Abstract
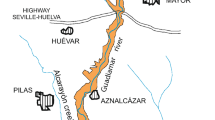
In April 1998, the Aznalcóllar mine tailings dam spilled 2 hm3 of slurry and 4 hm3 of acid waters into the Agrio River (affluent of the Guadiamar River). The pollutants reached the proximity of the Doñana National Park, 60 km downstream. The state of contamination of groundwaters and surface waters, from several samplings made subsequent to the spill, is described. Although the Guadiamar valley groundwaters remain contaminated, this situation cannot be attributed to the mining spill, but to the long history of pollution from mining activity at Aznalcóllar. Three zones can be distinguished: the most polluted zone, with pH values close to 4 and very high concentrations of metals (up to 18 mg/l of Al and 7 mg/l of Mn) and sulfates (up to 1263 mg/l); a second zone where pH values are higher (close to neutral) and, as a result, the concentration of metals is significantly lower; and a third zone, with pH exceeding 7, in which the concentration of metals has already fallen to normal levels but sulfate concentrations remain high (above 500 mg/l). The waters of the Agrio River present characteristics similar to those of the most-polluted groundwaters; on mixing with the waters of the Guadiamar River they are neutralized, precipitating firstly Al and then the rest of the metals. These metals remain deposited on the river-bed, where they are readily remobilized in later spates. Analysis of changes in groundwater quality shows a trend toward a lower content of Zn and the other metals in most wells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achterberg, E. P., Braungardt, C., Morley, N. H., Elbaz-Poulichet, F. and Leblanc, M.: 1999, ‘Impact of Los Frailes Mine Spill on riverine estuarine and coastal waters in southern Spain’, Water Res. 33, 3387–3394.
Arambarri, P., Cabrera, F. and González-Quesada, R.: 1996, ‘Quality evaluation of the surface waters entering the Doñana National Park (SW Spain)’, Sci. Total Environ. 191, 185–196.
Ayora, C., Guijarro, A., Doménech, C., Fernández, I., Gómez, P., Manzano, M., Mora, A., Moreno, L., Navarrete, P., Sánchez, M. and Serrano, J.: 2001a, ‘Actuaciones para la corrección y el seguimiento de la contaminación hídrica’, Boletín Geológico y Minero 112, 123–136.
Ayora, C., Bernet, O., Bolzicco, J., Carrera, J., Domènech, C., Cerón, J.C., Fernández, I., Gomez, P., Jaén, M., Mantecon, R., Manzano, M., Martín Machuca, M., Mediavilla, C., Moreno, L., Navarrete, P. and Salvany, J.M.: 2001b, ‘Hidrogeología del Valle del Guadiamar y zonas colindantes. Funcionamiento del sistema acuífero’, Boletín Geológico y Minero 112, 69–92.
ASTM: 1995, Annual Book of ASTM Standard. Part 31 Water, American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, 150 pp.
Cabrera, F., Toca, C. G., Diaz, E. and Arambarri, P.: 1984, ‘Acid mine water and agricultural pollution in a river skirting the Doñana National Park (Guadiamar River, South West Spain)’, Water Res. 18, 1469–1482.
Cabrera, F., Soldevilla, M., Cordón, R. and Arambarri, P.: 1987, ‘Heavy metal pollution in the Guadiamar River and the Guadalquivir estuary (South West Spain)’, Chemosphere 16, 463–468.
Fernández, I., Olías, M., Cerón, J. C. and De la Rosa, J.: 2005, ‘Application of lead stable isotopes to the Guadiamar aquifer study after the mine tailings spill in Aznalcóllar (SW Spain)’, Environ. Geol. 47, 197–204.
Grimalt, J. O., Ferrer, M. and Macpherson, E.: 1999, ‘The mine tailing accident in Aznalcollar’, Sci. Total Environ. 242, 3–11.
Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Maclin, M. G., Jamieson, H. E., Brever, P. A., Coulthard, T. J., Howard, A. J. and Turner, J. N.: 2003, ‘The impact of tailings dam spills and clean-up operations on sediment and water quality in river systems; the Ríos Agrio-Guadiamar, Aznalcóllar, Spain’, Appl. Geochem. 18, 221–239.
Lee, G., Bigham, J. M. and Faure, G.: 2002, ‘Removal of trace metals by coprecipitacion with Fe, Al and Mn from natural waters contaminated with acid mine drainage in the Ducktown Mining District, Tennessee’, Appl. Geochem. 17, 569–581.
Manzano, M., Ayora, C., Domenech, C., Navarrete, P., Garralon, A. and Turrero, M. J.: 1999, ‘The impact of the Aznalcóllar mine tailing spill on groundwater’, Sci. Total Environ, 242, 189–209.
Manzano, M., Soler, A., Carrera, J. and Custodio, E.: 2001, ‘Composición isotópica (δ18O, δ2H y δ34S) de las aguas del área afectada por el vertido minero de Aznalcóllar (SO España)’, in: A. Medina and J. Carreras (eds), Las Caras del Agua Subterráneas, ITGE, Madrid, Spain, vol. I, pp. 477–487.
Nordstrom, D. K. and Alpers, C. N.: 1999: ‘Geochemistry of acid mine waters’, in: G. S. Plumlee and M. J. Logson (eds.), The Environmental Geochemistry of Mineral Deposits, Rev. Econ. Geology, vol 6A, Soc. Econ. Geol. Inc, Littleton, CO, USA, pp. 133–160.
Pinedo, I.: 1963, ‘Piritas de Huelva. Su historia, minería y aprovechamiento’, Summa, Madrid, Spain, 1003 pp.
Prat, N., Toja, J., Solà, C., Burgos, M. D., Plans, M. and Rieradevall, M.: 1999, ‘Effect of dumping and cleaning activities on the aquatic ecosystems of the Guadiamar River following a toxic flood’, Sci. Total Environ. 242, 231–248.
Salvany, J. M.: 2004, ‘Tilting neotectonics of the Guadiamar Drainage Basin, SW Spain’, Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 29, 145–160.
Santos, A., Alonso, E., Callejón, M. and Jiménez, J. C.: 2002, ‘Distribution of Zn, Cd, Pb and Cu metals in groundwater of the Guadiamar River basin’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 134, 275–286.
Sassoon, M.: 1998, ‘Los Frailes aftermath’, Min. Environ. Manage. 1, 8–12.
Toja, J., Alcalá, E., Martín, G., Solà, C., Plans, M., Burgos, A., Plazuelo, A. and Prat, N.: 2003, ‘Evaluación del efecto del vertido tóxico sobre la calidad del agua y los sedimentos de los ríos Agrio y Guadiamar’, in: J. M. Arenas, F. R. Martínez, A. Mora, C. Montes and F. Borja (eds), Ciencia y Restauración del río Guadiamar, Consejería de Medio Ambiente, Sevilla, Spain, pp. 78–92.
van Geen, A., Takesue, R. and Chase, Z.: 1999, ‘Acid mine tailings in southern Spain’, Sci. Total Environ. 242, 221–229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
OlÍas, M., Cerón, J.C., Fernández, I. et al. State of Contamination of the Waters in the Guadiamar Valley Five Years after the AznalcÓllar Spill. Water Air Soil Pollut 166, 103–119 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-8201-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-8201-z