Abstract
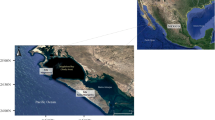
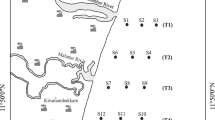
Metal (Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn, Fe) concentrations in marine sediment and zooplankton were investigated in Izmir Bay of the Eastern Aegean Sea, Turkey. The study aimed to assess the levels of metal in different environmental compartments of the Izmir Bay. Metal concentrations in the sediment (dry weight) ranged between 4.26–70.8 μg g−1 for Cu, 233–923 μg g−1 for Mn, 14.9–127 μg g−1 for Ni, 25.6–295 μg g−1 for Zn, 12,404–76,899 μg g−1 for Fe and 38,226–91,532 μg g−1 for Al in the Izmir Bay. Maximum metal concentrations in zooplankton were observed during summer season in the inner bay. Significant relationships existed between the concentrations of certain metals (Al, Fe, Mn and Ni) in sediment, suggesting similar sources and/or similar geochemical processes controlling such metals. Higher concentrations of Cu, Zn and percent organic matter contents were found in the middle-inner bays sediments. Based on the correlation matrix obtained for metal data, organic matter was found to be the dominant factor controlling Cu and Zn distributions in the sediment. In general, mean Cu and Zn levels in the bay were above background concentrations in Mediterranean sediments. Zooplankton metal concentrations were similar to sediment distributions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bryan, G. W. (1979). Bioaccumulation of marine pollutants. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B, 286, 483–505.
Bruland, K. W., Donat, J. R., & Hutchins, D. A. (1991). Interactive influences of bioactive trace metals on biological production on oceanic waters. Limnology and Oceanography, 36, 1555–1577.
Calvert, S. E., Mukherjee, S., & Morris, R. J. (1985). Trace metals in fulvic and humic acids from modern organic rich sediments. Oceanologica Acta, 8, 167–173.
Cosma, B., Contardi, V., Zanicchi, G., & Capelli, R. (1983). Heavy metals in superficial sediments of a contaminated estuary. Chemical Ecology, 1(4), 331–344.
Cosma, B., Frache, R., Baffi, F., & Dadone, A. (1982). Trace metals in sediments from the Ligurian coast, Italy. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 13(4), 127–132.
Duman, M., Avci, M., Duman, S., Demirkurt, E., & Duzbastilar, M. K. (2004). Surficial sediment distribution and net sediment transport pattern in Izmir Bay. Continental Shelf Research, 24, 965–981.
Emelianov, E. M., Romankevitch, E. A. (1979). In E. A. Romankevich (Ed.) Geochemistry of organic matter in the ocean p. 127. Berlin: Springer.
Ergin, M., Bodur, M. N., Ediger, D., Ediger, V., & Yilmaz, A. (1993a). Organic carbon distribution in the surface sediments of the Sea of Marmara and its control by the inflows from the adjacent water masses. Marine Chemistry, 41, 311e326.
Ergin, M., Bodur, M. N., Ediger, V., Yemenicioglu, S., Okyar, M., & Kubilay, N. (1993b). Sources and dispersal of heavy metals in surface sediments along the eastern Aegean shelf. Bolletino di Oceanoogia Teorica Applicato, 11(1), 27–44.
Ergin, M., Kazan, B., & Ediger, V. (1996). Sources and depositional controls on heavy metal distribution in marine sediments of Gulf of Iskenderun, Eastern Mediterranean. Marine Geology, 133, 223–239.
Förstner, U., & Wittman, G. T. W. (1983). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Fowler, S. W. (1985). Monitoring of the content of metallic trace elements in pelagic organisms in open regions of the Mediterranean Sea. (Paper presented at Kompleksn. Global’ ny Monit. Mirovoga Okeana. Tr, Mezhdunar, Simp. Ist, Vol. 2, 347–68)
Friligos, N., Moriki, A., Sklivagou, E., Krasakopoulou, E., & Hatzianestis, I. (1998). Geochemical characteristics of the surficial sediments of the Aegean Sea. (Paper presented at 35th CIESM Congress, Dubrovnik).
Giordano, R., Musmeci, L., Caralli, L., Vernillo, I., Chirico, M., Piccioni, A., et al. (1992). Total contents and sequential extractions of mercury, cadmium, and lead in coastal sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 24(7), 350–357.
Hach (1988). Procedures for water and wastewater analysis. Publication 3061.
Haraldsson, C., & Westerlund, S. (1991). Total and suspended cadmium, cobalt, copper, iron, lead, manganese, nickel and zinc in the water column of the Black Sea. Paper presented at Black Sea Oceanography pp. 161–172. Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Hardstedt-Roméo, M., & Laumond, F. (1980). Zinc, copper and cadmium in zooplankton from the N. W. Mediterranean. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 11, 133–138.
IMST (1990–1991). Environmental impact assesment of dredging works at the Izmir Harbour Ministry of Public Works. D.E.U. Institute of Marine Science and Technology, Izmir, Turkey.
IMST (1999). Marine research in the Izmir Bay Project (1994–1998). Final Report, D.E.U. Institute of Marine Science and Technology, Izmir, Turkey.
Kamidis, N. I., Stamatis, N., & Sylaios, G. (2004). Trace elements concentrations in the surface sediments and the water column of Kavala Gulf. (Paper presented at 37th CIESM Congress).
