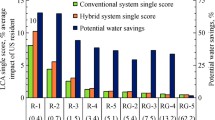
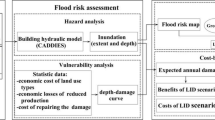
Abstract
The global phenomenon of urban flooding has become a pressing issue for cities worldwide. Conventional strategies to alleviate flooding, such as augmenting the capacity of drainage systems, are incompatible with the principle of sustainable development. In this regard, Low Impact Development (LID) techniques have emerged as a promising and sustainable approach to manage storm water. The objectives of the present study are to determine the enhancement in functional and structural resilience of an UDS after implementation of LIDs and Life Cycle Cost (LCC) analysis of implementation of LIDs. To showcase the role of LIDs in enhancing drainage system resilience, a case study was conducted in Gurugram, India, a city frequently impacted by flooding. The LID Performance Index is designed to measure the improvement in functional resilience and decrease in the number of vulnerable locations aims to quantify the enhancement in structural resilience. The LCC analysis is carried out to determine the Benefit–Cost Ratio (BCR) of implementing the LID. The study determined the optimal percentage of LIDs to incorporate into the urban drainage system through the creation of various scenarios that considered the impacts of urbanization, climate change, and the cost of implementing LIDs. Results indicated that a system incorporating 10% of LIDs (S1) with a Benefit–Cost ratio of 2.05 was the most suitable scenario for the case area. For the scenario S1 the functional resilience is enhanced by 21% and number of vulnerable locations decreases by 8.7%. The study also identifies the barriers to the implementation of LIDs in developing countries like India, categorizing them into planning, implementation, and maintenance stage barriers. Ultimately, the study provides a comprehensive understanding of nature-based solutions for the effective management of urban drainage infrastructure, offering valuable insights for urban planners, design engineers, and policy makers to protect cities from flood hazards.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All relevant data are included in the paper or its supplementary material.
References
Ahiablame L, Shakya R (2016) Modeling flood reduction effects of low impact development at a watershed scale. J Environ Manage 171:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.01.036
Almaaitah T, Appleby M, Rosenblat H, Drake J, Joksimovic D (2021) The potential of Blue-Green infrastructure as a climate change adaptation strategy: a systematic literature review. Blue-Green Systems 3(1):223–248. https://doi.org/10.2166/bgs.2021.016
Ayoublu SA, Vafakhah M, Pourghasemi HR (2024) Efficiency evaluation of low impact development practices on urban flood risk. J Environ Manage 356:120467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120467
Bisht DS, Chatterjee C, Kalakoti S, Upadhyay P, Sahoo M, Panda A (2016) Modeling urban floods and drainage using SWMM and MIKE URBAN: a case study. Nat Hazards 84(2):749–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2455-1
Butler D, Farmani R, Fu G, Ward S, Diao K, Astaraie-Imani M (2014) A new approach to urban water management: Safe and sure. Procedia Eng 89:347–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.11.198
Butler D, Digman C, Makropoulos C, Davies JW (2018) Urban drainage (Vol. 4th Ed.): Boca Raton: CRC Press
Chow VT, Maidment DR, Mays LW (1988) Applied hydrology. Water Resources Handbook; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA
Chui TFM, Liu X, Zhan W (2016) Assessing cost-effectiveness of specific LID practice designs in response to large storm events. J Hydrol 533:353–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.12.011
Cipolla SS, Maglionico M, Stojkov I (2016) A long-term hydrological modelling of an extensive green roof by means of SWMM. Ecol Eng 95:876–887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.07.009
CPHEEO (2019) Manual on storm water drainage system (Vol. I, Part- A Engineering Design). Cent. Public Heal. Environ. Eng. Organ. Minist. Hous. Urban Aff. Gov. India, New Delhi
Dadrasajirlou Y, Karami H, Mirjalili S (2023) Using AHP-PROMOTHEE for Selection of best low-impact development designs for urban flood mitigation. Water Resour Manage 37(1):375–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03378-9
Dietz ME (2007) Low impact development practices: A review of current research and recommendations for future directions. Water Air Soil Pollut 186(1):351–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9484-z
Dong X, Guo H, Zeng S (2017) Enhancing future resilience in urban drainage system: Green versus grey infrastructure. Water Res 124:280–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.038
Dwivedi A, Mohan BK (2018) Impact of green roof on micro climate to reduce Urban Heat Island. Remote Sens Appl: Society and Environment 10:56–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2018.01.003
ErshadSarabi S, Han Q, Romme LAG, de Vries B, Wendling L (2019) Key enablers of and barriers to the uptake and implementation of nature-based solutions in urban settings: A review. Resources 8(3):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8030121
Fu G, Zhang C, Hall JW, Butler D (2023) Are sponge cities the solution to China’s growing urban flooding problems? Wires Water 10(1):e1613. https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1613
