Abstract
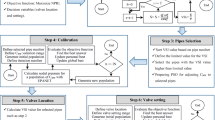
The water distribution system (WDS) hydraulic model is extensively used for design and management of WDS. The nodal water demand is the crucial parameter of the model that requires accurate estimating by the pressure measurements. Proper pressure sampling design is essential for estimating nodal water demand and improving model accuracy. Existing research has emphasized the need to enhance the observability of monitoring systems and mitigate the adverse effects of monitoring noise. However, methods that simultaneously consider both of these factors in sampling design have not been adequately studied. In this study, a novel two-objective sampling design method is developed to improve the system observability and mitigate the adverse effects of monitoring noise. The approach is applied to a realistic network and results demonstrate that the developed approach can effectively improve the observability and robustness of the system especially when considerable measurement noise is considered.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
All data, models, and codes that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abhijith GR, Mohan S (2020) Random Walk Particle Tracking Embedded Cellular Automata Model for Predicting Temporospatial Variations of Chlorine in Water Distribution Systems. Environ Process 7(1):271–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-019-00406-6
Behzadian K, Kapelan Z, Savic D, Ardeshir A (2009) Stochastic sampling design using a multi-objective genetic algorithm and adaptive neural networks. Environ Model Softw 24(4):530–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2008.09.013
Bush CA, Uber JG (1998) Sampling design methods for water distribution model calibration. J Water Resour Plan Manag 124(6):334–344. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(1998)124:6(334)
Carrera J, Usunoff E, Szidarovszky F (1984) A method for optimal observation network design for groundwater management. J Hydrol 73(1–2):147–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(84)90037-4
Chu SP, Zhang TQ, Zhou XH, Yu TC, Shao Y (2022) An efficient approach for nodal water demand estimation in large-scale water distribution systems. Water Resour Manag 36(2):491–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-03024-w
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.996017
Dini M, Tabesh M (2014) A new method for simultaneous calibration of demand pattern and hazen-williams coefficients in water distribution systems. Water Resour Manag 28(7):2021–2034. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0592-4
Ferreira B, Antunes A, Carrico N, Covas D (2023) NSGA-II parameterization for the optimal pressure sensor location in water distribution networks. Urban Water J 20(6):738–750. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2023.2209553
Holland JH (1992) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass. https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/1090.001.0001
Huang Y, Duan HF, Zhao M, Zhang QZ, Zhao HB, Zhang K (2017) Probabilistic analysis and evaluation of nodal demand effect on transient analysis in urban water distribution systems. J Water Resour Plan Manag 143(8). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000797
Huang Y, Zheng FF, Duan HF, Zhang QZ, Shen YG (2020) Impacts of nodal demand allocations on transient-based skeletonization of water distribution systems. J Hydraul Eng 146(9). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0001787
Kapelan ZS, Savic DA, Walters GA (2003) Multiobjective sampling design for water distribution model calibration. J Water Resour Plan Manag 129(6):466–479. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2003)129:6(466)
Klapcsik K, Varga R, Hos C (2018) Optimal pressure measurement layout design in water distribution network systems. Period Polytech-Mech Eng 62(1):51–64. https://doi.org/10.3311/PPme.11409
Lee BH, Deininger RA (1992) Optimal locations of monitoring stations in water distributions system. J Environ Eng 118(1):4–16. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1992)118:1(4)
Letting LK, Hamam Y, Abu-Mahfouz AM (2017) Estimation of water demand in water distribution systems using particle swarm optimization. Water 9(8):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080593
Li C, Du K, Tu JP, Dong WX (2017) Optimal placement of pressure sensors in water distribution system based on clustering analysis of pressure sensitive matrix. Procedia Engineering 186:405–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.03.242
Menapace A, Avesani D (2019) Global gradient algorithm extension to distributed pressure driven pipe demand model. Water Resour Manag 33(5):1717–1736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2174-3
Morales-Gonzalez IO, Santos-Ruiz I, Lopez-Estrada FR, Puig V (2021) Pressure sensor placement for leak localization using simulated annealing with hyperparameter optimization. Conf Control Fault-Tolerant Syst (SYSTOL 2021) 205–210. https://doi.org/10.1109/SysTol52990.2021.9595369
Morosini AF, Costanzo F, Veltri P, Savic D (2014) Identification of measurement points for calibration of water distribution network models. Procedia Eng 89(C):693–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.11.496
Perez R, Puig V, Pascual J, Quevedo J, Landeros E, Peralta A (2011) Methodology for leakage isolation using pressure sensitivity analysis in water distribution networks. Control Eng Pract 19(10):1157–1167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conengprac.2011.06.004
Piller O, Elhay S, Deuerlein J, Simpson AR (2017) Local sensitivity of pressure-driven modeling and demand-driven modeling steady-state solutions to variations in parameters. J Water Resour Plan Manag 143(2):04016074. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000729
Rossman LA (2000) EPANET 2 users manual. USEPA, Washington, DC
Sanz G, Pérez R (2015) Sensitivity analysis for sampling design and demand calibration in water distribution networks using the singular value decomposition. J Water Resour Plan Manag 141(10):4015020. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000535
Shao Y, Chu S, Zhang T, Yang YJ, Yu T (2019) Real-time water distribution system hydraulic modeling using prior demand information by formal bayesian approach. J Water Resour Plan Manag 145(12). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001137
Shiu CC, Chung CC, Chiang TP (2023) Enhancing the EPANET hydraulic model through genetic algorithm optimization of pipe roughness coefficients. Water Resour Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03672-0
Simone A, Giustolisi O, Laucelli DB (2016) A proposal of optimal sampling design using a modularity strategy. Water Resour Res 52(8):6171–6185. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016WR018944
Simone A, Laucelli D, Berardi L, Giustolisi O (2018) Modularity index for optimal sensor placement in WDNs. Advances in Hydroinformatics 433–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7218-5_31
Tabesh M, Jamasb M, Moeini R (2011) Calibration of water distribution hydraulic models: A comparison between pressure dependent and demand driven analyses. Urban Water J 8(2):93–102. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2010.548525
Taha AF, Wang S, Guo Y, Summers TH, Gatsis N, Giacomoni MH, Abokifa AA (2021) Revisiting the water quality sensor placement problem: Optimizing network observability and state estimation metrics. J Water Resour Plan Manag 147(7). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001374
Tufa G, Abate B (2022) Assessment of accessibility and hydraulic performance of the water distribution system of Ejere Town. AQUA-Water Infrastruct Ecosyst Soc 71(4):577–592. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2022.012
Walski TM (1983) Technique for calibrating network models. J Water Resour Plan Manag 109(4):360–372. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(1983)109:4(360)
Zhang QZ, Zheng FF, Duan HF, Jia YY, Zhang TQ, Guo XL (2018) Efficient numerical approach for simultaneous calibration of pipe roughness coefficients and nodal demands for water distribution systems. J Water Resour Plan Manag 144(10):31–40. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000986
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52270095) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.52200119).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yu Shao: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Funding acquisition. Kun Li: Writing-Original Draft, Software, Writing-Review & Editing. Tuqiao Zhan: Visualization, Investigation, Formal analysis, Resources, Project administration. Weilin Ao: Writing—Review & Editing. Shipeng Chu: Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Y., Li, K., Zhang, T. et al. Pressure Sampling Design for Estimating Nodal Water Demand in Water Distribution Systems. Water Resour Manage 38, 1511–1527 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03736-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03736-9