Abstract
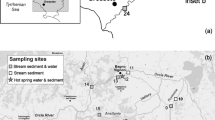
An intensive survey of mercury speciation was performed at a site on the Upper St. Lawrence River near Cornwall, Ontario, Canada with a history mercury contamination in sediments. Surface sediments were collected every 1.50 h. Total mercury (Hgtotal), methylmercury (MeHg), organic carbon, inorganic and organic sulphur were determined in the solid fraction. Dissolved Hgtotal, MeHg and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) were measured in pore waters. Concentrations of Hgtotal in the upper layers (first 5 cm) were high, ranging from 1.42 to 25.8 nmol g−1 in solids and from 125 to 449 pM in pore waters. MeHg levels were also high, ranging from 4.34 to 34.1 pmol g−1 in solids and from 40 to 96 pM in pore waters. This amounts to up to 1.4% of Hgtotal present as MeHg in solids and 64% in pore waters. A daily pattern for Hgtotal was observed in the solid fraction. The MeHg distribution in solids and pore waters was not correlated with Hgtotal or DOC, suggesting that the concentrations of MeHg are probably more influenced by the relative rates of methylation/demethylation reactions in the sediment–water interface. Acid volatile sulphide levels and DOC were inversely correlated with organic sulphur (Sorg) levels suggesting that both parameters are involved in the rapid production of Sorg. A positive correlation was also observed between Hgtotal and Sorg in solids (R = 0.87, p < 0.01) illustrating the importance of organic sulphur in the retention and distribution of Hg in the solid fraction of the sediments. The results suggest that variations of Hgtotal concentrations in Upper St. Lawrence River surface sediments were strongly influenced by the formation/deposition/retention of organic sulphur compounds in the sediment–water interface.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, P., Schmid, J. C., Mycke, B., Strazielle, C., Connan, J., & Hue, A., et al. (1993). Structural investigation of non-polar sulphur cross-linked macromolecules in petroleum. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 57, 3395–3419.
Alperin, M. J., Albert, D. B., & Martens, C. S. (1994). Seasonal variations in production and consumption rates of dissolved organic carbon in an organic-rich coastal sediment. Geochimica et Cosmochimimica Acta, 58, 4909–4929.
Anschutz, A., Zhong, S., Sundby, B., Mucci, A., & Gobeil, C. (1998). Burial efficiency of phosphorus and the geochemistry of iron in continental margin sediments. Limnology and Oceanography, 43, 53–64.
Baldi, F. (1997). Metal ions in biological systems, vol. 34. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Benner, B., & Storm, M. (1993). A critical evaluation of the analytical blank associated with DOC measurements by high-temperature catalytic oxidation. Marine Chemistry, 41, 153–160.
Bjerregaard, S. R., Bruty, D., Chester, R., & Padgham, R. C. (1999). Retention of methyl-mercury and inorganic mercury in rainbow trout Orcorhynchus mykiss (W): Effect of dietary selenium. Aquatic Toxicology, 45, 171–180.
Bloom, N. S., & Crecelius, E. A. (1987). Determination of mercury in sea water at sub-nanogram-per-liter levels. Marine Chemistry, 14, 49–59.
Boudreau, B. P. (1997). Diagenetic models and their implementation: Modeling transport and reactions in aquatic sediments. New York: Springer.
Burdige, D. J., & Gardner, K. G. (1998). Molecular weight distribution of dissolved organic carbon in marine sediment pore waters. Marine Chemistry, 62, 45–64.
Cai, Y., Jaffe, R., Alli, A., & Jones, T. (1996). Determination of organomercury compounds in aqueous samples by capillary gas chromatography-atomic fluorescence spectrometry following solid-phase extraction. Analytica Chimica Acta, 334, 251–259.
Cai, Y., Tang, G., Jaffe, R., & Jones, R. (1997). Evaluation of some isolation methods for organomercury determination in soil and fish samples by capillary gas chromatography-atomic fluorescence spectrometry. International Journal of Environmental Analitycal Chemistry, 68, 331–345.
Canário, J., Antunes, P., Lavrado, J., & Vale, C. (2004). Simple method for monomethylmercury determination in estuarine sediments. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 23(10–11), 798–805.
