Abstract
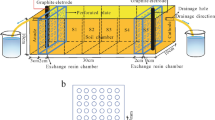
The feasibility of using chelate agents to enhance the electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils has been investigated in this study. Chelate agents were used as washing solutions as well as purging solutions at the electrode compartments. The pH value of the soil significantly affects the removal of heavy metal ions. Due to electrolysis reaction pH increases near the cathode. Without conditioning of the pH value metals precipitate as hydroxides. This problem is solved by the addition of an acid in the cathode compartment. The heavy metals that are dissolved will move to either the cathode or the anode, depending on their charges. This paper presents the results of electrokinetic extraction of cadmium using acetic acid, citric acid and pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid (PDA) as washing and purging solutions, and the removal of zinc using ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) and sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5) as washing and purging solutions, respectively. The results showed that the increased experimental time induced a higher removal efficiency of cadmium and zinc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abumaizar, R. J. and Smith, E. H.: 1999, ‘Heavy metal contaminants removal by soil washing’, Journal of Hazardous Materials B70, 71–86.
Acar, Y. and Alshawabkeh, A.: 1993, ‘Principles of electrokinetic remediation’, Environmental Science and Technology 27(13), 2638–2647.
Azzam, R. and Oey, W.: 2001, ‘The utilization of electrokinetics in geotechnical and environmental engineering’, Transport in Porous Media, 42, 293–314.
Barona, A., Aranguiz, I. and Elias, A.: 2001, ‘Metal associations in soils before and after EDTA extractive decontamination: Implications for the effectiveness of further clean-up procedures’, Environmental Pollution 113, 75–85.
Bassi, R., Prasher, S. O. and Simpson, B. K.: 2000, ‘Extraction of metals from a contaminated sandy soil using citric acid’, Environmental Progress 19(4), 275–282.
Chaiyaraksa, C. and Sriwiriyanuphap, N.: 2004, ‘Batch washing of cadmium from soil and sludge by a mixture of Na2S2O5 and Na2EDTA’, Chemosphere 56, 1129–1135.
Francis, A. J.: 1992, ‘Biodegradation of metal citrate complexes and interactions for toxic metal mobility’, Nature 356, 140–142.
Giannis, A. and Gidarakos, E.: 2005, ‘Washing enhanced electrokinetic remediation for removal cadmium from real contaminated soil’, Journal of Hazardous Materials B123, 165–175.
Hamed, J., Acar, Y. B. and Gale, R. J.: 1991, ‘Pb(II) removal from kaolinite using electrokinetics’, Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 117(2), 241–271.
Hong, A. P. K. and Chen, T. C.: 1996 ‘Chelating extraction and recovery of cadmium from soil using pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid’, Water Air and Soil Pollution 86, 335–346.
Hong, P. K. A., Li, C., Banerji, S. K. and Regmi, T.: 1999, ‘Extraction, recovery, and biostability of EDTA for remediation of trace metal-contamination soil’, Journal of Soil Contamination 8, 81–103.
Kim, S. O., Kim, S. H. and Kim, K. W.: 2001, ‘Removal of heavy metals from soils using enhanced electrokinetic soil processing’, Water Air and Soil Pollution 125, 259–272.
Kim, W. S., Kim, S. O. and Kim, K. W.: 2005, ‘Enhanced electrokinetic extraction of heavy metals from soils assisted by ion exchange membranes’, Journal of Hazardous Materials B118, 93– 102.
Li, R. S. and Li, L. Y.: 2000, ‘Enhancement of electrokinetic extraction from lead-spiked soils’, Journal of Environmental Engineering 126(9), 849–857.
Li, Z., Yu, J. W. and Neretnieks, I.: 1997, ‘Removal of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III) from sand by electromigration’, Journal of Hazardous Materials 55, 295–304.
Lo, I. and Yang, X. Y.: 1999, ‘EDTA extraction of heavy metals from different soil fractions and synthetic soil’, Water Air and Soil Pollution 109, 219–236.
Macauley, E. and Hong, A.: 1995, ‘Chelation extraction of lead from soil using pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid’, Journal of Hazardous Materials 40, 257–270.
Pamukcu, S. and Wittle, J. K.: 1992, ‘Electrokinetic removal of selected heavy metals from soil’, Environmental Progress 11(3), 241–250.
Papassiopi, N., Tambouris, S. and Kontopoulos, A.: 1999, ‘Removal of heavy metals from calcareous contaminated soils by EDTA leaching’, Water Air and Soil Pollution 109, 1–15.
Probstein, R. F. and Hicks, R. E.: 1993, ‘Removal of contaminants from soils by electric field’, Science 260, 498–503.
Puppala, S. K., Alshawabkeh, A. N., Acar, Y. B., Gale, R. J. and Bricka, M.: 1997, ‘Enhanced electrokinetic remediation of high sorption capacity soil’, Journal of Hazardous Materials 55, 203–220.
Reddy, K. and Chinthamreddy, S.: 2003, ‘Sequentially enhanced electrokinetic remediation of heavy metals in low buffering clayey soils’, Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 129(3), 263–277.
Reddy, K. R., Danda, S. R. and Saichek, E.: 2004, ‘Complicating factors of using ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid to enhance electrokinetic remediation of multiple heavy metals in clayey soils’, Journal of Environmental Engineering 130(11), 1357–1366.
Smith, R. M. and Martell, A. E.: 1989, Critical Stability Constants, 6, Plenum Publishing Corp., New York, NY.
Stegmann, R., Brunner, G., Calmano, W. and Matz, G.: 2001, Treatment of Contaminated Soil, Springer, New York, 471 pp.
Stumm, W. and Morgan, J. J.: 1996, Aquatic Chemistry, 3rd Ed., Wiley, New York.
Sun, B., Zhao, F. J., Lombi, E. and McGrath, S. P.: 2001, ‘Leaching of heavy metals from contaminated soil using EDTA’, Environmental Pollution 113, 111–120.
Virkutyte, J., Sillanpaa, M. and Latostenmaa, P.: 2002, ‘Electrokinetic soil remediation – critical overview’, The Science of the Total Environment 289, 97–121.
Yeung, A. T. and Hsu, C. N.: 2005 ‘Electrokinetic remediation of cadmium-contaminated clay’, Journal of Environmental Engineering 131(2), 298–304.
Yeung, A. T., Hsu, C. N. and Menon, R. M.: 1996, ‘EDTA-enhanced electrokinetic extraction of lead’, Journal of Environmental Engineering 122(8), 666–672.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gidarakos, E., Giannis, A. Chelate Agents Enhanced Electrokinetic Remediation for Removal Cadmium and Zinc by Conditioning Catholyte pH. Water Air Soil Pollut 172, 295–312 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9080-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9080-7