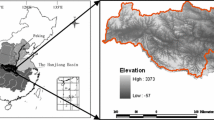
Abstract
The impact of future land-use and climate changes on the surface hydrology of a watershed was studied using an event-based hydrological model. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Monte-Carlo Cellular Automata (CA) based model was used to generate future land-use scenarios of an urbanizing watershed. Simulations were thereafter performed using a hydrological model to assess the expected changes in runoff. The spatial data inputs for the hydrological model were generated using satellite data, field observations, and data obtained from government agencies. Sensitivity analysis, calibration, and validation of the model were carried out using the observed storm and flow hydrographs, and the model performance was assessed using various statistical performance metrics. Historical land-use data for 2005, 2013, and 2017 was prepared using Landsat satellite imageries and Google Earth images. The land-use scenario generated for the year 2021 exhibited good agreement with the actual land-use map, with a Kappa value above 0.8. Future land-use scenarios were generated to assess the short-term (2025 and 2029) and long-term (2037, 2045, and 2053) changes in the characteristics of the flow hydrographs. The expected changes in the hydrographs due to urbanization were analyzed by applying a selected storm event and considering 2005 as the baseline year using the Two-Dimensional Runoff Erosion and Export (TREX) model. Results indicate that the peak discharge is likely to increase by 29%, and the time to peak is likely to decrease by 6% in 2053 when only land use change is considered. The corresponding values in the worst case considering the combined effect of climate and land use changes are 34.63% and 8.28%, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah J, Julien PY (2014) Distributed flood simulations on a small tropical watershed with the trex model. J Flood Eng 5(1–2):17–37
Abdullah J, Muhammad NS, Muhammad SA, Julien PY (2019) Envelope curves for the specific discharge of extreme floods in Malaysia. J Hydro-Environ Res 25:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2019.05.002
Astuti IS, Sahoo K, Milewski A, Mishra DR (2019) Impact of land use land cover (LULC) change on surface runoff in an increasingly urbanized tropical watershed. Water Resour Manag 33:4087–4103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02320-w
Bahati H, Ogenrwoth A, Sempewo JI (2021) Quantifying the potential impacts of land-use and climate change on hydropower reliability of Muzizi hydropower plant, Uganda. J Water Clim Chang 12:2526–2554
Batty M, Xie Y, Sun Z (1999) Modeling urban dynamics through GIS-based cellular automata. Comput Environ Urban Syst 23:205–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0198-9715(99)00015-0
England JF, Velleux ML, Julien PY (2007) Two-dimensional simulations of extreme floods on a large watershed. J Hydrol 347:229–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2007.09.034
Gharaibeh A, Shaamala A, Obeidat R, Al-Kofahi S (2020) Improving land-use change modeling by integrating ANN with Cellular Automata-Markov Chain model. Heliyon 6:e05092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05092
Gou J, Miao C, Duan Q, Tang Q, Di Z, Liao W, Wu J, Zhou R (2020) Sensitivity analysis based automatic parameter calibration of the VIC model for streamflow simulations over China. Water Resour Res 56(1):e2019WR025968. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019WR025968
Govt. of Kerala (2012) State urbanisation report, Kerala - a study on the scattered human settlement pattern of Kerala and its development issues, Department of Town and Country Planning - Government of Kerala, March 2012. https://townplanning.kerala.gov.in/town/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/SUR.pdf
Green WH, Ampt GA (1911) Studies on soil physics: Part I. The flow of air and water through soils. J Agric Sci 4:1–24
Gunacti MC, Gul OG, Cetinkaya CP, Gul A, Barbaros F (2022) Evaluating impact of land use and land cover change under climate change on the Lake Marmara system. Water Resour Manag 1–14. https://assets.researchsquare.com/files/rs-1712629/v1/93b452c4-d381-488b-83ba-0d13b9dead90.pdf?c=1655222404
Gupta HV, Sorooshian S, Yapo PO (1999) Status of automatic calibration for hydrologic models: comparison with multilevel expert calibration. J Hydrol Eng 4:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)1084-0699(1999)4:2(135)
Johnson BE, Julien PY, Molnar DK, Watson CC, Johnson BE, Julien PY et al (2000) The two-dimensional upland erosion model CASC2D-SED. J Am Water Resour Assoc 36:31–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2000.tb04246.x
Joseph S, Rahul R, Sukanya S (2021) Land use/land cover (LU/LC) changes and its impact on soil organic carbon stock in Killiar River basin, Kerala, India: a geospatial approach. Curr World Environ 16:662–664. https://doi.org/10.12944/cwe.16.3.2
Julien PY, Saghafian B, Ogden FL (1995) Raster-based hydrologic modeling of spatially-varied surface runoff. JAWRA J Am Water Resour Assoc 31:523–536. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1995.tb04039.x
Kafy AA, Al Rakib A, Roy S, Ferdousi J, Raikwar V, Kona MA, Al Fatin SA (2021) Predicting changes in land use/land cover and seasonal land surface temperature using multi-temporal landsat images in the northwest region of Bangladesh. Heliyon 7(1):e07623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07623
