Abstract
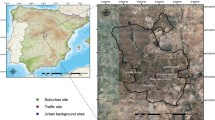
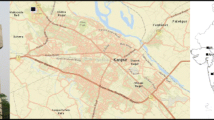
The major objective of this paper is to provide insights to sources and sinks of nitrous acid in urban areas, and their seasonal dependency on meteorology, photochemistry and long range transport. With this aim, nitrous acid (HONO) mixing ratios and other compounds were measured in Ashdod (south of Tel Aviv, Israel), a typical Mediterranean urban area. Statistical data analysis revealed the expected correlation between HONO and nitrogen oxides during the autumn campaign when HONO sources appeared to be traffic-, harbor-, and industry-related. Conversely, during summer HONO and NO2 were no longer correlated: NO2 at nighttime was probably deposited onto surfaces, soil and plants, whereas HONO at daytime was likely destroyed photolytically contributing to the OH concentration. Photolysis was expected to be the dominant HONO sink at daytime, especially during the summer period. Using modeled photolytical HONO lifetimes we estimate the magnitude of heterogeneous and/or organic electron transfer source reactions of HONO as 6–8 ppbv/h.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acker, K., Febo, A., Trick, S., Perrino, C., Bruno, P., & Wiesen, P., et al. (2006a). Nitrous acid in the urbane area of Rome. Atmospheric Environment, 40, 3123–3133.
Acker, K., Möller, D., Auel, R., Wieprecht, W., & Kalaß, D. (2005). Concentrations of nitrous acid, nitric acid, nitrite and nitrate in the gas and aerosol phase at a site in the emission zone during ESCOMPTE 2001 experiment. Atmospheric Research, 74, 507–524. DOI 10.1016/J.ATMOSRES.2004.04.009.
Acker, K., Möller, D., Wieprecht, W., Meixner, F. X., Bohn, B., & Gilge, S., et al. (2006b). Strong daytime production of OH from HNO2 at a rural mountain site. Geophysical Research Letters, 33, L02809 DOI 10.1029/2005GL024643.
Alicke, B., Platt, U., Stutz, J. (2002). Impact of nitrous acid photolysis on the total hydroxyl radical budget during the limitation of oxidant production/Pianura Padana Produzione di Ozono study in Milan. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 107, 8196.
Alicke, B., Geyer, A., Hofzumahaus, A., Holland, F., Konrad, S., & Pätz, H. W., et al. (2003). OH formation by HONO photolysis during the BERLIOZ experiment. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(D4), 8247 DOI 10.1029/2001 JD000579.
Alicke, B., & Platt, U. (2000). Impact of nitrous acid photolysis on the total hydroxyl radical budget during the limitation of oxidant production/Pianura Padana Produzione di Ozono Study in Milan. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107(D22), 8196 DOI 10.1029/2000JD000075.
Amoroso, A., Beine, H. J., Sparapani, R., Nardino, M., & Allegrini, I. (2006). Observation of coinciding arctic boundary layer ozone depletion and snow surface emissions of nitrous acid. Atmospheric Environment, 40, 1949–1956.
Andrés-Hernández, M. D., Notholt, J., Hjorth, J., & Schrems, O. (1996). A DOAS study on the origin of nitrous acid at urban and non-urban sites. Atmospheric Environment, 30(2), 175–180.
Appel, B. R., Winer, A. M., Tokiwa, Y., & Biermann, H. W. (1990). Comparison of atmospheric nitrous acid measurements by annular denuder and differential optical absorption system. Atmospheric Environment, 24A, 611–616.
Arndt, R. L., & Carmichael, G. R. (1995). Long-range transport and deposition of sulfur in Asia. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 85, 2283–2288, DOI 10.1007/BF01186174.
Aumont, B., Chervier, F., Laval, S. (2003). Contribution of HONO sources to the NO/HO/O chemistry in the polluted boundary layer. Atmospheric Environment, 37(4), 487–498.