Canário, J., Vale, C., & Caetano, M. (2005). Distribution of monomethylmercury and mercury in surface sediments of the Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 1142–1145.
Canário, J., Vale, C., Caetano, M., & Madureira, M. J. (2003). Mercury in contaminated sediments and pore waters enriched in sulphate (Tagus Estuary, Portugal). Environmental Pollution, 126(3), 425–433.
Canfield, D. E., Raiswell, R., Westrich, J. T., Reaves, C. M., & Berner, R. A. (1986). The use of chromium reduction in analysis of reduced inorganic sulphur in sediments and shale. Chemical Geology, 54, 149–155.
CCME (Canadian council of the Ministers of the Environment) (2005). Protocol for the derivation of Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: Summary tables—Update 2002. CCME EPC-98E. Prepared by Environment Canada, Guidelines Division, Technical Secretariat of the CCME Task Group on Water Quality Guidelines. Ottawa, Canada.
Celo, V., Ananth, R. V., Scott, S. L., & Lean, D. R. S. (2004). Methylmercury artifact formation during solid-phase extraction of water samples using sulfhydryl cotton fiber adsorbent. Analytica Chimica Acta, 516, 171–177.
Chester, R., & Huges, M. J. (1967). A chemical technique for the separation of ferromanganese minerals, carbonate minerals and adsorbed trace metals from pelagic sediments. Chemical Geology, 2, 249–262.
Cooper, D. C., & Morse, J. W. (1998a). Extractability of metal sulfide minerals in acidic solutions: Application to environmental studies of trace metal contamination within anoxic sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 1076–1078.
Cooper, D. C., & Morse, J. W. (1998b). Selective extraction chemistry of toxic metal sulfides from sediments. Aquatic Geochemistry, 5, 87–97.
Coquery, M., & Cossa, D. (1995). Mercury speciation in surface sediments of the North Sea. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 34, 245–257.
Coquery, M., Cossa, D., & Martin, J. M. (1995). The distribution of dissolved and particulate mercury in three Siberian Estuaries and adjacent artic coastal waters. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 80, 653–664.
Costley, C. T., Mossop, K. F., Dean, J. R., Garden, L. M., Marshall, J., & Carroll, J. (2000). Determination of mercury in environmental and biological samples using pyrolysis atomic absorption spectrometry with gold amalgamation. Analytica Chimica Acta, 405, 179–183.
Covelli, S., Faganeli, J., Horvat, M., & Brambati, A. (1999). Pore water distribution and benthic flux measurements of mercury and methylmercury in the Gulf of Trieste. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 48, 415–428.
Deming, J. W., & Baross, J. A. (1993). The early diagenesis of organic matter: Bacterial activity. In M. H. Engel & S. A. Macko (Ed.) Organic geochemistry (pp. 119–144). New York: Plenum.
Donazzolo, R., Merlin, O. H., Vitturi, J. M., & Pavoni, B. (1984). Heavy metal content and lithological properties of recent sediments in the North Adriatic. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 15(3), 93–101.
Drobner, E., Huber, H., Wachterhauser, G., Rose, D., & Steller, K. (1990). Pyrite formation linked with hydrogen sulphide evolution under anaerobic conditions. Nature, 546, 742–744.
Duinker, J. C. (1983). Effects of particle size and density on the transport of metals to the ocean. In Trace Metals in Sea Water, Series IV, Vol. 9, (pp. 209–226). New York: NATO Conference Series.
Gagnon, C., Pelletier, E., & Mucci, A. (1997). Behaviour of anthropogenic mercury in coastal marine sediments. Marine Chemistry, 59, 159–176.
Ghosh, D. (2005). Three-dimensional structures of sulfatases. Methods in Enzymology, 400, 273–293.
Gobeil, C., & Cossa, D. (1993). Mercury in sediments and sediment pore water in the Laurentian Trough. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 50, 1794–1800.
Golder Associated Ltd. (2004). Evaluation of the sediment management options for the St. Lawrence River (Cornwall) Area of Concern. Report submitted to: Ontario Ministry of the Environment. Kingston, Ontario, Canada.
