Abstract
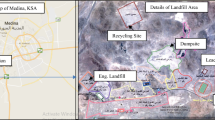
Landfilling of municipal solid waste (MSW) is associated with the generation of leachate that is highly contaminated. Contaminant migration from disposal areas to groundwater poses a threat to the environment and the human health. This study examined the contaminant migration at a landfill site in Kuwait. The migration characteristics of contaminants were analyzed using advanced computing systems to predict the long-term plume concentration in underlying soils and aquifers located directly below the final waste layer. Mathematical models of contaminant migration were applied to existing landfill sites using MIGRATEv9 computer program to illustrate the scope and extent of soil and water contamination. Two main cases were modeled as follows: (1) water table is deep below landfill and (2) water table is rising into the landfill. The models included advective-dispersion, and buried landfills systems. The comparison between models results suggested that vertical Darcy velocity had a significant impact on migration behavior of contaminants. The concentration was increased by 24.5% by increasing the vertical Darcy velocity from 0.005 to 0.009 m/year. Advection–dispersion models and water rising models with fixed top boundary and aquifer bottom boundary at 2 and 3.5 m showed almost the same migration behavior. In addition, models of buried landfill system where water table was 5 m from ground surface produced a maximum contaminant concentration of 17 630 mg/L after 25 years at 5 m depth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Yaqout, F. A.: 2003, ‘Assessment and analysis of industrial liquid waste and sludge disposal at unlined landfill sites in arid climates’, Waste Manage. 23, 817–824.
Al-Yaqout, F. A. and Hamoda, M. F.: 2002, ‘Evaluation of landfill leachate in arid climate – A case study’, Environ. Int. 29, 593–600.
Al-Yaqout, F. A. and Townsend, F.: 2001. ‘Strategy for landfill Design in Arid Regions’, Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioactive Waste Manage. 5(1), 2–13.
Al-Yaqout, F. A. and Townsend, F.: 2004. ‘Applicability of desert sands as liner/cover systems: Laboratory and field pad testing of permeability’, Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioactive Waste Manage.
Ball, J. M., Bredenhann, L. and Blight, G. E.: 1995, ‘Applications of minimum requirements for landfill design in Southern Africa’, in Proceedings of the Fifth International Landfill Symposium, Environmental Sanitary Engineering Center, S. Margherita di Pula, Caliari, Italy, October 2–6, pp. 111–121.
Hamoda, M. F.: 1997, Municipal quantities and characteristics in some Arab Countries. KFAS, Arab School on Science & Technology, in Proceeding of the Workshop on Solid Wastes, Kuwait, 15–19 November.
Mukhopadhyay, A., Al-Sulaimi, J. and Jean B.: 1994, ‘Numerical modeling of ground-water resources management options in Kuwait’, Groundwater 32(6), 917–928.
Rowe, R. K., Booker, J. R. and Fraser, M. J.: 1995, Migratev9 User Guide, GAEA Environmental Engineering Ltd., Windsor, Ontario, Canada.
Saeedy, H. S. and Abu-Eid, R.: 1984, ‘Effects of leaching on the geotechnical and geochemical properties of calcareous soil’, Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, Kuwait.
Saeedy, H. S. and Mollah, M. A.: 1990, ‘Geotechnical study of the North and Northwest Coast of the Arabian Gulf’, Eng. Geol. 28, 27–40.
Tchobanoglous, G., Theisen, H. and Vigil, S.: 1993, Integrated solid waste management: Engineering principles and management issues, McGraw-Hill, Boston, U.S.A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al Yaqout, A.F., Hamoda, M.F. Prediction of Contaminants Migration at Unlined Landfill Sites in an Arid Climate – a Case Study. Water Air Soil Pollut 162, 247–264 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-6574-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-6574-7