Abstract
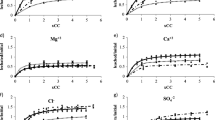
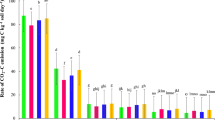
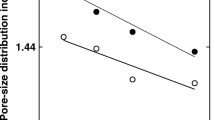
The retention and movement of water and atrazine (2-chloro-4-ethylamino-6-isopropylamino-s-triazine) was investigated in a calcareous soil (Krome) amended with three types of compost: (1) Clean organic waste (COW)- municipal solid waste cleaned of plastic materials and metal containers, (2) Biosolids (BSD)- sludge from municipal waste and (3) Bedminster (BDM)—a mixture containing 75% COW and 25% BSD. The research was conducted in two phases; a column-leaching study (dynamic) and a batch-equilibrium method (static). The column study demonstrated that while applying simulated rain, atrazine, leached out at a slower rate by 41, 24, and 18% from soil amended with BDM, BSD, and COW composts, respectively, during the first simulated storm event. BDM application resulted in lowest water movement and atrazine-leaching rate compared to the other composts tested. This study suggests that adding 134 t ha−1 of compost to the calcareous soil increased soil water holding capacity, reduced water movement and increased atrazine detention and reduced leaching potential of atrazine thereby reducing the potential for groundwater pollution. This study further demonstrates that soil amendment (particularly BDM) is effective in reducing the leaching potential of atrazine at the low rainfall amounts (corresponding to 0.5 pore volume). However, such amendment may not be effective in preventing leaching under more intense rain conditions or multiple rainfall events (corresponding to 3 or more pore volumes).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clay, A. S., Liu, Z., Clay, D. E. and Harper, S. S.: 1995, ‘Atrazine binding movement in soil as influenced by ammonia fertilizer’, Proceedings ASAE Clean Water Clean Environment, 21st Century. ASAE, Kansas City, MO, USA, Vol. I, pp. 41–44.
Crane, J. H. and Davis, F. S.: 1988, ‘Periodic and seasonal flooding effects on survival, growth, and stomatal conductance of young rabbiteye blueberry plants’, J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 113, 448–493.
Foster, G. R., Eppert, F. P. and Meyer, L. D.: 1979, ‘A programable rainfall simulator for field plots’, Proceedings of Workshop on Rainfall, Tucson, Arizona, USA, pp. 45–59.
Gaber, H. M., Inskeep, W. P., Comfort, S. D. and Wraith, J. M.: 1995, ‘Nonequilibrium transport of atrazine through large intact soil cores’, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 59, 60–67.
Kalouskova, N.: 1989, ‘Adsorption of atrazine on humic acids’, J. Environ. Sci. Health B24, 599–617.
Klute, A. and Dirksen, C.: 1986, ‘Hydraulic conductivity and diffusivity: Laboratory methods’, in A. Klute (ed), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1. 2nd ed. Agronomy, pp. 687–734.
Laird, D. A., Yen, P. Y., Koskinen, W. C., Steinheimer, T. R. and Dowdy, R. H.: 1994, ‘Sorption of atrazine on soil clay components’, Environ. Sci. Technol 28, 1054–1061.
Ma, L. and Selim, H. M.: 1994, ‘Predicting atrazine transport in soils: Second-order and multireaction approaches’, Water Resource Res. 30, 3489–3498.
Madsen, L., Lindhardt, B., Rosenberg, P., Clausen, L. and Fabricius, I.: 2000, ‘Pesticide sorption by low organic carbon sediments: A screening for seven herbicides’, J. Environ. Qual. 29, 1488–1500.
Maynard, A. A.: 1989, ‘Agricultural composts as amendments reduce nitrate leaching from soil’, Frontiers of Plant Sci. 42(1), 2–3.
Maynard, D. N. and Olson, S. M. (eds): 2000, Vegetable Production Guide for Florida, University of Florida, Citrus and Vegetable Magazine, SP 170.