Bari, A., Ferraro, V., Wilsonb, L. R., Luttinger, D., & Husain, L. (2003). Measurements of gaseous HONO, HNO3, SO2, HCl, NH3, particulate sulfate and PM2.5 in New York, NY. Atmospheric Environment, 37(20), 2825–2835.
Bejan, J., El Aal, Y. A., Barnes, I., Benter, T., Bohn, B., Wiesen, P., et al. (2006). The photolysis of ortho-nitrophenols: A new gas phase source of HONO. Physical Chemistry, Chemical Physics, DOI 10.1039/b516590c.
Carslaw, D. C., Beevers, S. D., & Fuller, G. (2001). An empirical approach for the prediction of annual mean nitrogen dioxide concentrations in London. Atmospheric Environment, 35, 1505–1515.
Carlsaw, N., & Carlsaw, D. (2001). The gas-phase chemistry of urban atmospheres. Surveys in Geophysics, 22, 31–53.
Febo, A., Perrino, C., & Allegrini, I. (1996). Measurement of nitrous acid in Milan, Italy, by DOAS and diffusion denuders. Atmospheric Environment, 30, 3599–3609.
Febo, A., Perrino, C., & Cortiello, M. (1993). A denuder technique for the measurement of nitrous acid in urban atmosphere. Atmospheric Environment, 27A, 1721–1728.
Geßler, A., Rienks, M., & Rennenberg, H. (2002). NH3 and NO2 fluxes between beech trees and the atmosphere correlation with climatic and physiological parameters. New Phytology, 147, 539–560.
George, C., Strekowski, R. S., Kleffmann, J., Stemmler, K., & Ammann, M. (2005). Photoenhanced uptake of gaseous NO2 on solid organic compounds: A photochemical source of HONO. Faraday Discussion, 130, 195–211.
Grosjean, D., Fung, K., Collins, J., Harrison, J., & Breitung, E. (1984). Portable generator for on-site calibration of peroxyacetyl nitrate. Analytical Chemistry, 56, 569–573.
Gut, A., Scheibe, M., Rottenberger, S., Rummel, U., Welling, M., Ammann, C., et al. (2002). Exchange fluxes of NO2 and O3 at soil and leaf surfaces in an Amazonian rain forest. Journal of Geophysical Research, Atm ISI: 000180466200017, ISSN: 0747-7309, DOI 10.1029/2001JD000654. Local id: 2158/S 37876.
Harris, G. W., Carter, W. P. L., Winer, A. M., Pitts Jr., J. N., Platt, U., & Perner, D. (1982). Observations of nitrous acid in the Los Angeles atmosphere and the implications for the ozone precursor relationships. Environment Science and Technology, 16, 414–419.
Harrison, R. M., Jones, A. M., & Barrowcliffe, R. (2004). Field study of the influence of meteorological factors and traffic volumes upon suspended particle mass at urban roadside sites of differing geometries. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 6361–6369.
Harrison, R. M., Peak, J. D., & Collins, G. M. (1996). Tropospheric cycle of nitrous acid. Journal of Geophysical Research, 101(D9) 14429–14439.
Kirchstetter, T. W., Harley, R. A., & Littlejohn, D. (1996). Measurement of nitrous acid in motor vehicle exhaust. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 2843–2849.
Kleffmann, J., Becker, K. H., & Wiesen, P. (1998). Heterogeneous NO2 conversion processes on acid surfaces: Possible atmospheric implications. Atmospheric Environment, 32, 2721.
Kleffmann, J., & Gavriloaiei, T. (2005). Daytime formation of nitrous acid: A major source of OH radicals in a forest. Geophysical Research Letters, 32, L05818 DOI 10.1029/2005GL022524.
Kleffmann, J., Kurtenbach, R., Orzer, J. L., Wiesen, P., Kalthoff, N., & Vogel, B., et al. (2003). Measured and simulated vertical profiles of nitrous acid Part I: Field measurements. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 2949–2955.
