Abstract
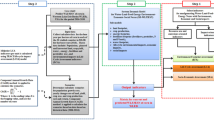
Investigating links between water, energy, and carbon emissions requires more attention on the path toward economic prosperity. This study aims to develop a framework for modeling water-energy-carbon interdependencies by considering the nonlinear relationships in their dynamic feedback processes. The main contribution of this research is the quantification of the carbon footprint of industrial water use through the development of an Industrial Water-Energy-Carbon (I-WEC) nexus model. It is a system dynamics model that is developed with a scenario-driven framework. The GDP as a representative of economic growth is assessed. The proposed methodology is tested on the Netherlands' industrial sector as a pilot due to the relatively good data structure. Based on policy-based complementary scenarios, the results show a 3% increase in total water use by 2030. Energy use and carbon emissions will fall as much as 10% and 25% that year, respectively. It is concluded that the industrial GDP share could be maintained with a 0.76% loss, which is close to the 0.5% loss projected by authorities. This study presents a unique approach that can be used in other regions.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
All input data used in this research can be found from the publicly available dataset domains by filtering the years 1990–2018 and selecting the Netherlands as a geopolitical entity: World bank, Eurostat, CBS -Statistics Netherlands, and Statista.
References
Acheampong AO (2018) Economic growth, CO2 emissions and energy consumption: what causes what and where? Energy Econ 74:677–692
Agana BA, Reeve D, Orbell JD (2013) An approach to industrial water conservation–a case study involving two large manufacturing companies based in Australia. J Environ Manag 114:445–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.10.047
Aşıcı AA (2013) Economic growth and its impact on environment: a panel data analysis. Ecol Indic 24:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.06.019
Cai X, Wallington K, Shafiee-Jood M, Marston L (2018) Understanding and managing the food-energy-water nexus–opportunities for water resources research. Adv Water Resour 111:259–273
CBS (2021) Statistics Netherlands. https://opendata.cbs.nl/statline/portal.html?_la=nl&_catalog=CBS
Climate Agreement (2019) The government of the Netherlands. https://www.government.nl/binaries/government/documents/reports/2019/06/28/climate-agreement/Climate+Agreement.pdf
Cook MA, King CW, Davidson FT, Webber ME (2015) Assessing the impacts of droughts and heat waves at thermoelectric power plants in the United States using integrated regression, thermodynamic, and climate models. Energy Rep 1:193–203
De Stercke S, Mijic A, Buytaert W, Chaturvedi V (2018) Modelling the dynamic interactions between London’s water and energy systems from an end-use perspective. Appl Energy 230:615–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.08.094
Ebrahimi SE, Karamouz M (2022) Dynamic water balance accounting-based vulnerability evaluation considering social aspects. Water Resour Manag 36:659–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-03046-4
Ebrahimi SE, Zarghami M (2019) Sustainability assessment of restoration plans under climate change by using system dynamics: Application on Urmia Lake, Iran. J Water Clim Chang 10(4):938–952. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2018.209
Endo A, Tsurita I, Burnett K, Orencio PM (2017) A review of the current state of research on the water, energy, and food nexus. J Hydrol Reg Stud 11:20–30
Eurostat (2021) European commission. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/main/data/database
Eurostat (2017) Archive: Consumption of energy - statistics explained. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Archive:Consumption_of_energy.
Förster J (2014) Archive: Water use in industry - statistics explained. Statistics in Focus 14/2014, ECOSTAT. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Archive:Water_use_in_industry
Giampietro M, Aspinall RJ, Ramos-Martin J, Bukkens SG (2014) Resource accounting for sustainability assessment: the nexus between energy, food, water and land use. Routledge
IEA (2020) The Netherlands 2020, IEA, Paris. https://www.iea.org/reports/the-netherlands-2020
Inam A, Adamowski J, Halbe J, Prasher S (2015) Using causal loop diagrams for the initialization of stakeholder engagement in soil salinity management in agricultural watersheds in developing countries: A case study in the Rechna Doab watershed, Pakistan. J Environ Manage 152:251–267
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2014) Mitigation of climate change. Contribution of Working Group III to the 5th Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 1454. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg3/
Karamouz M, Zare M (2021) Carbon Footprint of Water Use in Industrial Expansion. World Environ Water Resour Congress 593–606. https://ascelibrary.org/doi/abs/10.1061/9780784483466.054
Karamouz M, Barkhordari H, Ebrahimi E (2021) Dynamics of water allocation: Tradeoffs between allocator’s and farmers’ benefits of irrigation practices. J Irrig Drain Eng 147(6):04021017
Kashem MA, Rahman MM (2019) CO2 emissions and development indicators: a causality analysis for Bangladesh. Environ Process 6:433–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-019-00365-y
Kaya Y (1989) Impact of carbon dioxide emission control on GNP growth: interpretation of proposed scenarios. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change/Response Strategies Working Group, May
Li H, Zhao Y, Lin J (2020) A review of the energy–carbon–water nexus: Concepts, research focuses, mechanisms, and methodologies. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Energy Environ 9(e358):1. https://doi.org/10.1002/wene.358
