Abstract
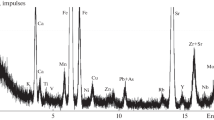
Low-level actinium contamination (228Ac) of petroleum sludge is reported. The sludge is earmarked for road-building and soil enrichment, hence long-term radiation in low doses is not desirable. We subsequently investigated the distribution of this radioactivity over a one-year period. Collection was conducted at different sites, and the sludge was subjected to high-resolution gamma-ray measurement with a Geenlarge this page detector. Samples of 1 kg dry weight were prepared in suitable Marinelli beakers and counted for 12 h. The approximate literature guideline for this radioistope in soil and regular sludge is about 60 Bq/kg. The levels in many of our samples were several times higher, and activities up to 600 Bq/kg were observed. The general distribution was studied; and suggestions for possible preventative remediation to deplete the activity levels in the sludge prior to its use as a building material and on sludge-farms are outlined. The study, therefore, formed an interesting contribution to research associated with radioactivity in the environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baggoura, B., Noureddine, A., & Benkrid, M. (1998). Level of natural and artificial radioactivity in Algeria. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 49, 867–873.
Bou-Rabee, F. (1997). Soil radioactivity atlas of Kuwait. Environment International, 23, 5–15.
Chang, R. (2004). Chemistry (951 pp.). Boston, USA: McGraw-Hill.
Chase, R., & Rabinowitz, L. (1960). Radioisotope methodology (325 pp.). Philadelphia, USA: Butterworth Scientfic Publications.
De, A.K. (1994). Environmental chemistry (75 pp.). New Delhi, India: Wiley.
De Moraes, M.A., & Daltro, T.F.L. (2000). Environmental gamma radiation and natural radioactivity in soils in Centro Experimental Aramar (CTMSP-Brazil) and region. Radiat Protect Dosimetry, 87, 207–211.
Faure, G. (1986). Principles of isotope geology (2nd ed., 589 pp.). New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Fifield, F.W., & Haines, P.J. (2000). Invironmental analytical chemistry (395 pp.). Oxford, UK: Blackwell Science.
Harrison, R.M. (1998). Understanding our environment (198 pp.). Cambridge, UK: The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Manahan, S.E. (1994). Environmental chemistry (249 pp.). Florida, USA: Lewis Publishers.
Pillay, A.E., Williams, J.R., El Mardi, M.O., Hassan, S.M., & Al Hamdi, A. (2002). Monitoring of cadmium in “on” and “off” date palms. Environment International, 28, 273–276.
Pillay, A.E., Williams, J.R., El Mardi, M.O., Hassan, S.M., & Al Hamdi, A. (2003). Risk assessment of chromium and arsenic in date palm leaves used as livestock feed. Environment International, 29, 541–545.
Salih, F.M., Pillay, A.E., Jayasekara, K. (2004). Be levels in sewage sludge: A baseline study. Instrumentation Science and Technology, 32, 433–444.
Spera, G., Cardone, F., Cherubini, G., & Leandri, A. (2003). Natural specific radioactivity in different soils. Communications in Agricultural and Applied Biological Sciences, 68, 817–826.
Taha, R., Ba-Omar, M., Pillay, A.E., Roos, G., & Al-Hamdi, A. (2001). Recycling of petroleum-contaminated sand. Journal of Environmental Monitor, 3, 417–420.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pillay, A.E., Salih, F.M. & Jayasekara, K. Environmental Impact of using actinium (228Ac)-contaminated sludge as soil conditioner and sand substitute. Water Air Soil Pollut 176, 69–75 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9147-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9147-5