Abstract
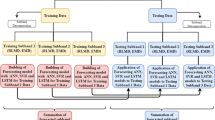
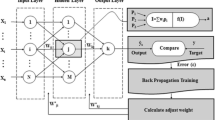
The generation of streamflow is linked with different factors such as water level, rainfall intensity, meteorological variables, and many more. In this study, we have developed a new hybrid approach (named LASSO-HF-SAA) by integrating the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and Hampel filter (HF) with three data-driven models i.e. support vector machine (SVM), artificial neural network (ANN) and autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL). Firstly, LASSO selects meteorological variables important in daily streamflow prediction. Next, the HF detects and correct outliers in the variables to handle the randomness and noise of data. Thirdly, the HF-corrected data is fed to SVM, ANN, and ARDL models to obtain the predictions of the proposed LASSO-HF-SVM, LASSO-HF-ANN, and LASSO-HF-ARDL models. The performance of these models is checked using performance indices and the Diebold-Mariano (DM) test. The proposed hybrid approach is illustrated on the streamflow data of the Kabul River (Nowshera station) of Pakistan. Based on Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE), it is revealed that the prediction accuracy of the LASSO-HF-SVM hybrid model (NSE = 0.52) is better than SVM (NSE = 0.43), HF-SVM (NSE = 0.49) and LASSO-SVM (NSE = 0.47) models in testing phase. Similar findings are for the proposed LASSO-HF-ARDL and LASSO-HF-ANN hybrid models. Overall, the suggested LASSO-HF-ARDL hybrid model has shown winning performance compared to all models in the study. The root mean squared error (RMSE) and NSE of the proposed LASSO-HF-ARDL model is 443.5m3/s and 0.68 on the test data. The DM test confirms that the prediction accuracy of the proposed hybrid models is better than their respective single, HF-based, and LASSO-based models versions of SVM, ANN, and ARDL models respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abba S, Abdulkadir R, Sammen S, Pham Q, Lawan A, Esmaili P, . . . Al-Ansari N (2022) Integrating feature extraction approaches with hybrid emotional neural networks for water quality index modeling. Appl Soft Comput 114:108036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.108036
Abbasi M, Dehban H, Farokhnia A, Roozbahani R (2022) Long-term streamflow prediction using hybrid SVR-ANN based on bayesian model averaging. J Hydrol Eng 27:05022018. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0002218
Adnan R, Yuan X, Kisi O, Yuan Y (2017) Streamflow forecasting using artificial neural network and support vector machine models. Am Sci Res J Eng Technol Sci(ASRJETS) 29:286–294
Al-Juboori AM (2021) A hybrid model to predict monthly streamflow using neighboring rivers annual flows. Water Resour Manag 35:729–743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02757-4
Ali S, Shahbaz M (2020) Streamflow forecasting by modeling the rainfall–streamflow relationship using artificial neural networks. Model Earth Syst Environ 6:1645–1656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00780-3
Alizadeh Z, Shourian M, Yaseen Z (2020) Simulating monthly streamflow using a hybrid feature selection approach integrated with an intelligence model. Hydrol Sci J 65:1374–1384. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2020.1755436
Breiman L (1995) Better subset regression using the nonnegative garrote. Technometrics 37:373–384. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1995.10484371
Chu H, Wei J, Wu W (2020) Streamflow prediction using LASSO-FCM-DBN approach based on hydro-meteorological condition classification. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124253
Duan J, Zuo H, Bai Y, Duan J, Chang M, Chen B (2021) Short-term wind speed forecasting using recurrent neural networks with error correction. Energy 217:119397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119397
Ebtehaj I, Bonakdari H (2022) A reliable hybrid outlier robust non-tuned rapid machine learning model for multi-step ahead flood forecasting in Quebec, Canada. J Hydrol 614:128592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128592
El Harraki W, Ouazar D, Bouziane A et al (2021) Streamflow prediction upstream of a dam using SWAT and assessment of the impact of land use spatial resolution on model performance. Environ Process 8:1165–1186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-021-00532-0
Elsersy WF, Anuar NB, Razak MFA (2023) ROOTECTOR: robust android rooting detection framework using machine learning algorithms. Arab J Sci Eng 48:1771–1791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06949-5
Feng ZK, Niu WJ, Cheng CT (2019) China’s large-scale hydropower system: operation characteristics, modeling challenge and dimensionality reduction possibilities. Renew Energy 136:805–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.059
Gonçalves JA, Pessoa AL, Viana ER, Branco HM, Rodrigues JJ, Rabêlo RA (2021) A hybrid algorithm for load curve filtering and clustering. Energy Sour Part A: Recover Utili Environ Eff 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2021.1991528
Hampel FR (1974) The influence curve and its role in robust estimation. J Am Stat Assoc 69:353–393. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1974.10482962
