2), 22–35. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2008.02.004.
Edwards, D. A., Luthy, R. G., & Liu, Z. (1991). Solubilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in micellar nonionic surfactant solutions. Environmental Science & Technology, 25(1), 127–133. doi:10.1021/es00013a014.
Enfield, C. G., Wood, A. L., Brooks, M. C., & Annable, M. D. (2002). Interpreting tracer data to forecast remedial performance. In S. Thorton & S. Oswald (Eds.), Groundwater quality 2001: Natural and enhanced restoration of groundwater pollution. Proceedings of the groundwater quality 2001 conference. IAHS publ. no. 275, pp. 11–16. Wallingford: IAHS.
Falta, R. W., Lee, C. M., Brame, S. E., Roeder, E., Coates, J. T., Wright, C., et al. (1999). Field test of high molecular weight alcohol flushing for subsurface nonaqueous phase liquid remediation. Water Resources Research, 35(7), 2095–2108. doi:10.1029/1999WR900097.
Falta, R. W., Rao, P. S. C., & Basu, N. (2005). Assessing the impacts of partial mass depletion on DNAPL source-zones: I. Analytical modeling of source strength functions and plume response. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 78, 259–280. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2005.05.010.
Fountain, J. C., Klimek, A., Beikirch, M. G., & Middleton, T. M. (1991). The use of surfactants for in situ extraction of organic pollutants from a contaminated aquifer. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 28(3), 295–311. doi:10.1016/0304-3894(91)87081-C.
Fure, A. D., Jawitz, J. W., & Annable, M. D. (2006). DNAPL source-zone depletion: Linking architecture and response. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 85, 118–140. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2006.01.002.
Hasegawa, M. A., Sabatini, D. A., & Harwell, J. H. (1997). Liquid–liquid extraction for surfactant contaminant separation and surfactant reuse. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 7, 691–697. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1997)123:7(691).
Imhoff, P.T. (1992). Dissolution of a nonaqueous phase liquid in saturated porous media, Ph.D. dissertation, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ.
Imhoff, P. T., Gleyzer, S. N., McBride, J. F., Vancho, L. A., Okuda, I., & Miller, C. T. (1995). Cosolvent-enhanced remediation of residual dense nonaqueous phase liquid; experimental investigation. Environmental Science & Technology, 29(8), 1966–1976. doi:10.1021/es00008a014.
Jawitz, J. W., Sillan, R. K., Annable, M. D., Rao, P. S. C., & Warner, K. (2000). In-situ alcohol flushing of a DNAPL source zone at a dry cleaner site. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(17), 3722–3729. doi:10.1021/es9913737.
Jawitz, J. W., Fure, A. D., Demmy, G. G., Berglund, S., & Rao, P. S. C. (2005). Groundwater contaminant flux reduction resulting from nonaqueous phase liquid mass reduction. Water Resources Research, 41(10), 10408–10423. doi:10.1029/2004WR003825.
Johnson, G. R., Zhang, Z., & Brusseau, M. L. (2003). Characterizing and quantifying the impact of immiscible-liquid dissolution and non-linear, rate-limited sorption/desorption on low-concentration elution tailing. Water Resources Research, 39, 1120. doi:10.1029/2002WR001435..
Lemke, L. D., & Abriola, L. M. (2006). Modeling dense nonaqueous phase liquid mass removal in nonuniform formations: Linking source-zone architecture and system response. Geosphere, 2, 74–82. doi:10.1130/GES00025.1.
Lemke, L. D., Abriola, L. M., & Lang, J. R. (2004). Influence of hydraulic property correlation on predicted dense nonaqueous phase liquid source-zone architecture, mass recovery and contaminant flux. Water Resources Research, 40(12), W12417. doi:10.1029/2004WR003061.
Marble, J. C., DiFilippo, E. L., Zhang, Z., Tick, G. R., & Brusseau, M. L. (2008). Application of a lumped-process mathematical model to dissolution of non-uniformly distributed immiscible liquid in heterogeneous porous media. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 100, 1–10.
Mayer, A. S., & Miller, C. T. (1996). The influence of mass transfer characteristics and porous media heterogeneity on nonaqueous phase liquid dissolution. Water Resources Research, 32, 1551–1567. doi:10.1029/96WR00291.
McCray, J. E., & Brusseau, M. L. (1998). Cyclodextrin-enhanced in situ flushing of multiple-component immiscible organic liquid contamination at the field scale: mass removal effectiveness. Environmental Science & Technology, 32(9), 1285–1293. doi:10.1021/es970579+.
