Abstract
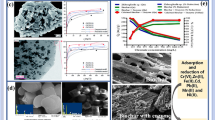
We experimentally determined the adsorption characteristics of natural, freshly precipitated Al(OH)3 for SO4 and PO4. The fresh Al precipitate occurred in stream sediment of Jachymov Stream (Czech Republic). The Al-rich sediment strongly adsorbed added PO4 prior to acidification experiment; this sorbed PO4 was released only after substantial dissolution of the sediment, at pH < 3.67. Sorption of P by Al(OH)3 appears to be an important control on dissolved PO4 concentration in surface waters, unless there is a large excess of PO4. Acidification of the sediment-solution system caused protonation of the sediment surface, thereby increasing the adsorption capacity for SO4. Maximum SO4 adsorption occurred at pH 4.2, below which dissolution of the sediment offset the increasing anion adsorption capacity, and formation of AISO4 + inhibited the increasing SO4 adsorption capacity. This research demonstrates that there are important pH thresholds for anion adsorption in freshwaters below which dissolution of the Al(OH)3 substrate reduces total capacity for anion adsorption. In freshwaters, with sufficient concentrations of suspended Al(OH)3, or in Al(OH)3-rich sediment, PO4 mobility will be severely restricted. Suspended Al(OH)3 in acidified surface waters cannot strongly influence SO4 concentrations because of the considerably higher total SO4 concentrations compared to the available surface area.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alewell, C., Mitchell, M. J., Likens, G. E., & Krouse, H. R. (1999). Sources of stream sulfate at the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest: Long-term analyses using stable isotopes. Biogeochemistry, 44, 281–299.
Amirbahman, A., Pearce, A., Bouchard, R. J., Norton, S. A., & Kahl, J. S. (2003). Relationship between hypolimnetic phosphorus and iron release from eleven lakes in Maine, USA. Biogeochemistry, 65, 369–386. doi:10.1023/A:1026245914721.
Auvray, F., van Hullebush, E., Deluchat, V., & Baudu, M. (2006). Laboratory investigation of the phosphorus removal (SRP and TP) from eutrophic lake water treated with aluminium. Water Research, 40, 2713–2719. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.04.042.
Cosby, B. J., Hornberger, G. M., Galloway, J. N., & Wright, R. F. (1985). Modeling the effects of acid deposition: assessment of a lumped parameter model of soil water and streamwater chemistry. Water Resources Research, 21, 51–63. doi:10.1029/WR021i001p00051.
Geelhoed, J. S., Hiemstra, T., & van Riemsdijk, W. H. (1998). Competitive interaction between phosphate and citrate on goethite. Environmental Science & Technology, 32, 1219–1223. doi:10.1021/es970908y.
Georgantas, D. A., & Grigoropoulou, H. P. (2007). Orthophosphate and metaphosphate ion removal from aqueous solution using alum and aluminum hydroxide. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 315(1), 70–79. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2007.06.058.
Goldberg, S. (1986). Chemical modeling of arsenate adsorption on aluminum and iron oxide minerals. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 50, 1154–1157.
Goldberg, S., Lebron, I., Suarez, D. L., & Hinedi, Z. R. (2001). Surface characterization of amorphous aluminum oxides. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 78–86.
He, L. M., Zelazny, L. W., Baligar, V. C., Ritchey, K. D., & Martens, D. C. (1997). Ionic strength effects on sulfate and phosphate adsorption on g-alumina and kaolinite: Triple layer model. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61, 784–793.
Hodson, M. E., Langan, S. J., Kennedy, F. M., & Bain, D. C. (1998). Variation in soil surface area in a chronosequence of soils from Glen Feshie, Scotland and its implications for mineral weathering calculations. Geoderma, 85, 1–18. doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(98)00013-5.
Chao, T. T., Harward, M. E., & Fang, S. C. (1962). Adsorption and desorption phenomena of sulfate ions in soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 26, 234–237.
Jara, A. A., Violante, A., Pigna, M., & Mora, M. L. (2006). Mutual interactions of sulfate, oxalate, citrate, and phosphate on synthetic and natural allophanes. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 70, 337–346. doi:10.2136/sssaj2005.0080.
Kopacek, J., Hejzlar, J., Kana, J., Porcal, P., & Klementova, S. (2003). Photochemical, chemical, and biological transformations of dissolved organic carbon and its impact on alkalinity production in acidified lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 48, 106–117.
Kopacek, J., Borovec, J., Hejzlar, J., Ulrich, K. U., Norton, S. A., & Amirbahman, A. (2005). Aluminum control of phosphorus sorption by lake sediments. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 8784–8789. doi:10.1021/es050916b.
Kopacek, J., Maresova, M., Hejzlar, J., & Norton, S. A. (2007). Natural inactivation of phosphorus by aluminum in preindustrial lake sediments. Limnology and Oceanography, 52, 1147–1155.
Labar, J. L. (2002). A tool to help phase identification from electron diffraction powder patterns. Microscopy and Analysis, 16, 21.
Larsen, O., & Postma, D. (2001). Kinetics of reductive dissolution of lepidocrocite, ferrihydrite and goethite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(9), 1367–1379. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00623-2.
Lijklema, L. (1980). Interaction of orthophosphate with iron(III) and aluminum hydroxides. Environmental Science & Technology, 14, 537–541. doi:10.1021/es60165a013.