Gao J, Li J, Li Y, Xia J, Lv P (2021) A distribution optimization method of typical LID facilities for sponge city construction. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol 21(1):13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2020.09.003
Ghodsi SH, Zahmatkesh Z, Goharian E, Kerachian R, Zhu Z (2020) Optimal design of low impact development practices in response to climate change. J Hydrol 580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124266
Ghosh P, Sudarsan JS, Nithiyanantham S (2024) Nature-based disaster risk reduction of floods in Urban Areas. Water Resour Manage 38(6):1847–1866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03757-4
Gironás J, Roesner LA, Rossman LA, Davis J (2010) A new applications manual for the Storm Water Management Model(SWMM). Environ Model Softw 25(6):813–814
Gogate NG, Kalbar PP, Raval PM (2017) Assessment of stormwater management options in urban contexts using Multiple Attribute Decision-Making. J Clean Prod 142:2046–2059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.11.079
Kabisch N, Frantzeskaki N, Pauleit S, Naumann S, Davis M, Artmann M, Haase D, Knapp S, Korn H, Stadler J, Zaunberger K, Bonn A (2016) Nature-based solutions to climate change mitigation and adaptation in urban areas perspectives on indicators, knowledge gaps, barriers, and opportunities for action. Ecol Soc 21(2). https://www.jstor.org/stable/26270403
Kumar S, Guntu RK, Agarwal A, Villuri VGK, Pasupuleti S, Kaushal DR, Gosian AK, Bronstert A (2022) Multi-objective optimization for stormwater management by green-roofs and infiltration trenches to reduce urban flooding in central Delhi. J Hydrol 606:127455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127455
Liao Z, Chen H, Huang F, Li H (2014) Cost–effectiveness analysis on LID measures of a highly urbanized area. Desalination Water Treat 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.964327
Lin J, Uchiyama S, Bhattacharya Y, Nakamura H (2023) Efficacy of rain barrels and rain gardens to reduce urban pluvial flooding in densely built-up residential areas: a case study on Miyahara-Cho in Saitama City, Japan. City Built Environ 1(1):19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44213-023-00024-x
Liu W, Feng Q, Engel BA, Zhang X (2023) Cost-effectiveness analysis of extensive green roofs for urban stormwater control in response to future climate change scenarios. Sci Total Environ 856:159127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159127
Locatelli L, Mark O, Mikkelsen PS, Arnbjerg-Nielsen K, Deletic A, Roldin M, Binning PJ (2017) Hydrologic impact of urbanization with extensive stormwater infiltration. J Hydrol 544:524–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.11.030
Mani M, Bateni S, Bozorg-Haddad O, Cording A (2021) Stormwater management by low impact development practices. In Water Resources: Future Perspectives, Challenges, Concepts and Necessities (pp. 0): IWA Publishing. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.2166/9781789062144_0063
Mehta O, Kansal ML, Bisht DS (2022) A comparative study of the time of concentration methods for designing urban drainage infrastructure. AQUA - Water Infrastruct Ecosyst Soc 71(10):1197–1218. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2022.107
Mei C, Liu J, Wang H, Yang Z, Ding X, Shao W (2018) Integrated assessments of green infrastructure for flood mitigation to support robust decision-making for sponge city construction in an urbanized watershed. Sci Total Environ 639:1394–1407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.199
Mell IC (2018) Greening Ahmedabad—creating a resilient Indian city using a green infrastructure approach to investment. Landsc Res 43(3):289–314. https://doi.org/10.1080/01426397.2017.1314452
Moazzem S, Bhuiyan M, Muthukumaran S, Fagan J, Jegatheesan V (2024) A critical review of Nature-based Systems (NbS) to treat stormwater in response to climate change and urbanization. Curr Pollut Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-024-00297-8
Montalto F, Behr C, Alfredo K, Wolf M, Arye M, Walsh M (2007) Rapid assessment of the cost-effectiveness of low impact development for CSO control. Landsc Urban Plan 82(3):117–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2007.02.004
Mugume SN, Diao K, Astaraie-Imani M, Fu G, Farmani R, Butler D (2015a) Enhancing resilience in urban water systems for future cities. Water Supply 15(6):1343–1352. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2015.098
Mugume SN, Gomez DE, Fu G, Farmani R, Butler D (2015b) A global analysis approach for investigating structural resilience in urban drainage systems. Water Res 81:15–26
Mugume SN, Kibibi H, Sorensen J, Butler D (2024) Can Blue-Green Infrastructure enhance resilience in urban drainage systems during failure conditions? Water Sci Technol 89(4):915–944. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2024.032
Osheen, Singh KK (2019) Rain Garden—a solution to urban flooding: A review. In: Agnihotri, A., Reddy, K., Bansal, A. (eds) Sustainable Engineering. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 30. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6717-5_4
Osheen, Kansal ML, Bisht (2022) Evaluation of an urban drainage system using functional and structural resilience approach. Urban Water J 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2022.2044495
Osheen, Kansal ML, Bisht DS (2023) Characterization, complexities, and strategic planning for urban flood management: A case study of Gurugram. Proc World Environ Water Res Congr 2023. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784484852.0