Karageorgis, A. P., Anagnostou, C. L., & Kaberi, H. (2005). Geochemistry and mineralogy of the NW Aegean Sea surface sediments: Implications for river runoff and anthropogenic impact. Applied Geochemistry, 20, 69–88.
Kontas, A. (2006). Mercury in Izmir Bay: An assessment of contamination. Journal of Marine Systems, 61, 67–78.
Kontas, A., Kucuksezgin, F., Altay, O., & Uluturhan, E. (2004). Monitoring of eutrophication and nutrient limitation the Izmir Bay (Turkey) before and after wastewater treatment plant. Environment International, 29, 1057–1062.
Kucuksezgin, F., Kontas, A., Altay, O., & Uluturhan, E. (2005). Elemental composition of particulate matter and nutrient dynamics in the Izmir Bay (Eastern Aegean). Journal of Marine Systems, 56(1–2), 67–84.
Larsen, B., & Jensen, A. (1989). Evaluation of the sensitivity og sediment monitoring stations in pollution monitoring. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 20, 556–560.
Loder, T. C., & Liss, P. S. (1985). Control by organic coatings of the surface charge of estuarine suspended particles. Limnology and Oceanography, 30, 418–421.
Loring, D. H. (1984). Trace metal geochemistry of sediments from Baffin Bay. Canada Journal of Earth Sciences, 16, 1196–1209.
Mason, B., & Moore, C. R. (1982). Principles of geochemistry p. 344. New york, N. Y.: Wiley.
Nieboer, E., & Richardson, D. H. S. (1980). The replacement of the nondescript term heavy metals_ by a biologically and chemically significant classification of metal ions. Environmental Pollution, B, 1, 3–26.
Phillips, D. J. H., & Rainbow, P. S. (1993). Biomonitoring of aquatic trace contaminants. London: Chapman and Hall.
Pruysers, P. A., de Lange, G. J., & Middelburg, J. J. (1991). Geochemistry of esatern Mediterranean sediments: Primary sediment composition and diagenetic alterations. Marine Geology, 100, 137–154.
Rainbow, P. S. (1992). The significance of accumulated heavy metal concentrations in marine organisms. (Paper presented at Miskiewicz AG, editor. Assessment of the distribution, impacts and bioaccumulation of contaminants in aquatic environments, Proceedings of a bioaccumulation Workshop. Water Board and Australian Marine Science Association Inc., Sydney).
Salomons, W., & Fostner, U. (1984). Metals in the hydrocycle p. 349. Berlin: Springer.
Scoullos, M. (1979). Chemical studies in the Gulf of Elefsis, Greece. PhD Thesis, Dept of Oceanography, The University of Liverpool, U. K.
Steele, J. (2001). Encyclopedia of ocean sciences. (X Imprint: Academic press)
Summerhayes, C. P., & Thorpe, S. A. (1996). Oceanography—an illustred guide p. 148. London, UK: Manson Publishing Ltd.
UNEP (1984a). Sampling of selected marine organisms and sample preparation for trace metal analysis. Reference Methods for Marine Pollution Studies, (7).
UNEP (1984b). Determination of total Cd, Zn, Pb and Cu in selected marine organisms by flameless AAS. Reference Methods for Marine Pollution Studies, 11.
UNEP (1986a). Determination of total manganese in marine sediments by flame atomic absorption spectrophometry, No: (38).
UNEP (1986b). Determination of total iron in marine sediments by flame atomic absorption spectrophometry, No: 37.
UNEP (1993). Preliminary assessment of the state of pollution of the Mediterranean Sea by zinc, copper and their compounds and proposed measures. UNEP/MED/WG.66/Inf.3, 121 p.
Varnavas, S. P., & Ferentinos, G. (1982). Heavy metal distribution in the surface sediments of Patraikos bay. (Paper presented at Greece.VIes Journ.Etud.Pollut. Cannes, CIESM. 6, 405–409).
Voutsinou-Taliadouri, F., & Satsmadjis, J. (1982). Concentration of some metals in east Aegean sediments. Review International Oceanography Mediterranean, 66–67, 71–76.
Voutsinouu-Taliadouri, F. (1983). Metal concentration in polluted and unpolluted Greek sediments: a comparative study. Review International Oceanography Mediterranean, 113–114, 71–76.
Wangersky, P. J. (1986). Biological control of trace metal residue time and speciation: A review and synthesis. Marine Chemistry, 18, 269–297.
Whitehead, N. E., Oregioni, B., & Fukai, R. (1985). Background levels of trace metals in Mediterranean sediments. (Paper presented at Journ.Etud.Pollut. CIESM. 7, 233–240.
Yucesoy, F., & Ergin, M. (1992). Heavy metal geochemistry of surface sediments from the southhern Black Sea shelf and upper slope. Chemical Geology, 99, 265–287.
Zafiropoulos, D., & Grimanis, A. P. (1977). Trace elements in Acartia clausi from Elefsis Bay of the upper Saranikos Gulf, Greece. (Paper presented at Journ.Etud.Pollut. CIESM, 3, 63–67).
Zvonaric, T., & Odzak, N. (1998). Distribution of Hg, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in surface sediments from the coastal region of the central Adriatic. (Paper presented at Rapp Comm Int Mer Medit 1998, 35:312).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kontas, A. Trace metals (Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn, Fe) Contamination in Marine Sediment and Zooplankton Samples from Izmir Bay. (Aegean Sea, Turkey). Water Air Soil Pollut 188, 323–333 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9547-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9547-1