Linderhof V, Dekkers K, Polman N (2020) The role of mitigation options for achieving a low-carbon economy in the netherlands in 2050 using a system dynamics modelling approach. Climate 8(11):132
Martin D Jr, Prabhakaran V, Kuhlberg J, Smart A, Isaac WS (2020) Participatory problem formulation for fairer machine learning through community based system dynamics. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.07572
Masters GM, Ela WP (2008) Introduction to environmental engineering and science (No. 60457). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall
Mavromatidis G, Orehounig K, Richner P, Carmeliet J (2016) A strategy for reducing CO2 emissions from buildings with the Kaya identity–A Swiss energy system analysis and a case study. Energy Policy 88:343–354
Menyah K, Wolde-Rufael Y (2010) Energy consumption, pollutant emissions and economic growth in South Africa. Energy Econ 32(6):1374–1382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2010.08.002
Mi Z, Zheng J, Meng J, Shan Y, Zheng H, Ou J, Guan D, Wei YM (2018) China’s energy consumption in the new normal. Earth’s Future 6(7):1007–1016. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018EF000840
Mingran W, Min Z, Zhaodan W (2018) The coordination and dynamic relationship of the industrial energy consumption, economic growth and SO2 emission —analysis of time series data of China from 1990 to 2016. Environ Process 5:789–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-018-0339-y
Mirchi A, Madani K, Watkins D, Ahmad S (2012) Synthesis of system dynamics tools for holistic conceptualization of water resources problems. Water Resour Manag 26(9):2421–2442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0024-2
Nakicenovic N, Swart R (eds) (2000) Special report on emissions scenarios. A Special Report of Working Group III of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Osobajo OA, Otitoju A, Otitoju MA, Oke A (2020) The impact of energy consumption and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions. Sustainability 12(19):7965
Raihan A, Muhtasim DA, Pavel MI et al (2022) Dynamic impacts of economic growth, renewable energy use, urbanization, and tourism on carbon dioxide emissions in Argentina. Environ Process 9:38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-022-00590-y
Raihan A, Muhtasim DA, Farhana S et al (2023) Dynamic linkages between environmental factors and carbon emissions in Thailand. Environ Process 10:5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-023-00618-x
Razmjoo A, Khalili N, Nezhad MM, Mokhtari N, Davarpanah A (2020) The main role of energy sustainability indicators on the water management. Model Earth Syst Environ 6(3):1419–1426
Si Y, Li X, Yin D, Li T, Cai X, Wei J, Wang G (2019) Revealing the water-energy-food nexus in the Upper Yellow River Basin through multi-objective optimization for reservoir system. Sci Total Environ 682:1–18
Statista (2021) Gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate in the Netherlands 2026. https://www.statista.com/statistics/263609/gross-domestic-product-gdp-growth-rate-in-the-netherlands/
The Paris Agreement (2015) Report of the conference of the parties on its Twenty-First Session, Held in Paris from 30 November to 11 December 2015; UNFCC: Paris, France, 2015
Van Vliet MT, Wiberg D, Leduc S, Riahi K (2016) Power-generation system vulnerability and adaptation to changes in climate and water resources. Nat Clim Chang 6(4):375–380. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2903
Varbanov PS (2014) Energy and water interactions: Implications for industry. Curr Opin Chem Eng 5:2–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2014.03.005
Wang B, Wang X, Zhang X (2019) An empirical research on influence factors of industrial water use. Water 11(11):2267
Wang F, Wang C, Su Y, Jin L, Wang Y, Zhang X (2017) Decomposition analysis of carbon emission factors from energy consumption in Guangdong Province from 1990 to 2014. Sustainability 9(2):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9020274
Wang Y, Chang X, Chen Z, Zhong Y, Fan T (2014) Impact of subsidy policies on recycling and remanufacturing using system dynamics methodology: a case of auto parts in China. J Clean Prod 74:161–171
Wen L, Bai L, Zhang E (2016) System dynamic modeling and scenario simulation on Beijing industrial carbon emissions. Environ Eng Res 21(4):355–364. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2016.049
World Bank (2021a) GDP (current US$) - Netherlands. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD?locations=NL&year_high_desc=true
World Bank (2021b) Industry, value added (% of GDP) - Netherlands. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NV.IND.TOTL.ZS?locations=NL&year_high_desc=true
Yang X, Wang Y, Sun M, Wang R, Zheng P (2018) Exploring the environmental pressures in urban sectors: An energy-water-carbon nexus perspective. Appl Energy 228:2298–2307
Zeng R, Cai X, Ringler C, Zhu T (2017) Hydropower versus irrigation—an analysis of global patterns. Environ Res Lett 12(3):034006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohammad Karamouz: Development of the original idea, concept, and the scope of the work; Materials and methods validation; Manuscript preparation; Review and editing. Mohammadreza Zare: Conceptualization; Data acquisition and preparation; Materials and methods; Modeling setup; Software Application, Analysis, and presentation. Elham Ebrahimi: Modeling setup; Materials and methods; Analysis and presentation, Manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The authors have observed all the ethical responsibilities.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karamouz, M., Zare, M. & Ebrahimi, E. System Dynamics-based Carbon Footprint Assessment of Industrial Water and Energy Use. Water Resour Manage 37, 2039–2062 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03473-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03473-5