Löfgren, S., Bringmark, L., Aastrup, M., Hultberg, H., Kindbom, K., & Kvarnäs, H. (2001). Sulphur balances and dynamics in three forested catchments in Sweden. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 130, 631–636. doi:10.1023/A:1013840309681.
Martinson, L., & Alveteg, M. (2004). The importance of including the pH dependence of sulfate adsorption in a dynamic soil chemistry model. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 154, 349–356. doi:10.1023/B:WATE.0000022976.01342.2c.
Navratil, T., Vach, M., Norton, S. A., Skrivan, P., Hruska, J., & Maggini, L. (2003). Chemical response of a small stream in a forested catchment (central Czech Republic) to a short-term in-stream acidification. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 7, 411–423.
Nodvin, S. C., Driscoll, C. T., & Likens, G. E. (1986). The effect of pH on sulfate adsorption by a forest soil. Soil Science, 142, 69–75.
Norton, S., Kahl, J., Fernandez, I., Haines, T., Rustad, L., Nodvin, S., et al. (1999). The Bear Brook watershed, Maine U.S.A. (BBWM). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 55, 7–51. doi:10.1023/A:1006115011381.
Norton, S. A., Fernandez, I., Amirbahman, A., Coolidge, K., & Navrátil, T. (2006). Aluminum, phosphorus, and oligotrophy—Assembling the pieces of the puzzle. Verhandlungen-Internationale Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie, 29, 1877–1886.
Pansu, M., & Gautheyrou, J. (2006). Handbook of soil analysis. Berlin: Springer.
Parfitt, R. L., & Smart, S. C. (1978). The mechanism of sulfate adsorption on iron oxides. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42, 48–50.
Parfitt, R. L. (1982). Competitive adsorption of phosphate and sulphate on goethite (a-FeOOH): A note. New Zealand Journal of Science, 25, 147–148.
Peak, D., Ford, R. G., & Sparks, D. L. (1999). An in situ ATR-FTIR investigation of sulfate bonding mechanisms on goethite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 218, 289–299. doi:10.1006/jcis.1999.6405.
Pittauerova, D., & Golias, V. (2002). Weathering of mine wastes after historical silver mining in the Jáchymov ore district (Czech Republic) and migration of uranium. In B. Kribek, & J. Zeman (Eds.), Uranium deposits—from their genesis to the environmental aspects, proceedings (pp. 157–160). Prague: Czech Geological Survey.
Pommerenk, P., & Schafran, G. C. (2005). Adsorption of inorganic and organic ligands onto hydrous aluminum oxide: evaluation of surface charge and the impacts on particle and NOM removal during water treatment. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 6429–6434. doi:10.1021/es050087u.
Porcal, P., Amirbahman, A., Kopacek, J., Novak, F., Norton, S.A. (2008). Photochemical release of humic and fulvic acid-bound metals from simulated soil and streamwater. Journal of Environmental Monitoring (in press)
Prechtel, A., Alewell, C., Armbruster, M., Bittersohl, J., Cullen, J. M., Evans, C. D., et al. (2001). Response to sulphur dynamics in European catchments to decreasing sulphate deposition. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 5, 311–325.
Rebhum, M., & Lurie, M. (1993). Control of organic matter by coagulation and flocs separation. Water Science and Technology, 27, 1–20.
Reitzel, K., Hansen, J., Andersen, F. Ø., Hansen, K. S., & Jensen, H. S. (2005). Lake restoration by dosing aluminum relative to mobile phosphorus in the sediment. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 4134–4140. doi:10.1021/es0485964.
Rydin, E., & Welch, E. B. (1998). Aluminum dose required to inactivate phosphate in lake sediments. Water Research, 32, 2969–2976. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00055-4.
Schecher, W. D., & McAvoy, D. C. (1992). A software environment for chemical equilibrium modeling. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 16, 65–76. doi:10.1016/0198-9715(92)90053-T.
Stoddard, J. L., Jefferies, D. S., Lükewille, A., Clair, T. A., Dillon, P. J., Driscoll, C. T., et al. (1999). Regional trends in aquatic recovery from acidification in North America and Europe. Nature, 401, 575–578. doi:10.1038/44114.
Strahm, B. D., & Harrison, R. B. (2007). Mineral and organic matter controls on the sorption of macronutrient anions in variable-charge soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 71, 1926–1933. doi:10.2136/sssaj2006.0424.
Warfvinge, P., Falkengren-Grerup, U., Sverdrup, H., & Andersen, B. (1993). Modeling long-term cation supply in acidified forest stands. Environmental Pollution, 80, 209–221. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(93)90041-L.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the help of Maria Hojdova in the field and Irena Dobesova in the laboratory. TEM imaging was done by M. Klementova at the Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, ASCR, v.v.i.. BET measurements were done by A. Zukal at the J. Heyrovsky Institute of Physical Chemistry, ASCR, v.v.i.. The National Science Foundation (DEB-0415348 and DEB-0210257) supported Norton, Fernandez, and Amirbahman. Rohovec was supported by institutional project no. AV0Z30130516 and Navratil by project KONAKT ME 840 and the J.W. Fulbright Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navratil, T., Rohovec, J., Amirbahman, A. et al. Amorphous Aluminum Hydroxide Control on Sulfate and Phosphate in Sediment-Solution Systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 201, 87–98 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9929-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9929-z