Kurtenbach, R., Becker, K. H., Gomes, J. A. G., Kleffmann, J., Lörzer, J. C., & Splitter, M., et al. (2001). Investigations of emissions and heterogeneous formation of HONO in a road traffic tunnel. Atmospheric Environment, 35, 3385–3394.
Jenkin, M. E., Cox, R. A., & Williams, D. J. (1988). Laboratory studies of the kinetics of formation of nitrous acid from the thermal reaction of nitrogen dioxide and water vapour. Atmospheric Environment, 22, 497–498.
Lammel, G., & Cape, J. N. (1996). Nitrous acid and nitrite atmosphere. Chemical Society Reviews Articles, 25, 361–369.
Lee, H. S., Kang, C. M., Kang, B. W., & Kim, H. K. (1999). Seasonal variations of acidic air pollutants in Seoul, South Korea. Atmospheric Environment, 33, 3143–3152.
Li, L., Chen, Z. M., Zhang, Y. H., Zhu, T., Li, J. L., & Ding, J. (2006). Kinetics and mechanism of heterogeneous oxidation of sulfur dioxide by ozone on surface of calcium carbonate. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussion, 6, 579–613 SRef-ID: 1680-7375/acpd/2006-6-579.
Matsumoto, M., & Okita, T. (1998). Long term measurements of atmospheric gaseous and aerosol species using an annular denuder system in Nara, Japan. Atmospheric Environment, 32(8), 1419–1425.
Moussiopoulos, N., Papalexiou, S., Lammel, G., & Arvanitis, T. (2000). Simulation of nitrous acid formation taking into account heterogeneous pathways: Application to the Milan metropolitan area. Environmental Modeling & Software, 15, 629–637.
Perrino, C., Pietrodangelo, A., & Febo, A. (2001). An atmospheric stability index based on radon progeny measurements for the evaluation of primary urban pollution. Atmospheric Environment, 35, 5235–5244.
Pitts, J. N., Biermann, H. W., Winner, A. M., Tuazon, E. C. (1984). Spectroscopic identification and measurement of gaseous nitrous acid in dilute auto exhaust. Atmospheric Environment, 18, 847–854.
Reisinger, A. R. (2000). Observation of HNO2 in the polluted winter atmosphere: Possible heterogeneous production on aerosols. Atmospheric Environment, 34, 3865–3874.
Ren, X., Harder, H., Martinez, M., Lesher, R. L., Oliger, A., & Shirley, T., et al. (2003). OH and HO2 chemistry in urban atmosphere of New York City. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 3639–3651. DOI 10.1016/S1352-2310(03)00459-X.
Rondon, A., & Sanhueza, E. (1998). High HONO atmospheric concentrations during vegetation burning in the tropical savannah. Tellus, 41B, 474–477.
Sakamaki, F., Hatakeyama, S., & Akimoto, H. (1983). Formation of nitrous acid and nitric oxide in the heterogeneous dark reaction of nitrogen dioxide and water vapor in a smog chamber. International Journal of Chemical Kinetics, 15, 1013–1029.
Schiller, C. L., Locquiao, S., Johnson, T. J., & Harri, G. W. (2001). Atmospheric measurements of HONO by tunablediode laser absorption spectroscopy. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 40, 275–293.
Schimang, R., Folkers, A., Kleffmann, J., Kleist, E., Miebach, M., & Wildt, J. (2006). Uptake of gaseous nitrous acid (HONO) by several plant species. Atmospheric Environment, 40, 1324–1335.
Sillman, S. (1999). The relation between ozone, NOx; and hydrocarbons in urban and polluted rural environments. Atmospheric Environment, 33, 1821–1845.
Sjodin, A., & Ferm, M. (1985). Measurement of nitrous acid in urban air. Atmospheric Environment, 19, 985–992.
Sparks, J. P., Monson, R. K., Sparks, K. L., & Lerdau, M. (2001). Leaf uptake of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) in a tropical wet forest: Implications for tropospheric chemistry. Oecologia, 127, 214–221.
