Abstract
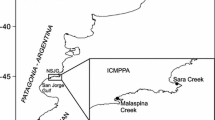
Encerrada Bay (EB) is located in the far south of Argentina, on the north coast of the Beagle Channel and is artificially connected with Ushuaia Bay (UB). This study was carried out between 2004 and 2005; and assesses the impact of Ushuaia city to the nutrient dynamics in EB. It was focused on physical and chemical characterization of discharges, water and sediment quality, nutrient benthic fluxes, and water exchange with UB. The average ammonium, nitrate, phosphate and silicate concentrations in the water bay were 99.5 ± 30.7; 10.0 ± 4.2; 2.0 ± 0.7; 23.5 ± 2.9 µM, respectively. Benthic fluxes showed a consumption of oxygen (50–450 mg m−2 h−1) and nitrate (20–416 µmol m−2 h−1) by sediment and release of ammonium (79−4,772 µmol m−2 h−1) and phosphate (27–36 µmol m−2 h−1) into the water column. The daily contributions of nitrogen and phosphate from the effluents to EB were between 102 and 517 kg day−1 and between 4 and 22 kg day−1 respectively, while the net average export fluxes to UB were 41.7 kg day−1 of nitrogen and 15.7 kg day−1 of phosphate. The difference between received and exported nutrients is consumed in EB by primary producers, partially buffering the impact of wastewater in UB at its own eutrophication risk.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA. (1980). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (15th ed.), p. 1134. Washington, District of Columbia: American Public Health Association.
Boynton, W.R., Kemp, W.M., & Keefe, C.W. (1982). A comparative analysis of nutrients and other factors influencing estuarine phytoplankton production. In National Academy Press (Ed.), Managing wastewater in coastal urban areas. The Role of nutrients in coastal Waters. Appendix A (pp. 177-202). Washington, D.C.
Christensen, B., Vedel, A., & Kristensen, E. (2000). Carbon and nitrogen fluxes in sediment inhabited by suspension-feeding (Nereis diversicolor) and non-suspension-feeding (N. virens) polychaetes. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 192, 203–217. doi:10.3354/meps192203.
Clavero, V., Izquierdo, J. J., Fernández, J. A., & Niell, F. X. (2000). Seasonal fluxes of phosphate and ammonium across the sediment-water interface in a shallow small estuary (Palmones River, southern Spain). Marine Ecology Progress Series, 198, 51–60. doi:10.3354/meps198051.
Conley, D. J., Stockenberg, A., Carman, R., Johnstone, R. W., Rahm, L., & Wulff, F. (1997). Sediment-water nutrient fluxes in the Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 45, 591–598. doi:10.1006/ecss.1997.0246.
Cotano, U., & Villate, F. (2006). Anthropogenic influence on the organic fraction of sediments in two contrasting estuaries: A biochemical approach. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52, 404–414. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.09.027.
Diaz, S., Deferrari, G., Booth, D. R., Martinioni, D., & Oberto, A. (2001). Solar irradiances over Ushuaia (54.49º S, 68.19º W) and San Diego (32.45º N, 117.11º W) geographical and seasonal variation. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 63, 309–320. doi:10.1016/S1364-6826(00)00178-4.
Esteves, J. L., Bonin, P., Blanc, F., Mille, G., & Bertrand, J. C. (1986). Reduction du nitrate dans les sediments marins comparaison des activites mesurees in vitro et in situ. Deuxième Colloque International de Bactèriologie Marine. Actes de Colloques., 3, 319–324.
GESAMP. (1990). Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Pollution: the State of the Marine Environment. UNEP. Regional Seas Reports and Studies. Nº 115. 87 pp.
Gil, M.N. (2001). Eutroficación: Rol del nitrógeno en ecosistemas marinos costeros. Ph.D. Thesis. Universidad Nacional del Sur, Bahía Blanca, Buenos Aires. 132 pp.
Graca, B., Witek, Z., Burska, D., Bialkowska, I., Lukawska-Matuszewska, K., & Bolalek, J. (2006). Pore water phosphate and ammonia below the permanent halocline in the south-eastern Baltic Sea and their benthic fluxes under anoxic conditions. Journal of Marine Systems, 63, 141–154. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2006.06.003.
InfoStat. (2008). Grupo InfoStat, FCA, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. versión 2008. Córdoba, Argentina.
Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas y Censo, (INDEC). (2008). Retrieved from http://www.indec.mecon.ar/censo2001s2_2/ampliada_index.asp?mode=94
Iturraspe, R., Sottini, R., Schroder, C., & Escobar, J. (1989). Hidrología y variables climáticas del territorio de Tierra del Fuego. Centro Austral de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Contribución Científica Nº7. 196 pp.
Kemp, W. M., Sampou, P., Caffrey, J., Mayer, M., Henriksen, K., & Boynton, W. R. (1990). Ammonium recycling versus denitrification in Chesapeake Bay sediments. Limnology and Oceanography, 35(7), 1545–1563.
Kontas, A., Kucuksezgin, F., Altay, O., & Uluturhan, E. (2004). Monitoring of eutrophication and nutrient limitation in the Izmir Bay (Turkey) before and after wastewater treatment plant. Environment International, 29, 1057–1062. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00098-9.
Maksymowska-Brossard, D., & Piekarek-Jankowska, H. (2001). Seasonal variability of benthic ammonium release in the surface sediments of the gulf of Gdansk (southern Baltic Sea). Oceanologia, 43(1), 113–136.
Metcalf, & Eddy. (1991). Wastewater engineering treatment disposal and reuse (Thirdth ed.), p. 1334. Singapore: McGraw-Hill.
Nicholson, G. J., Longmore, A. R., & Berelson, W. M. (1999). Nutrient fluxes measured by two types of benthic chamber. Marine & Freshwater Research, 50, 567–572. doi:10.1071/MF98047.
Niencheski, L. F., & Jahnke, R. A. (2002). Bentic respiration and inorganic nutrient fluxes in the estuarine region of Patos Lagoon (Brazil). Aquatic Geochemistry, 8, 135–152. doi:10.1023/A:1024207220266.
Pinto, A., Von Sperling, E., & Moreira, R. (2001). Chlorophyll-a determination via continuous measurement of plankton fluorescence: methodology development. Water Research, 35(16), 3977–3981. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00102-6.
Pollehne, F. (1986). Benthic nutrient regeneration processes in different sediment types of Kiel Bight. Ophelia, 26, 359–368.
Sakamaki, T., Nishimura, O., & Sudo, R. (2006). Tidal time-scale variation in nutrients flux across the sediment-water interface of an estuarine tidal flat. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 67, 653–663. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2006.01.005.
Saunders, J. E., Al Zahed, K. M., & Paterson, D. M. (2007). The impact of organic pollution on the macrobenthic fauna of Dubai Creek (UAE). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54, 1715–1723. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.07.002.
Servicio de Hidrografía Naval, (SHN). (2008). Retrieved from http://www.hidro.gov.ar/Oceanografia/Tmareas/R_Mareas.asp
Strickland, J.D.H., & Parsons, T.R. (Eds.). (1972). A Practical Handbook of the Seawater Analysis. (Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Bulletin 167). 310 pp.
Tuominen, L., Mäkelä, K., Lehtonen, K. K., Haahti, H., Hietanen, S., & Kuparinen, J. (1999). Nutrient fluxes, porewater profiles and denitrification in sediment influenced by algal sedimentation and bioturbation by Monoporeia affinis. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 49, 83–97. doi:10.1006/ecss.1999.0492.
Vollenweider, R.A. (1992). Coastal marine eutrophication: principles and control. In R. A. Vollenweider, R. Marchetti & R. Vicviani - Elsevier (Ed.), Science of the Total Environment, Supplement: Marine Coastal Eutrophication (pp. 1-120). Amsterdam.
Yakub, G. P., Castric, D. A., Stadterman-Knauer, K. L., Tobin, M. J., Blazina, M., Heineman, T. N., et al. (2002). Evaluation of Colilert and Enterolert defined substrate methodology for wastewater applications. Water Environment Research, 74(2), 131–135. doi:10.2175/106143002X139839.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (PICT-REDES 2002 No. 090) and GEF-UNDP Project ARG 02/G31. We wish to thank Dra. Laura Comoglio, Sr. Ricardo Samaniego, Lic. Erica Giarratano, Lic. Alicia Nizovoy, and Dr. Adrián Schiavini for their help during the campaigns.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torres, A.I., Gil, M.N., Amín, O.A. et al. Environmental Characterization of a Eutrophicated Semi-Enclosed System: Nutrient Budget (Encerrada Bay, Tierra del Fuego Island, Patagonia, Argentina). Water Air Soil Pollut 204, 259–270 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0042-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0042-8