Abstract
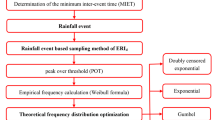
Combined sewer overflow (CSO) posed a great threat to the urban aquatic environment of many Chinese cities during the wet weather. For CSO from the specific interceptor well, the drainage capacity of the adjacent downstream interceptor sewer can be viewed as one of the critical thresholds. In this study, the generalized Pareto distribution (GPD) combined with peak over threshold (POT) sampling was used to characterize the excess rainfall intensity (ERI) of CSO events, which is significant for evaluating the severity and intensity of CSO events. First, the 10-year rainfall series were divided into different rainfall events, and the maximum rainfall intensity for the specific rainfall duration (30 min used in this study) over the drainage capacity of interceptor sewers (i.e., ERI) was calculated and sampled from each rainfall event, and its statistic characteristics were analyzed. Moreover, the empirical frequency of excess rainfall intensity (ERI) was calculated by the Weibull formula. Finally, GPD was used for fitting the empirical frequency distribution and its shape, scale parameters were optimized based on the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm. It was concluded that: (1) POT sampling combining rainfall event division was appropriate for ERI estimation of CSO events; (2) The Coefficient of skewness (Cs) of ERI was greater than zero for the studied scenarios, which showed that its distribution was right-skewed; (3) The kurtosis of the ERI was greater than three for the studied scenarios, which indicated that its distribution was thick-tailed; (4) GPD was suitable for modeling the theoretical frequency distribution of ERI.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The authors confirm that some data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CSO:
-
Combined sewer overflow
- Cs:
-
Coefficient of skewness
- Cv:
-
Coefficient of variation
- ERI:
-
Excess rainfall intensity
- GPD:
-
Generalized Pareto distribution
- MCMC:
-
Markov chain Monte Carlo
- MIET:
-
The minimum inter-event time
- POT:
-
Peak over threshold
References
Alonso AM, de Zea Bermudez P, Scotto MG (2014) Comparing generalized Pareto models fitted to extreme observations: an application to the largest temperatures in Spain. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 28(5):1221–1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-013-0809-8
Andrés-Doménech I, Múnera JC, Francés F, Marco JB (2010) Coupling urban event-based and catchment continuous modelling for combined sewer overflow river impact assessment. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 14(10):2057–2072. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-14-2057-2010
Botturi A, Ozbayram EG, Tondera K, Gilbert NI, Rouault P, Caradot N et al (2020) Combined sewer overflows: A critical review on best practice and innovative solutions to mitigate impacts on environment and human health. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 51(15):1585–1618. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1757957
Campisano A, Creaco E, Modica C (2016) Application of real-time control techniques to reduce water volume discharges from quality-oriented CSO devices. J Environ Eng 142(1):04015049. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001013
Fortier C, Mailhot A (2015) Climate change impact on combined sewer overflows. J Water Resour Plan Manag 141(5):04014073. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000468
Gao JJ, Du J (2021) Extreme precipitation simulation and forecast of the Yarlung Zangbo River basin. J Glaciol Geocryol 43(02):580–588. https://doi.org/10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2020.0095. (in Chinese)
Liao Z, Zhang Z, Tian W, Gu X, Xie J (2022) Comparison of real-time control methods for CSO reduction with two evaluation indices: Computing load rate and double baseline normalized distance. Water Resour Manag 36(12):4469–4484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03221-1
Liu XP, Ouyang CM, Zhou YW (2023) A low-return-period rainfall intensity formula for estimating the design return period of the combined interceptor sewers. Water Resour Manag 37(1):289–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03369-w
Liu XP, Xia CF, Tang YF, Tu JY, Wang HM (2021) Parameter optimization and uncertainty assessment for rainfall frequency modeling using an adaptive Metropolis-Hastings algorithm. Water Sci Technol J Int Assoc Water Pollut Res 83(5):1085–1102. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.032
Mailhot A, Talbot G, Lavallée B (2015) Relationships between rainfall and Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO) occurrences. J Hydrol 523:602–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.01.063
Martin J, Parra MI, Pizarro MM, Sanjuan EL (2022) Baseline methods for the parameter estimation of the generalized pareto distribution. Entropy 24(2):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020178
Mohammed MB, Adam MB, Ali N, Zulkafli HS (2020) Improved frequency table’s measures of skewness and kurtosis with application to weather data. Communi Stat Theory Methods 51(3):581–598. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610926.2020.1752386
Quaranta E, Fuchs S, Jan Liefting H, Schellart A, Pistocchi A (2022) A hydrological model to estimate pollution from combined sewer overflows at the regional scale: Application to Europe. J Hydrol: Reg Stud 41:101080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2022.101080
Ruggaber TP, Talley JW, Montestruque LA (2007) Using embedded sensor networks to monitor, control, and reduce CSO events: A pilot study. Environ Eng Sci 24(2):172–182. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2006.0041
Schroeder K, Riechel M, Matzinger A, Rouault P, Sonnenberg H, Pawlowsky-Reusing E, Gnirss R (2011) Evaluation of effectiveness of combined sewer overflow control measures by operational data. Water Sci Technol 63(2):325–330. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2011.058
Sun W (2021) Pollution characteristics and selection of core treatment process of CSOs. Water Wastewater Eng 47(S1):138–144. https://doi.org/10.13789/j.cnki.wwe1964.2021.S1.029. (in Chinese)
Weibull W (1939) A statistical theory of the strength of material. Stockh: Ingeniors Vetensk Acad Handl 1–45
Yu L, Yan Y, Pan X, Yang S, Liu J, Yang M, Meng Q (2022) Research on the comprehensive regulation method of combined sewer overflow based on synchronous monitoring - a case study. Water 14(19):3067. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193067
Yu Y, Zhang SZ, An AK, Furumai H (2018) Simple method for calculating hydraulic behavior of combined sewer overflow from rainfall event data. J Water Resour Plan Manag 144(10):04018061. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000972
Zhang C, Ma XL, Lu F, Li P (2016) Code for design of outdoor wastewater engineering (GB 50014). Beijing: China Plan Press 1–248 (in Chinese)
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant No. 51008191].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xingpo Liu designed the study, co-worte the the initial draft of the manuscript. Wenke Zang performed the research and co-wrote the initial draft of the manuscript. Yuwen Zhou contributed to the roadmap of the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This paper has neither been published nor been under review for publication elsewhere.
Consent to Participate
The authors have participated in the preparation of this paper for publication in the Water Resources Management.
Consent to Publish
The authors declare their consent to publication of the manuscript in “Water Resources Management” journal.
Competing Interests
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• POT coupled rainfall event division sampled ERI of CSO.
• The statistical distribution of ERI is right-skewed and thick-tailed.
• GPD was suitable for modeling the theoretical frequency distribution of ERI.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zang, W. & Zhou, Y. A Method For Estimating Excess Rainfall Intensity (ERI) of Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO) Based on Peak Over Threshold (POT) Sampling And The Generalized Pareto Distribution (GPD). Water Resour Manage 38, 1045–1060 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03708-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03708-5