Abstract
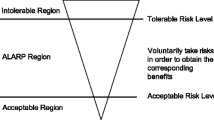
While reservoir dams have created significant social and economic benefits, dam failure caused by various reasons bring about great threats to the downstream areas. Many countries determine management investment according to the risk level of reservoir dams and the “as low as reasonably practicable” (ALARP) principle. However, life cannot be directly quantified in currency, and the traditional “cost-benefit” method cannot be effectively applied to reservoir dam management decisions. Hence, the life quality index (LQI) was introduced and improved to solve this problem based on the targeted analysis of the parameters of the life quality index, considering the fact that the per capita GDP changes over time. Without monetary quantification of life, an annual economic investment was determined to effectively control the risk level of the reservoir dam in a certain period of time in the future to ensure people’s life safety and quality of life. The improved LQI method was applied to a small-scale reservoir in China. The results showed that (a) the annual investment in dam risk management calculated by the improved LQI method was 20.07% higher than that of the traditional LQI method; (b) the annual investment in dam management changed 24 times due to changes in warning time and public risk awareness; and (c) dam management investment should be used not only to ensure the safety of the structure but also to improve early warning capacity and public risk awareness. This study focuses on how to reasonably determine the management investment of reservoir dams when the dam risk is in the ALARP region, which can effectively promote the application of dam risk standards.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur WB (1980) The economics of risks to life. Am Econ Rev 71(1):54–64
Bowles DS (2012) Tolerable risk guidelines for dams: principles and applications. Risk analysis, dam safety, Dam Security and Critical Infrastructure Management, 215–225. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316282558_Tolerable_risk_guidelines_for_dams_principles_and_applications. Accessed 25 Jan 2023
Chen C, Reniers G, Khakzad N (2020) A thorough classification and discussion of approaches for modeling and managing domino effects in the process industries. Saf Sci 125:104618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104618
Chen C, Reniers G, Khakzad N (2020) Cost-benefit management of intentional domino effects in chemical industrial areas. Process Saf Environ 134:392–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.10.007
Ditlevsen O, Friis-Hansen P (2005) Life quality time allocation index - an equilibrium economy consistent version of the current life quality index. Struct Saf 27(3):262–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2004.12.001
Fu C, Xue M, Chang W, Xu D, Yang S (2020) An evidential reasoning approach based on risk attitude and criterion reliability. Knowl-Based Syst 199(7):105947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105947
Ge W, Li Z, Li W, Wu M, Li J, Pan Y (2020) Risk evaluation of dam-break environmental impacts based on the set pair analysis and cloud model. Nat Hazards 104:1641–1653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04237-9
Ge W, Wang X, Li Z, Zhang H, Guo X, Wang T, Gao W, Lin C, van Gelder P (2021) Interval analysis of loss of life caused by dam failure. J Water Res Plan Man 147(1):04020098. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001311
Ge W, Jiao Y, Wu M, Li Z, Wang T, Li W, Zhang Y, Gao W, van Gelder P (2022) Estimating loss of life caused by dam breaches based on the simulation of floods routing and evacuation potential of population at risk. J Hydrol 612:128059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128059
Gu S (2011) F-N curved surface method for establishing the integrated risk criteria of dam failure. Sci China Technol Sc 54:597–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-011-4290-7
Günter B, Andrea K, Alberto V, Mariano B, Oliver B, Rudolf B, Denis C, Gaston D (2020) Current european flood-rich period exceptional compared with past 500 years. Nature 583:560–566. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2478-3
Hicks JR (1939) The foundation of welfare economics. Econ J 49:696–712
Hu J, Su H (2012) Evaluation method of reinforcement effect of dangerous reservoirs based on life quality index. J Hydraul Eng 43(7):852–859
Jonkman SN, Jongejan R, Maaskant B (2011) The use of individual and societal risk criteria within the dutch flood safety policy - nationwide estimates of societal risk and policy applications. Risk Anal 31:282–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.2010.01502.x
Larraz B, San-Martin E (2021) A tale of two dams: the impact of reservoir management on rural depopulation in central Spain. Water Resour Manag 35(14):4769–4787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02938-9
Li S, Zhou X, Wang Y, Zhou J, Du X, Chen Z (2015) Study of risk acceptance criteria for dams. Sci China Technol Sc 58:1263–1271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-015-5864-6
Li Z, Wang T, Ge W, Wei D, Li H (2019) Risk analysis of earth-rock dam breach based on dynamic bayesian network. Water 11(11):2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112305
Li Z, Zhang Y, Wang J, Ge W, Li W, Song H, Guo X, Wang T, Jiao Y (2021) Impact evaluation of geomorphic changes caused by extreme floods on inundation area considering geomorphic variations and land use types. Sci Total Environ 754:142424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142424
Li X, Qi X, Li Y (2021) On sales effort and pricing decisions under alternative risk criteria. Eur J Oper Res 293:603–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2020.12.025