McCray, J. E., & Brusseau, M. L. (1999). Cyclodextrin-enhanced in-situ flushing of multiple-component immiscible organic liquid contamination at the field scale: analysis of dissolution behavior. Environmental Science & Technology, 33(1), 89–95. doi:10.1021/es980117b.
McCray, J. E., Boving, T. B., & Brusseau, M. L. (2000). Cyclodextrin-enhanced solubilization of organic contaminants with implications for aquifer remediation. Ground Water Monitoring Review, 20, 94–103. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6592.2000.tb00256.x.
Mercer, J. W., & Cohen, R. M. (1990). A review of immiscible fluids in the subsurface: Properties, models, characterization and remediation. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 54, 174–193.
Nambi, I. M., & Powers, S. E. (2000). Immiscible-liquid dissolution in heterogeneous systems: An experimental investigation in a simple heterogeneous system. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 44, 161–184. doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(00)00095-4.
National Research Council (NRC) (U.S.). (1994). Alternatives for groundwater cleanup. Washington, DC: National Academic.
National Research Council (NRC) (U.S.). (1997). Innovation in groundwater and soil cleanup. Washington, DC: National Academic.
National Research Council (NRC) (U.S.). (1999). Groundwater and soil cleanup: improving management of persistent contaminants. Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences.
National Research Council (NRC) (U.S.). (2000). Research needs in subsurface science. Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences.
National Research Council (NRC) (U.S.). (2005). Contaminants in the subsurface: Source zone assessment and remediation. Washington, DC: National Academic.
Nkedi-Kizza, P., Rao, P. S. C., & Hornsby, A. G. (1985). Influence of organic cosolvents on sorption of hydrophobic organic chemicals by soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 19(10), 975–979. doi:10.1021/es00140a015.
Pankow, J. F., & Cherry, J. A. (eds). (1996). Dense chlorinated solvents and other DNAPLs in groundwater. Portland, OR: Waterloo.
Parker, J. C., & Park, E. (2004). Modeling field-scale dense nonaqueous phase liquid dissolution kinetics in heterogeneous aquifers. Water Resources Research, 40, W05109. doi:10.1029/2003WR002807.
Pennel, K. D., Abriola, L. M., & Weber, W. J. (1993). Surfactant enhanced solubilization of residual dodecane in soil columns: Experimental investigation. Environmental Science & Technology, 27(12), 2332–2340. doi:10.1021/es00048a005.
Peters, C. A., & Luthy, R. G. (1993). Coal tar dissolution in water-miscible solvent: Experimental evaluation. Environmental Science & Technology, 27(13), 2831–2843. doi:10.1021/es00049a025.
Powers, S. E., Nambi, I. M., & Curry, G. W. (1998). Non-aqueous phase liquid dissolution in heterogeneous systems: mechanisms and a local equilibrium modeling approach. Water Resources Research, 34, 3293–3302. doi:10.1029/98WR02471.
Rao, P. S. C., Hornsby, A. G., Kilcrease, D. P., & Nkedi-Kizza, P. (1985). Sorption and transport of toxic organic chemicals in mixed-solvent systems: Model development and preliminary evaluation. Journal of Environmental Quality, 14, 376–383.
Rao, P. S. C., Annable, M. D., Sillan, R. K., Dai, D., Hatfield, K., & Graham, W. D. (1997). Field-scale evaluation of in situ cosolvent flushing for enhanced aquifer remediation. Water Resources Research, 33(12), 2673–2686. doi:10.1029/97WR02145.
Rao, P. S. C., Jawitz, J. W., Enfield, C. G., Falta, R. W., Annable, M. D., & Wood, A. L. (2002). Technology integration for contaminated site remediations: Clean-up goals and performance criteria. In S. Thorton & S. Oswald (Eds.), Groundwater quality 2001: Natural and enhanced restoration of groundwater pollution. Proceedings of the groundwater quality 2001 conference. IAHS publ. no. 275, pp. 571–578. IAHS Publication: Wallingford.
Rao, P. S. C., & Jawitz, J. W. (2003). Comment on “Steady state mass-transfer from single-component dense nonaqueous phase liquids in uniform flow fields” by. T.C. Sale and D.B. McWhorter. Water Resources Research, 39(3), 1068–1070. doi:10.1029/2001WR000599.
Rivett, M. O., Feenstra, S., & Cherry, J. A. (2001). A controlled field experiment on groundwater contamination by multicomponent DNAPL: Creation of the emplaced-source and overview of dissolved plume. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 49, 111–149. doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(00)00191-1.
Rouse, J. D., Sabatini, D. A., & Harwell, J. H. (1993). Minimizing surfactant losses using twin head anionic surfactants in subsurface remediation. Environmental Science & Technology, 27(10), 2072–2078. doi:10.1021/es00047a012.
