Abstract
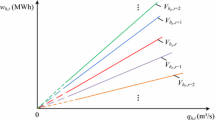
Sampling stochastic dynamic programming (SSDP), which considers the uncertainty of streamflow, is a popular and useful method for solving release decisions of reservoirs. It is easy to implement the long-term operation for cascaded hydropower system with poor inflow prediction ability. Furthermore, SSDP describes the temporal and spatial structure of the stochastic streamflow processes implicitly through inflow scenarios instead of representing the multivariate distribution of inflow by conditional probabilities in stochastic dynamic programming (SDP). However, computation time of SSDP procedure will increase exponentially with the growth inflow scenarios. Thus, clustering algorithm is employed to reduce the number of inflow scenarios in order to improve the efficiency and operability of SSDP in practical applications. The calculation results of SSDP with inflow clustering are analyzed with different cluster numbers. The principle of how to find the least inflow scenarios to represent all inflow sequences has also been proposed. The least inflow scenarios and relevant probabilities found by clustering algorithm can approximate the empirical distribution of all streamflow scenarios used in this study without obviously decreasing the energy and exacerbating the shortage of firm power.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
The code used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Afshar A, EmamiSkardi MJ, Masoumi F (2015) Optimizing water supply and hydropower reservoir operation rule curves: an imperialist competitive algorithm approach. Eng Optim 47(9):1208–1225. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2014.958732
Alfieri L, Lorini V, Hirpa FA, Harrigan S, Zsoter E, Prudhomme C, Salamon P (2020) A global streamflow reanalysis for 1980–2018. J Hydrol X 6:100049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydroa.2019.100049
Anvari S, Mousavi SJ, Morid S (2014) Sampling/stochastic dynamic programming for optimal operation of multi-purpose reservoirs using artificial neural network-based ensemble streamflow predictions. J Hydroinformat 16(4):907–921. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2013.236
Arora P, Varshney S (2016) Analysis of k-means and k-medoids algorithm for big data. Proced Comput Scienc 78:507–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2016.02.095
Arunkumar R, Jothiprakash V (2013) Chaotic evolutionary algorithms for multi-reservoir optimization. Water Resour Manage 27:5207–5222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0463-4
Carpentier PL, Gendreau M, Bastin F (2014) Managing hydroelectric reservoirs over an extended horizon using benders decomposition with a memory loss assumption. IEEE Trans Power Syst 30(2):563–572. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2014.2332402
Catalão JDS, Pousinho HMI, Mendes VMF (2010) Scheduling of head-dependent cascaded hydro systems: Mixed-integer quadratic programming approach. Energ Convers Manage 51(3):524–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2009.10.017
Cheng C, Wang S, Chau KW, Wu X (2014) Parallel discrete differential dynamic programming for multireservoir operation. Environ Modell Softw 57:152–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.02.018
Côté P, Arsenault R (2019) Efficient implementation of sampling stochastic dynamic programming algorithm for multireservoir management in the hydropower sector. J Water Resour Plan Manage 145(4):05019005. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001050
Côté P, Leconte R (2016) Comparison of stochastic optimization algorithms for hydropower reservoir operation with ensemble streamflow prediction. J Water Resour Plan Manage 142(2):04015046. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000575
Doganis P, Sarimveis H (2014) Optimization of power production through coordinated use of hydroelectric and conventional power units. Appl Math Model 38(7–8):2051–2062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2013.10.025
Faber BA, Stedinger JR (2001) Reservoir optimization using sampling SDP with ensemble streamflow prediction (ESP) forecasts. J Hydrol 249(1–4):113–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00419-X
Gal S (1979) Optimal management of a multireservoir water supply system. Water Resour Res 15(4):737–749. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR015i004p00737
Haguma D, Leconte R (2018) Long-term planning of water systems in the context of climate non-stationarity with deterministic and stochastic optimization. Water Resour Manage 32(5):1725–1739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1900-6
