Abstract
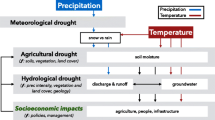
Drought propagation analysis is of great significance to develop reliable drought-resistant schemes. In this study, based on the construction of time-variant meteorological and agricultural drought indicators SPIt and SSMIt through Generalized Additive Models for Location, Scale and Shape (GAMLSS) method, the static and dynamic drought propagation time were defined and determined by Five-element Subtraction Set Pair Potential (FSSPP) and Copula function methods. Then, the driving factors resulted in meteorological to agricultural drought propagation were recognized through Pearson Correlation Coefficient (PCC) indicator. And finally, the application results of the proposed approach in Anhui province, China indicated that, (1) the static propagation time of meteorological to agricultural drought process varied within 1 to 4 months, and differed slightly in different seasons. And drought propagation time in spring and summer was noticeably longer than that of autumn and winter. (2) the dynamic drought propagation time presented decreasing trend in winter, spring and summer but displayed slight increasing trend in autumn in Anhui province. On the whole, the research findings are beneficial for theoretical and practical research of drought propagation system.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alehu BA, Bitana SG (2023) Assessment of climate change impact on water balance of lake Hawassa Catchment. Environ Process 10:14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-023-00626-x
Bai X, Jin JL, Wu CG, Zhou YL, Zhang LB, Cui Y, Tong F (2023) Construction of a time-variant integrated drought index based on the GAMLSS approach and Copula function. Water 15(9):1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091653
Chu JD (2022) Spatio-temporal Evolution characteristics of groundwater drought in northwest China and its response to meteorological drought and temperature index. Dissertation, Northwest A&F University, Shaanxi province, China (in Chinese)
Dai M (2021) Study on the propagation characteristics and laws of drought in meteorology-agriculture-disaster loss. Dissertation, Xi’an University of Technology, Shaanxi province, China (in Chinese)
Das S, Das J, Umamahesh NV (2022) A non-stationary based approach to understand the propagation of meteorological to agricultural droughts. Water Resour Manag 37(6):2483–2504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03297-9
Huang SZ, Li P, Huang Q, Leng GY, Hou BB, Ma L (2017) The propagation from meteorological to hydrological drought and its potential influence factors. J Hydrol 547:184–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.01.041
Jin JL, Shen SX, Pan ZW, Wang MW, Cui Y (2017) Advances in theoretical and applied research on Set Pair Analysis method for water resources system. J North China Univ Water Resour Electr Power (Nat Sci Ed) 38(4):54–66 (in Chinese)
Kim JS, Seo GS, Jang HW, Lee JH (2017) Correlation analysis between Korean spring drought and large-scale teleconnection patterns for drought forecasting. KSCE J Civ Eng 21(1):458–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0580-8
Mo SH, Li CX, Xing H, Jiang HK (2022) GAMLSS model-based analysis on annual runoff in Xiaoli river basin. J Basic Sci Eng 30(1):40–49 (in Chinese)
Padhiary J, Patra KC, Dash SS (2022) A novel approach to identify the characteristics of drought under future climate change scenario. Water Resour Manag 36:5163–5189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03296-w
Rashid MM, Beecham S (2019) Development of a non-stationary standardized precipitation index and its application to a south Australian climate. Sci Total Environ 657:882–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.052
Raposo VDB, Costa VAF, Rodrigues AF (2023) A review of recent developments on drought characterization, propagation, and influential factors. Sci Total Environ 898:165550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165550
Song SB, Singh VP (2010) Frequency analysis of droughts using the Plackett copula and parameter estimation by genetic algorithm. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 24(5):783–805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-010-0364-5
Stasinopoulos DM, Rigby RA (2007) Generalized additive models for location scale and shape (GAMLSS) in R. J Stat Softw 23(7):1–46. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v023.i07
Shiau JT (2006) Fitting drought duration and severity with two-dimensional copulas. Water Resour Manag 20:795–815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-005-9008-9
Shin JY, Chen S, Lee JH, Kim TW (2018) Investigation of drought propagation in South Korea using drought index and conditional probability. Terr Atmospheric Ocean Sci 29(2):231–241. https://doi.org/10.3319/TAO.2017.08.23.01
Tang SM (2016) Nonstationary flood frequency analysis based on covariates. Dissertation, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China (in Chinese)
Tsakiris GP, Loucks DP (2023) Adaptive water resources management under climate change: an introduction. Water Resour Manag 37:2221–2233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03518-9
Wang YX (2017) Driving mechanism and quantitative assessment of drought in Luanhe River Basin under changing environment. Dissertation, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China (in Chinese)
Wu HJ, Su XL, Singh VP, Feng K, Niu JP (2021) Agricultural drought prediction based on conditional distributions of Vine Copulas. Water Resour Res 57(8):e2021WR02956. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021WR029562
Xiong B, Xiong LH (2016) Nonstationary frequency analysis of low-flow series considering both baseflow recession process and rainfall. J Hydraul Eng 47(7):873–883 (in Chinese)
Xu Y, Zhang X, Wang X, Hao ZC, Singh VP, Hao FH (2019) Propagation from meteorological drought to hydrological drought under the impact of human activities: A case study in northern China. J Hydrol 579:124147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124147
Yuan X, Zhang M, Wang LY, Zhou T (2017) Understanding and seasonal forecasting of hydrological drought in the Anthropocene. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 21(11):5477–5492. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-21-5477-2017
Zhao KQ (2022) Application overview of set pair analysis in intelligent prediction system. CAAI Trans Intell Syst 17(2):233–247 (in Chinese)
Zhou RX, Jin JL, Cui Y, Ning SW, Bai X, Zhang LB, Zhou YL, Wu CG, Tong F (2022) Agricultural drought vulnerability assessment and diagnosis based on entropy fuzzy pattern recognition and subtraction set pair potential. Alex Eng J 61:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.04.090
Funding
The authors would like to thank the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U2240223, 52209012 and 52109009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chengguo Wu: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, writing-original draft, reparation, writing-review and editing; Yin Xu: conceptualization, writing-original draft, reparation; Juliang Jin: methodology, writing-original draft, preparation; Yuliang Zhou: data curation; Boyu Nie, Rui Li and Yi Cui: validation, funding acquisition; Fei Tong, Rui Li and Libing Zhang: investigation, data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
All the authors agree with the participation of this article.
Consent to Publish
All the authors agree with the publication of this article.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Xu, Y., Jin, J. et al. Meteorological to Agricultural Drought Propagation Time Analysis and Driving Factors Recognition Considering Time-Variant Characteristics. Water Resour Manage 38, 991–1010 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03705-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03705-8