Miles, J. C. and Pfeuffer, J. R.: 1997, ‘Pesticides in canals of south Florida’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 32, 337–345.
Nkedi-Kizza, P. and Owusu-Yaw, J.: 1992, ‘Simultaneous high-performance liquid chromatographic determinations of nitrate, nitrite, and organic pesticides in soil solution using a multidimensional column with ultraviolet detection’, J. Environ. Sci. Health. Part A Environ. Sci. Eng. 27(1), 245–259.
Nkedi-Kizza, P., Brusseau, M. L., Rao, P. S. C. and Hornsby, A. G.: 1989, ‘Nonequilibrium sorption of hydrophobic organic chemicals and 45Ca through soil columns with aqueous and mixed solvent’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 23(7), 814–820.
Nkedi-Kizza, P., Rao, P. S. C. and Hornsby, A. G.: 1985, ‘Influence of organic cosolvent on sorption of toxic organic substances (TOS) in soils’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 975–979.
Nkedi-Kizza, P., Rao, P. S. C. and Hornsby, A. G.: 1987, ‘The influence of organic cosolvents on leaching of hydrophobic organic chemicals through soils’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 107–111.
Nkedi-Kizza, P., Rao, P. S. C. and Johnson, J. W.: 1983, ‘Adsorption of diuron and 2, 4, 5-T on soil particle-size separates’, J. Environ. Qual. 12, 195–197.
Nyamangara, J.: 1998, ‘Use of sequential extraction to evaluate zinc and copper in a soil amended with biosolids and inorganic metal salts’, Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 69(2), 135–141.
Parr, J. F. and Hornick, S. B.: 1992, ‘Utilization of municipal wastes’, in F. B. Metting (ed), Soil Microbial Ecology: Applications in Agricultural and Environmental Management, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp. 545–559.
Pinamonti, F., Stringari, G., Gasperi, F. and Zorzi, G.: 1997, ‘Heavy metal levels in apple orchards after the application of two composts’, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 28, 1403–1419.
Roe, N. E., Stoffela, P. J. and Bryan, H. H.: 1993, ‘Utilization of composts and other organic mulches on commercial vegetable crops’, Comp. Sci. Util. 1(3), 73–74.
Savabi, M. R.: 2001, ‘Determining soil water characteristics for application of a hydrologic model in south Florida’, Trans. ASAE 44(1), 59–70.
Shea, P. J.: 1989, ‘Role of humified organic matter in herbicide adsorption’, Weed Technol. 3, 190–197.
Shinde, D., Savabi, M. R., Nkedi-Kizza, P. and Vazquez, A.: 2001, ‘Modeling transport of atrazine through calcareous soils from south Florida’, Trans. ASAE 44(2), 251–258.
Sokal, R. R. and Rohlf, F. J.: 1995, Biometry, 3rd edn., W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, 87 pp.
Statistical Analysis System (SAS).: 1999, Software 8.2 (TS2MO), SAS Institute Inc., Cary, North Carolina.
Travis, C. C. and Etnier, E. L.: 1981, ‘A survey of sorption relationships for reactive solutes in soil’, J. Environ. Qual. 10, 8–17.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA).: 1996, ‘Environmental indicators of water quality in the United States’, EPA publication 841-R-96-002.
Wang, Z., Gamble, D. S. and Langford, C. H.: 1992, ‘Interaction of atrazine with Laurentian soil’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 26, 560–565.
Weber, J. B.: 1993, ‘Ionization and sorption of fomesafen and atrazine by soils and soil constituents’, Pestic. Sci. 39, 31–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konomi, K., Savabi, M.R., Shinde, D. et al. Water and Atrazine Movement in a Calcareous Compost Applied Soil During Simulated Multiple Storms Events. Water Air Soil Pollut 165, 365–377 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-6569-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-6569-4