Roy, S. B., Dzombak, D. A., & Ali, M. A. (1995). Assessment in situ solvent extraction for remediation of coal tar sites: Column studies. Water Environment Research, 67(1), 4–15. doi:10.2175/106143095X131141.
Saba, T., & Illangasekare, T. H. (2000). Effect of groundwater flow dimensionality on mass transfer from entrapped nonaqueous phase liquid contaminants. Water Resources Research, 36, 971–979. doi:10.1029/1999WR900322.
Schwille, F. (1988). Dense chlorinated solvents in porous and fractured media, p. 144. Chelsea, MI: Springer.
Shiau, B. J., Sabatini, D. A., & Harwell, J. H. (1994). Solubilization and microemulsification of chlorinated solvents using direct food additive (edible) surfactants. Ground Water, 32(4), 561–569. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.1994.tb00891.x.
Sillan, R. K., Annable, M. D., Rao, P. S. C., Dai, D., Hatfield, K., Graham, W. D., et al. (1998). Evaluation of in situ co-solvent flushing dynamics using a network of multi-level samplers. Water Resources Research, 34(9), 2191–2202. doi:10.1029/98WR00938.
Soga, K., Page, J. W. E., & Illangasekare, T. H. (2004). A review of NAPL source zone remediation efficiency and the mass flux approach. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 110, 13–27. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.02.034.
Tick, G. R., Lourenso, F., Wood, A. L., & Brusseau, M. L. (2003). Pilot-scale demonstration of cyclodextrin as a solubility-enhancement agent for the remediation of a tetrachloroethene-contaminated aquifer. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(24), 5829–5834. doi:10.1021/es030417f.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (U.S.).(1985). Treatment of contaminated soils with aqueous surfactants. Report EPA/600/2-285/129.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (U.S.).(2003). The DNAPL remediation challenge: Is there a case for source depletion? Expert panel on DNAPL remediation, Kavanaugh, MC. and P.S.C. Rao, Co-Chairs, EPA/600/R-03/143. http://www.epa.gov/ada/pubs/reports.html. March, 2007.
Van Genuchten, M.T. (1981). CFITIM Model: Estimates parameters in several equilibrium and non-equilibrium transport models from solute breakthrough curves. Research Report No. 119, USDA Salinity Laboratory, Riverside, CA.
Wang, X., & Brusseau, M. L. (1993). Solubilization of low-polarity organic compounds by hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Environmental Science & Technology, 27(12), 2821–2825. doi:10.1021/es00049a023.
Wang, X., & Brusseau, M. L. (1995a). Cyclopentanol-enhanced solubilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by cyclodextrins. Environmental Science & Technology, 29(9), 2346–2351. doi:10.1021/es00009a029.
Wang, X., & Brusseau, M. L. (1995b). Simultaneous complexation of organic compounds and heavy metals by a modified cyclodextrin. Environmental Science & Technology, 29(10), 2632–2635. doi:10.1021/es00010a026.
Wang, J., Marlowe, E. M., Miller, R. M., & Brusseau, M. L. (1998). Cyclodextrin-enhanced biodegradation of phenanthrene. Environmental Science & Technology, 9(13), 1907–1912. doi:10.1021/es980011g.
Wood, A.L. (1995). Influence of cosolvents on the transport of hydrophobic organic chemicals in soils under isocratic and gradient conditions. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Oklahoma, Norman.
Wood, A. L., Carl, G., Enfield, C. G., Espinoza, F. P., Annable, M. D., Brooks, M. C., et al. (2005). Design of aquifer remediation systems: (2) Estimating site-specific performance and benefits of partial source removal. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 81, 148–166. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2005.08.004.
Zhang, Z. H., & Brusseau, M. L. (1999). Nonideal transport of reactive solutes in heterogeneous porous media 5. Simulating regional-scale behavior of a trichloroethene plume during pump-and-treat remediation. Water Resources Research, 35, 2921–2935. doi:10.1029/1999WR900162.
Zhu, J., & Sykes, J. F. (2004). Simple screening models of NAPL dissolution in the subsurface. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 72, 245–258. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2003.11.002.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for the comments and suggestions provided. This research was supported in part from startup funds used to purchase analytical equipment, instruments, supplies, and chemicals by the College of Arts & Sciences, The University of Alabama.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tick, G.R., Rincon, E.A. Effect of Enhanced-Solubilization Agents on Dissolution and Mass Flux from Uniformly Distributed Immiscible Liquid Trichloroethene (TCE) in Homogeneous Porous Media. Water Air Soil Pollut 204, 315–332 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0047-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0047-3