Grapentine, L., Milani, D., & Mackay, S. (2003). Assessment of the potential for mercury biomagnifications from sediment in the St. Lawrence River (Cornwall) area of concern. Canada: Environment Canada Publication.
Henneke, E., Luther, G. W., & De Lange, G. J. (1991). Determination of inorganic sulphur speciation with polarographic techniques: Some preliminary results from recent hypersaline anoxic environments. Marine Geology, 100, 115–123.
Henrichs, S. M. (1992). Early diagenesis of organic matter in marine sediments: Progress and perplexity. Marine Chemistry, 39, 119–149.
Hintelmann, H., & Wilken, R. D. (1995). Levels of total and methylmercury compounds in sediments of the polluted Elbe River: Influence of seasonally and spatially varying environmental factors. Science of the Total Environment, 166, 1–10.
Holmes, J., & Lean, D. (2006). Factors that influence methylmercury flux rates from wetland sediments. Science of the Total Environment, 368, 306–319.
Jackson, T. A. (1998). Mercury in aquatic systems. In W. J. Langsttron, & M. J. Bebianno (Eds.) Metal metabolism in aquatic environment (pp. 77–138). London: Chapman and Hall Lda. Publishers.
Jenne, E. A. (1968). Controls of Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn concentrations in soils and water: The significant role of hydrous Mn and Fe-oxides. In R. F. Gould (Ed.), Trace inorganics in water (pp. 337–387). Washington DC: Advanc. Chem. Ser. 73, Am Chem Soc.
Kauss, P., Hamdy, Y. S., & Hamma, B. S. (1988). St. Lawrence River environmental investigations, vol. 1. Background: Assessment of water, sediment and biota in the Cornwall, Ontario and Massena, New York section of the St. Lawrence River, 1979–1982.
Kohen, M. E. L., Sinninghe Damsté, J. S., ock-van-Daken, A. C., Haven, H. L., Rullkotter, J., & de Leeuw, J. W. (1990). Origin and diagenetic transformations of C25 and C30 highly branched isoprenoid sulphur compounds: Further evidence for the formation of the organically bound sulphur during early diagenesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 54, 3053–3063.
LaRiviere, E. (2005). The use of stable isotopes (d 13 C and d 15 N) as indicators for mercury accumulation in yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Dissertation, University of Ottawa, Canada.
Lepage, S., Biberhofer, J., & Lorrain, S. (2000). Sediment dynamics and transport of suspended matter in the upstream area of Lake St. Francis. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 57(Suppl. 1), 52–62.
Likens, G. E., Driscoll, C. T., Buso, D. C., Mitchell, M. J., Lovett, G. M., & Bailey, S. W., et al. (2002). The biogeochemistry of sulphur at Hubbard Brook. Biogeochemistry, 60, 235–316.
Luther, G. W., Giblin, A. E., & Varsolona, R. (1985). Polarographic analysis of sulphur species in marine porewaters. Limnology and Oceanography, 30, 727–736.
Madureira, M.-J., Vale, C., & Simões Gonçalves, M. L. (1997). Effect of plants on sulphur geochemsitry in the Tagus salt-marshes sediments. Marine Chemistry, 58, 27–37.
Mantoura, R. F. C., Dickson, A., & Riley, J. P. (1978). The complexation of metals with humic materials in natural waters. Estuarine Coastal and Marine Science, 6, 387–408.
Mason, R. P., & Lawrence, A. L. (1999). Concentration distribution and bioavailability of mercury and methylmercury in sediments of Baltimore Harbour and Chesapeake Bay, Maryland, USA. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18, 2438–2447.
Matty, J. M., & Long, D. T. (1995). Early diagenesis of mercury in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 21, 574–586.
Milliman, J. D., & Meade, R. H. (1983). World wide delivery of river sediments ti the oceans. Journal of Geology, 91, 1–21.
Moreno, F. N., Anderson, C. W. N., Stewart, R. B., & Robinson, B. H. (2005). Mercury volatilization and phytoextraction from base-metal mine tailings. Environmental Pollution, 136, 341–352.
Morse, J. W., & Luther, G. W. (1999). Chemical influence on trace metal-sulphide interactions in anoxic sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63, 3373–3378.