Staffelbach, T., Neftel, A., Blatter, A., Gut, A., Fahrni, M., & Stähelin, J., et al. (1997). Photochemical oxidant formation over Southern Switzerland, 1. Results from summer 1994. Journal Geophysical Research, 102, 23345–23362.
Stemmler, K., Ammann, M., Donders, C., Kleffmann, J., & George, C. (2006). Photosensitized reduction of nitrogen dioxide on humic acid as source of nitrous acid. Nature, 440, 195–198. DOI 10.1038/nature04603, 2006.
Stemmler, K., Ammann, M., Elshorbany, Y., Kleffmann, J., Ndour, M., & D’Anna, B., et al. (2007). Light induced conversion of nitrogen dioxide into nitrous acid on submicron humic acid aerosol. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussion, 7, 4035–4064, 2007 www.atmos-chem-phys-discuss.net/7/4035/2007/.
Svensson, R., Ljungström, E., & Lindqvist, O. (1987). Kinetics of the reaction between nitrogen dioxide and water vapour. Atmospheric Environment, 21, 1529–1539.
Syomin, D. A., & Finlayson-Pitts, B. J. (2003). HONO decomposition on borosilicate gass surfaces: Implication for environmental chamber studies and field experiments. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 5, DOI 1039/b309851f.
Vecera, Z., & Dasgupta, P. K. (1994). Indoor nitrous acid levels: Production of nitrous acid from open flame sources. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 56, 311–316.
Volpe Horii, C., Munger, J. W., Wofsy, S. C., Zahniser, M., Nelson, D., & McManus, B. (2004). Fluxes of nitrogen oxides over a temperature deciduous forest. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109, D08305 DOI 10.1029/2003JD004326.
Wang, H., & Shooter, D. (2004) Atmospheric concentrations of HCl, HONO, HNO3, SO2 and NH3 in Auckland. New Zealand Clean Air and Environmental Quality, 38(2).
Winer, A. M., & Biermann, H. W. (1994). Long pathlength differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) measurement of gaseous HONO, NO2 and HCHO in the California South Coast Air Basin.. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 20, 423–445.
Zhou, X., Beine, H. J., Honrath, R. E., Fuentes, J. D., Simpson, W., & Shepson, P. B., et al. (2001). Snowpack photochemical production as a source for HONO in the arctic boundary layer in spring time. Geophysical Research Letters, 28(21), 4087–4090.
Zhou, X., Civerolo, K., & Dai, H. (2002). Summertime nitrous acid chemistry in the atmospheric boundary layer at a rural site in New York State, 2002. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107, D21, 4590, DOI 10.1029/2001JD001539.
Acknowledgements
This work has been part of a bilateral Italian–Israeli cooperation on environmental technologies (“Modeling system for urban air pollution” Project). Financial support mainly from Italian Ministry for Environment, Land and Sea (Department for Environmental Research and Development) is gratefully acknowledged. The authors are grateful to Drs. Anat Rozen, Doron Lahav, Karol Soudry of the “Ashdod–Yavneh Regional Association for Environmental Protection,” and Yaacov Mamane of the Technion for the hospitality, the local support, and the meteorological data, NOx, O3, PM2.5 and SO2 data used in this publication. Useful comments from Francesca Costabile (CNR) are also gratefully acknowledged. The authors further gratefully acknowledge the WMO (World meteorological organization) for the data overhead ozone column website (http://www.wmo.ch/pages/prog/arep/gaw/ozone/index.html) and the NCAR’s on-line TUV model (http://cprm.acduncar.edu/models/interactive.TUV/) for the photolysis ratio used in this publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amoroso, A., Beine, H.J., Esposito, G. et al. Seasonal Differences in Atmospheric Nitrous Acid near Mediterranean Urban Areas. Water Air Soil Pollut 188, 81–92 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9526-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9526-6