He S, Guo S, Chen K, Deng L, Liao Z, Xiong F, Yin J (2019) Optimal impoundment operation for cascade reservoirs coupling parallel dynamic programming with importance sampling and successive approximation. Adv Water Resour 131:103375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2019.07.005
Kelman J, Stedinger JR, Cooper LA, Hsu E, Yuan SQ (1990) Sampling stochastic dynamic programming applied to reservoir operation. Water Resour Res 26(3):447–454. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR026i003p00447
Kişi Ö (2009) Neural network and wavelet conjunction model for modelling monthly level fluctuations in Turkey. Hydrol Process 23(14):2081–2092. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7340
Lei XH, Tan QF, Wang X, Wang H, Wen X, Wang C, Zhang JW (2017) Stochastic optimal operation of reservoirs based on copula functions. J Hydrol 557:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.12.038
Loucks DP, Stedinger JR, Haith DA (1981) Water resource systems planning and analysis. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Mariño MA, Mohammadi B (1983) Reservoir operation by linear and dynamic programming. J Water Resour Plan Manage 109(4):303–319. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(1983)109:4(303)
Mohanavelu A, Soundharajan BS, Kisi O (2022) Modeling multi-objective Pareto-optimal reservoir operation policies using state-of-the-art modeling techniques. Water Resour Manage 36(9):3107–3128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03191-4
Park HS, Jun CH (2009) A simple and fast algorithm for K-medoids clustering. Expert Syst Appl 36(2):3336–3341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.01.039
Rahimi H, Ardakani MK, Ahmadian M, Tang X (2020) Multi-reservoir utilization planning to optimize hydropower energy and flood control simultaneously. Enviro Proces 7(1):41–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-019-00404-8
Shen JJ, Zhu WL, Cheng CT, Zhong H, Jiang Y, Li XF (2021) Method for high-dimensional hydropower system operations coupling random sampling with feasible region identification. J Hydrol 599:126357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126357
Stedinger JR, Sule BF, Loucks DP (1984) Stochastic dynamic programming models for reservoir operation optimization. Water Resour Res 20(11):1499–1505. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR020i011p01499
Tong B, Zhai Q, Guan X (2013) An MILP based formulation for short-term hydro generation scheduling with analysis of the linearization effects on solution feasibility. IIEEE Trans Power Syst 28(4):3588–3599. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2013.2274286
Wu X, Cheng C, Miao S, Li G, Li S (2020) Long-term market competition analysis for hydropower stations using SSDP-games. J Water Resour Plan Manage 146(6):04020037. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001195
Wu X, Chen Z, Cheng C, Yin S, Su H (2022) DNN-SSDP for hydropower system operation using small state sets. J Hydrol 128612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128612
Xu W, Zhang C, Peng Y, Fu G, Zhou H (2014) A two stage B ayesian stochastic optimization model for cascaded hydropower systems considering varying uncertainty of flow forecasts. Water Resour Res 50(12):9267–9286. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013WR015181
Zhao T, Zhao J, Lei X, Wang X, Wu B (2017) Improved dynamic programming for reservoir flood control operation. Water Resour Manage 31(7):2047–2063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1599-4
Acknowledgements
The research work described in this paper is supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (52179005 and 91647113).
Funding
The research work described in this paper is supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (52179005 and 91647113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xinyu Wu: Conceptualization, Software, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Resources. Shuai Yin: Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing—original draft. Chuntian Cheng: Supervision, Investigation. Zhiyong Chen: Writing—review & editing. Huaying Su: Data curation, Formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
All authors have read and approved the manuscript being submitted, and agree to its submittal to this journal, and have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
We confirm that this work is original and has not been published elsewhere, nor is it currently under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Yin, S., Cheng, C. et al. SSDP Model with Inflow Clustering for Hydropower System Operation. Water Resour Manage 37, 1109–1123 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03417-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03417-5