Hassan M, Hassan I (2020) Improving ANN-based streamflow estimation models for the Upper Indus Basin using satellite-derived snow cover area. Acta Geophys 68:1791–1801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-020-00491-4
He Y, Qin Y, Wang S, Wang X, Wang C (2019) Electricity consumption probability density forecasting method based on LASSO-Quantile regression neural network. Appl Energy 233:555–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.10.061
Ishfaque M, Dai Q, Wahid A, Saddique B, Jadoon K, Janjuhah H, Shahzad S (2023) Trend analysis of hydro-climatological parameters and assessment of climate impact on dam seepage using statistical and machine learning models. Environ Earth Sci 82:542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11216-3
Joo D, Na R, Kim HY, Choi GH, Yoo SH (2022) Analysis of the optimal window size of hampel filter for calibration of real-time water level in agricultural reservoirs. J Korean Soc Agric Eng 64:9–24. https://doi.org/10.5389/KSAE.2022.64.3.009
Kang Y, Cheng X, Chen P, Zhang S, Yang Q (2023) Monthly runoff prediction by a multivariate hybrid model based on decomposition-normality and Lasso regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:27743–27762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23990-x
Kişi Ö (2009) Neural networks and wavelet conjunction model for intermittent streamflow forecasting. J Hydrol Eng 14:773–782. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000053
Koue J (2023) Modeling the effects of river inflow dynamics on the Deep Layers of Lake Biwa, Japan. Environ Process 10:62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-023-00673-4
Li Y, DeLiberty T (2020) Assessment of urban streamflow in historical wet and dry years using SWAT across Northwestern Delaware. Environ Process 7:597–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-020-00428-5
Lian Y, Luo J, Wang J, Zuo G, Wei N (2022) Climate-driven Model based on long short-term memory and Bayesian optimization for multi-day-ahead daily streamflow forecasting. Water Resour Manag 36:21–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-03002-2
Mehr AD, Gandomi AH (2021) MSGP-LASSO: an improved multi-stage genetic programming model for streamflow prediction. Inf Sci 561:181–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.02.011
Pesaran MH, Shin Y (1999) An Autoregressive distributed lag modelling approach to cointegration Analysis. In: Strom S (ed) Econometrics and Economic Theory in the 20th Century: The Ragnar Frisch Centennial Symposium. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rasouli K, Hsieh WW, Cannon AJ (2012) Daily streamflow forecasting by machine learning methods with weather and climate inputs. J Hydrol 414:284–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.10.039
Rezaie-Balf M, Kişi O (2018) New formulation for forecasting streamflow: evolutionary polynomial regression vs. extreme learning machine. Hydrol Res 49:939–935. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2017.283
Shabbir M, Chand S, Iqbal F (2022) A novel hybrid method for river discharge prediction. Water Resour Manag 36:253–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-03026-8
Shabbir M, Chand S, Iqbal F (2024) Novel hybrid and weighted ensemble models to predict river discharge series with outliers. Kuwait J Sci 51:100188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjs.2024.100188
Shahani M, Rezaverdinejad V, Hosseini S, Azad N (2023) Assessing climate change impact on river flow extreme events in different climates of Iran using hybrid application of LARS-WG6 and rainfall-runoff modeling of deep learning. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol 23:224–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2023.02.002
Sibtain M, Li X, Nabi G, Azam M, Bashir H (2020) Development of a three-stage hybrid model by utilizing a two-stage signal decomposition methodology and machine learning approach to predict monthly runoff at Swat River Basin, Pakistan. Discre Dyn Nat Soc 2020:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7345676
Tao H, Al-Bedyry N, Khedher K, Shahid S, Yaseen Z (2021) River water level prediction in coastal catchment using hybridized relevance vector machine model with improved grasshopper optimization. J Hydrol 598:126477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126477
Tibshirani R (1996) Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J R Stat Soc:Ser B (Method) 58:267–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1996.tb02080.x
Vapnik V (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Wang ZY, Qiu J, Li FF (2018) Hybrid models combining EMD/EEMD and ARIMA for long-term streamflow forecasting. Water 10:853–866
Zhu N, Xu J, Li W, Li K, Zhou C (2018) A comprehensive approach to assess the hydrological drought of inland river basin in Northwest China. Atmosphere 9:370–386. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shabbir, M., Chand, S., Iqbal, F. et al. Hybrid Approach for Streamflow Prediction: LASSO-Hampel Filter Integration with Support Vector Machines, Artificial Neural Networks, and Autoregressive Distributed Lag Models. Water Resour Manage (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03858-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03858-0