Lin C, Li T, Liu X, Zhao L, Chen S, Qi H (2019) A deformation separation method for gravity dam body and foundation based on the observed displacements. Struct Control Hlth 26:e2304. https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2304
Lind N (2021) Objective inequality indexes joining income with life expectancy through the Life Quality Index of sub-populations. Soc Indic Res 153:783–794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-020-02504-7
Meacham BJ, Straalen I, Ashe B (2021) Roadmap for incorporating risk as a basis of performance objectives in building regulation. Saf Sci 141(2):105337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2021.105337
Pandey MD, Nathwani JS (2003) A conceptual approach to the estimation of societal willingness-to-pay for nuclear safety programs. Nucl Eng Des 224(1):65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0029-5493(03)00062-1
Pandey MD, Nathwani JS (2004) Life Quality Index for the estimation of societal willingness-to-pay for safety. Struct Saf 26:181–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2003.05.001
Pandey MD, Nathwani JS, Lind NC (2006) The derivation and calibration of the Life-Quality index (LQI) from economic principles. Struct Saf 28(4):341–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2005.10.001
Piróg D, Fidelus-Orzechowska J, Wiejaczka U (2022) Local authority vs community visions of dam project land development: a text mining approach. Water Resour Manag 36(6):1833–1848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03110-7
Pisaniello JD, Dam TT, Tingey-Holyoak JL (2015) International small dam safety assurance policy benchmarks to avoid dam failure flood disasters in developing countries. Hydrol 531:1141–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.09.077
Rackwitz R (2002) Optimization and risk acceptability based on the Life Quality Index. Struct Saf 24:297–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-4730(02)00029-2
Shang Z, Liu X (2010) Life risk value assessment of debris flow disaster based on LQI. Trop Geogr 30(3):289–293
Shepard DS, Zechhauser RJ (1984) Survival vs consumption. Manage Sci 30(4):423–439
Singto C, Vries M, Hofstede GJ, Fleskens L (2021) Ex ante impact assessment of reservoir construction projects for different stakeholders using Agent-Based modeling. Water Resour Manag 35(3):1047–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02771-0
Skinner J (1985) Variable life span and the intertemporal elasticity of consumption. Rev Econ Stat 67(4):616–623
Usher D (1973) An imputation to the measure of economic growth for changes in life expectancy. National accounting and economic theory: the collected papers of Dan Usher. Edward Elgar, Cheltenham, pp 193–232
Wang T, Li Z, Ge W, Zhang Y, Jiao Y, Sun H, Zhang H (2022) Calculation of dam risk probability of cascade reservoirs considering risk transmission and superposition. J Hydrol 609:127768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127768
Wang T, Li Z, Ge W, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Sun H, Jiao Y (2023) Risk consequence assessment of dam breach in cascade reservoirs considering risk transmission and superposition. Energy 265:126315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.126315
Wu M, Ge W, Wu Z, Guo X, Di D, Huang S (2020) Evaluation of the benefits of urban water resource utilization based on the catastrophe and emergy methods. Water Resour Manag 34:1843–1853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02530-7
Wu M, Wu Z, Ge W, Wang H, Shen Y, Jiang M (2021) Identification of sensitivity indicators of urban rainstorm flood disasters: a case study in China. J Hydrol 599:126393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126393
Yaari ME (1965) Uncertain lifetime, life insurance, and the theory of the consumer. Rev Econ Stud 32(2):137–150
Zamarrón-Mieza I, Yepes V, Moreno-Jiménez JM (2017) A systematic review of application of multi-criteria decision analysis for aging-dam management. J Clean Prod 147:217–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.092
Zhang Y, Li Z, Ge W, Chen X, Xu H, Guan H (2021) Evaluation of the impact of extreme floods on the biodiversity of terrestrial animals. Sci Total Environ Sci Total Environ 790:148227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148227
Zhang Y, Li Z, Ge W, Wang J, Guo X, Wang T, Li W (2022) Assessment of the impact of floods on terrestrial plant biodiversity. J Clean Prod 339:130722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130722
Zhu Y, Niu X, Gu C, Yang D, Sun Q, Rodriguez EF (2020) Using the DEMATEL-VIKOR method in dam failure path identification. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(5):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051480
Zhu Y, Niu X, Gu C, Dai B, Huang L (2021) A fuzzy clustering logic life loss risk evaluation model for dam-break floods. Complexity 15:7093256. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/7093256
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52079127, 52179144, U2243244, U2040224), Program for Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (HASTIT) (Grant No. 22HASTIT011), the Young Talent Support Project of Henan Province (Grant No. 2021HYTP024), the Fund of National Dam Safety Research Center (Grant No. CX2021B01), and the Programs for Science and Technology Development of Henan Educational Committee (Grant No. 202102310394).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing - original draft. WG: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing, Review & editing. YZ: Data curation, Review & editing. ZL: Data curation, Review & editing. WL: Review & editing. JZ: Review & editing. WW: Visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Ge, W., Zhang, Y. et al. Risk Management Decision of Reservoir Dams Based on the Improved Life Quality Index. Water Resour Manage 37, 1223–1239 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03426-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03426-y