Kumar SD, Arya DS, Vojinovic Z (2013) Modeling of urban growth dynamics and its impact on surface runoff characteristics. Comput Environ Urban Syst 41:124–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2013.05.004
Lal P, Nair SB (2017) Urbanization in Kerala—what does the census data reveal? Indian J Hum Dev 11:356–386. https://doi.org/10.1177/0973703018763241
Li T, Li W (2015) Multiple land use change simulation with Monte Carlo approach and CA-ANN model, a case study in Shenzhen, China. Environ Syst Res 4:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-014-0026-6
Lin YP, Chu HJ, Wu CF, Verburg PH (2011) Predictive ability of logistic regression, auto-logistic regression and neural network models in empirical land-use change modeling - a case study. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 25:65–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658811003752332
McCuen RH (1973) The role of sensitivity analysis in hydrologic modeling. J Hydrol 18:37–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(73)90024-3
Mikaeili O, Shourian M (2022) Assessment of the analytic and hydrologic methods in separation of watershed response to climate and land use changes. Water Resour Manag 2022:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11269-022-03324-9
Mishra V, Bhatia U, Tiwari AD (2020) Bias-corrected climate projections for South Asia from Coupled Model Intercomparison Project-6. Sci Data 7(7):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-020-00681-1
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Van Liew MW et al (2007) Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Am Soc Agric Biol Eng 50:885–900
Mustafa A, Ebaid A, Omrani H, McPhearson T (2021) A multi-objective Markov Chain Monte Carlo cellular automata model: Simulating multi-density urban expansion in NYC. Comput Environ Urban Syst 87:101602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2021.101602
Mustafa A, Rienow A, Saadi I et al (2018) Comparing support vector machines with logistic regression for calibrating cellular automata land use change models. Eur J Remote Sens 51:391–401. https://doi.org/10.1080/22797254.2018.1442179
Ogden FL, Sharif HO, Senarath SUS et al (2000) Hydrologic analysis of the Fort Collins, Colorado, flash flood of 1997. J Hydrol 228:82–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00146-3
Palmate SS, Wagner PD, Fohrer N, Pandey A (2022) Assessment of uncertainties in modelling land use change with an integrated Cellular Automata–Markov Chain Model. Environ Model Assess 27(2):275–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-021-09804-3
Philip S, Shahul F (2019) Rainfall-runoff modelling using artificial neural network and Arc GIS - a case study at Karamana River Basin, International Conference on Advanced Innovation in Science, Engineering & Technology (ICAISET 2019) organized by Academy of Sree Ayyappa College, Chengannur, Kerala. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/349465684_Rainfall-Runoff_Modelling_Using_Artificial_Neural_Network_and_Arc_GIS_-A_Case_Study_at_Karamana_River_Basin
Raj R, Thampi SG (2022) Urban flood modelling of Thiruvananthapuram City. National Institute of Technology, Calicut
Raju KS, Kumar DN (2020) Review of approaches for selection and ensembling of GCMs. J Water Clim Chang 11:577–599. https://doi.org/10.2166/WCC.2020.128
Sajikumar N, Remya RS (2015) Impact of land cover and land use change on runoff characteristics. J Environ Manag 161:460–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.12.041
Salvadore E, Bronders J, Batelaan O (2015) Hydrological modelling of urbanized catchments: a review and future directions. J Hydrol 529:62–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.06.028
Silva LPE, Xavier APC, da Silva RM, Santos CAG (2020) Modeling land cover change based on an artificial neural network for a semiarid river basin in northeastern Brazil. Glob Ecol Conserv 21:e00811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00811
Simwanda M, Murayama Y, Ranagalage M (2020) Modeling the drivers of urban land use changes in Lusaka, Zambia using multi-criteria evaluation: an analytic network process approach. Land Use Policy 92:104441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.104441
Teklay A, Dile YT, Asfaw DH et al (2021) Impacts of climate and land use change on hydrological response in Gumara watershed, Ethiopia. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol 21:315–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOHYD.2020.12.001
Velleux ML, England JF, Julien PY (2008) TREX: Spatially distributed model to assess watershed contaminant transport and fate. Sci Total Environ 404:113–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.05.053
Velleux ML, Julien PY, Rojas-Sanchez R et al (2006) Simulation of metals transport and toxicity at a mine-impacted watershed: California Gulch, Colorado. Environ Sci Technol 40:6996–7004. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0608592
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SNM – Methodology, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting of the manuscript. SGT – Study concept, Editing the draft, Supervision. SKD – Methodology, Writing-review and editing, Resources, Supervision. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sabitha, N.M., Thampi, S.G. & Kumar, D.S. Application of a Distributed Hydrologic Model to Assess the Impact of Climate and Land-use Change on Surface Runoff from a Small Urbanizing Watershed. Water Resour Manage 37, 2347–2368 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03349-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03349-0