Palermo SA, Talarico VC, Turco M (2020) On the LID systems effectiveness for urban stormwater management: case study in Southern Italy. IOP Conf Ser: Earth and Environmental Science 410(1):012012. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/410/1/012012
Pampaloni M, Sordo-Ward A, Lompi M, Pacetti T, Zubelzu S, Rodríguez-Sinobas L, Bianucci P, Caporali E, Garrote L (2024) Performance of low impact development on peak flow reduction in an urban system. JAWRA J Am Water Res Assoc 60(2):427–441. https://doi.org/10.1111/1752-1688.13188
Prudencio L, Null SE (2018) Stormwater management and ecosystem services: a review. Environ Res Lett 13(3):033002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aaa81a
Qin HP, Li ZX, Fu G (2013) The effects of low impact development on urban flooding under different rainfall characteristics. J Environ Manage 129:577–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.08.026
Rawls WJ, Brakensiek DL, Miller N (1983) Green-ampt infiltration parameters from soils data. J Hydraul Eng 109(1):62–70. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1983)109:1(62)
Rodriguez M, Fu G, Butler D, Yuan Z, Sharma K (2021) Exploring the spatial impact of green infrastructure on urban drainage resilience. Water 13(13):1789
Rong Q, Liu Q, Yue W, Xu C, Su M (2024) Optimal design of low impact development at a community scale considering urban non-point source pollution management under uncertainty. J Clean Prod 434:139934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.139934
Rossman L, Huber W (2016) Storm water management model reference manual Volume III–Water Quality National Risk Management Research Laboratory, Office of Research and Development USEPA, Cincinnati, OH, USA
Rossman LA (2010) Storm Water Management Model (SWMM) User Manual, Version 5.0: National Risk Management Research Laboratory, Office of Research and Development, US Environmental Protection Agency
Sousa BJDO, Mattos TS, Taffarelo D, Mendiondo EM, Vasconcelos JG, Oliveira PTS (2024) Low-impact development scenarios in terms of construction costs and runoff reduction. J Hydrol Eng 29(1):05023025. https://doi.org/10.1061/JHYEFF.HEENG-6059
Sutton PC, Anderson SJ, Elvidge CD, Tuttle BT, Ghosh T (2009) Paving the planet: impervious surface as proxy measure of the human ecological footprint. Prog Phys Geogr: Earth and Environment 33(4):510–527. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309133309346649
Tansar H, Duan H-F, Mark O (2022) Catchment-scale and local-scale based evaluation of LID effectiveness on urban drainage system performance. Water Resour Manage 36(2):507–526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-03036-6
Tauhid FA, Zawani H (2018) Mitigating climate change related floods in urban poor areas: green infrastructure approach. J Reg City Plan 29(2):98–112
Thoms A, Köster S (2022) Potentials for Sponge City implementation in Sub-Saharan Africa. Sustainability 14(18):11726
Wang M, Zhang DQ, Su J, Dong JW, Tan SK (2018) Assessing hydrological effects and performance of low impact development practices based on future scenarios modeling. J Clean Prod 179:12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.096
Wang Z, Zhou S, Wang M, Zhang D (2020) Cost-benefit analysis of low-impact development at hectare scale for urban stormwater source control in response to anticipated climatic change. J Environ Manage 264:110483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110483
Wang R, Brent D, Wu H (2022) Willingness to pay for ecosystem benefits of green stormwater infrastructure in Chinese sponge cities. J Clean Prod 371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133462
Winston RJ, Dorsey JD, Hunt WF (2016) Quantifying volume reduction and peak flow mitigation for three bioretention cells in clay soils in northeast Ohio. Sci Total Environ 553:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.081
Wu J, Yang R, Song J (2018) Effectiveness of low-impact development for urban inundation risk mitigation under different scenarios: a case study in Shenzhen, China. Nat Hazard 18(9):2525–2536. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-18-2525-2018
Yang Y, Chui TFM (2018) Rapid assessment of hydrologic performance of low impact development practices under design storms. JAWRA J Am Water Res Assoc 54(3):613–630. https://doi.org/10.1111/1752-1688.12637
Zhang Z, Hu W, Wang W, Zhou J, Liu D, Qi X, Zhao X (2022) The hydrological effect and uncertainty assessment by runoff indicators based on SWMM for various LID facilities. J Hydrol 613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128418
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Osheen: Conceptualization, Software, Investigation, Visualization, Writing- original draft.
Mitthan Lal Kansal: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Deepak Singh Bisht: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The author declares that the manuscript has not been submitted to other journals.
Consent to Publish
The author agrees to publish.
Competing Interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Osheen, Kansal, M.L. & Bisht, D.S. Enhancing Urban Drainage Infrastructure Through Implementation of Low Impact Development Techniques. Water Resour Manage (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03877-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03877-x