Muhaia, B. B. M., Leermakers, M., & Baeyens, W. (1997). Total mercury and methylmercury in sediments and in polychaete Nereis diversicolor at Groot Buitenschoor (Scheldt Estuary, Belgium). Water, Air and Soil, Pollution, 94, 109–123.
Pacyna, E. G., Pacyna, J. M., Steenhuisen, F., & Wilson, S. (2006). Global anthropogenic mercury emission inventory for 2000. Atmospheric Environment, 40, 4048–4063.
Pereira, M. E., Duarte, A. C., Millward, G. E., Abreu, S., & Vale, C. (1998). An estimation of industrial mercury stored in sediments of a confined area of the lagoon of Aveiro (Portugal). Water Science Technology, 36(6–7), 125–130.
Persaud, D., Jaagumagi, R., & Hayton, A. (1993). Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediment quality in Ontario. Ontario Ministry of the Environment and Energy, Ontario, Canada.
Quémerais, B., Cossa, D., Rondeau, B., Pham, T. T., & Fortin, B. (1998). Mercury distribution in relation to iron and manganese in the waters of the St. Lawrence River. Science of the Total Environment, 213, 193–201.
Rantala, R. T. T., & Loring, D. H. (1975). Multi-element analysis of silicate rocks and marine sediments by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Atomic Absorption Newsletter, 14, 117–120.
Ravichandran, M. (2004). Interactions between mercury and dissolved organic matter—A review. Chemosphere, 55(3), 319–331.
Reavie, E. D., Smol, J. P., Carignan, R., & Lorrain, S. (1998). Diatom paleolimnology of two fluvial lakes in the St. Lawrence River: A reconstruction of environmental changes during the last century. Journal of Phycology, 34, 446–456.
Rickard, D., & Morse, J. W. (2005). Acid volatile sulfide. Marine Chemistry, 97, 141–197.
Sérodes, J.-B., Cartolano, M., Duval, Y., Labonte, D., Lee, K., Leport, S., et al. (1978). Qualité des sediments de fond du fleuve Saint-Laurent entre Cornwall et Montmagny. Rapport soumi au Comite D`Etude sur le Fleuve Saint-Laurent par La Direction Regionale des Eaux Interieures, p. 467.
SLRRT (St. Lawrence River RAP Team). (1992). Remedial action plan for the St. Lawrence River (Cornwall) Area of Concern. Stragel Report: Environmental conditions and problem definitions. Environment Canada and Environment Ontario, ISBN 0-662-19958-8.
Stempvoort, D. R., & Krouse, H. R. (1994). Controls of d18O in sulfate: Review of experimental data and application to specific environments. In C. N. Alpers & D. W. Blowes (Eds.), Environmental geochemistry of sulfide oxidation (pp. 466–480). New York: Amer. Chem. Soc. Sympos. Ser.
Sundby, B., Silverberg, N., & Chesselet, R. (1981). Pathways of manganese in an open estuarine system. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta, 45(3), 293–307.
USEPA (2001). Method 1631: Guidelines establishing test procedures for the analysis of pollutants: Measurements of mercury in water. Federal Register, 67(209), 65876–65888.
Valisolalao, J., Perakis, N., Chappe, B., & Albrecht, P. (1984). A novel sulphur-containing C35 hopanoid in sediments. Tetrahedron Letters, 14, 555–567.
Wakeham, S. G., Sinninghe Damsté, J. A., Kohnem, M. E. L., & Leeuw, J. W. (1995). Organic sulphur compounds formed during early diagenesis in Black Sea sediments. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta, 59(3), 521–533.
Zar, J. H. (1996). Biostatistical analysis (4th ed.). New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Environment Canada and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) through strategic grant number 0703-240-01. João Canário also acknowledges the grant from the Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian (Portugal) and Dr. Marta Nogueira (IPIMAR) for the carbon and total sulphur analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canário, J., Poissant, L., O`Driscoll, N. et al. Mercury Partitioning in Surface Sediments of the Upper St. Lawrence River (Canada): Evidence of the Importance of the Sulphur Chemistry. Water Air Soil Pollut 187, 219–231 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9510-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9510-1