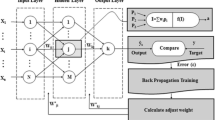
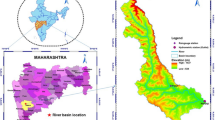
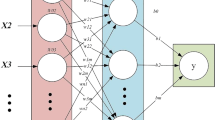
Abstract
The development of a river inflow prediction is a prerequisite for dam reservoir management. Precise forecasting leads to better irrigation water management, reservoir operation refinement, enhanced hydropower output and mitigation of risk of natural hazards such as flooding. Dam created reservoirs prove to be an essential source of water in arid and semi-arid regions. Over the years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been used for development of models for prediction of various natural variables in different engineering fields. Also, several AI models have been proved to be beneficial over the conventional models in efficient prediction of various natural variables. In this study, four AI models, namely, Artificial Neural Network (ANN), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random Forest (RF) and Boosted Tree Regression (BTR) were developed and trained over 130-years of monthly historical rainfall data to forecast streamflow at Aswan High Dam, Egypt. The input parameters were selected according to the Autocorrelation Function (ACF) plot. The findings revealed that RF model outperformed other techniques and could provide precise monthly streamflow prediction with the lowest RMSE (2.2395) and maximum WI (0.998462), R2 (0.9012). The input combination for the optimum RF model was Qt-1, Qt-11, and Qt-12 (i.e., one-, eleven- and twelve-months delay inputs). The optimum RF model provides a reliable source of data for inflow predictions, which allows improved utilization of water resources and long-term water resource planning and management.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Adnan RM, Yuan X, Kisi O, Adnan M, Mehmood A (2018) Stream flow forecasting of poorly gauged mountainous watershed by least square support vector machine, fuzzy genetic algorithm and M5 model tree using climatic data from nearby station. Water Resour Manag 32(14):4469–4486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2033-2
Aljarah I, Faris H, Mirjalili S (2018) Optimizing connection weights in neural networks using the whale optimization algorithm. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-016-2442-1
Bilen S, Turan V (2022) Enzymatic analyses in soils. In: Amaresan N, Patel P, Amin D (eds) Practical Handbook on Agricultural Microbiology. Springer Protocols Handbooks. Humana, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1724-3_50
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Döpke J, Fritsche U, Pierdzioch C (2017) Predicting recessions with boosted regression trees. Int J Forecast 33(4):745–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijforecast.2017.02.003
Egrioglu E, Uslu VR, Yolcu U, Basaran MA, Hakan AC (2009) A new approach based on artificial neural networks for high order bivariate fuzzy time series. Adv Intell Soft Comput 58:265–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-89619-7_26
Elsahabi M, Negm A, El Tahan AHMH (2016) Performances evaluation of surface water areas extraction techniques using Landsat ETM+ Data: Case Study Aswan High Dam Lake (AHDL). Procedia Technol 22:1205–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2016.02.001
El-Shafie A, Taha MR, Noureldin A (2007) A neuro-fuzzy model for inflow forecasting of the Nile river at Aswan high dam. Water Resour Manag 21(3):533–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-9027-1
Fahad S, Ullah A, Ali U, Ali E, Saud S, Hakeem KR, Alharby H, Sabagh AEL, Barutcular C, Kamran M, Turan V, Adnan M, Arif M, Amanullah (2019) Drought tolerance in plantsrole of phytohormones and scavenging system of ROS. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203705315-7
Faris H, Aljarah I, Mirjalili S (2016) Training feedforward neural networks using multi-verse optimizer for binary classification problems. Appl Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-016-0767-1
Friedman JH (2002) Stochastic gradient boosting. Comput Stat Data Anal. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-9473(01)00065-2
Hadiyan PP, Moeini R, Ehsanzadeh E (2020) Application of static and dynamic artificial neural networks for forecasting inflow discharges, case study: Sefidroud Dam reservoir. Sustain Comput Inform Syst 27:100401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suscom.2020.100401
Hassan A, Ismail SS, Elmoustafa A, Khalaf S (2018) Evaluating evaporation rate from high Aswan Dam Reservoir using RS and GIS techniques. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 21(3):285–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2017.10.001
Heddam S (2016) Use of optimally pruned extreme learning machine (OP-ELM) in forecasting dissolved oxygen concentration (do) several hours in advance: a case study from the Klamath River, Oregon, USA. Environ Process 3:909–937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0172-0
Heidari E, Sobati MA, Movahedirad S (2016) Accurate prediction of nanofluid viscosity using a multilayer perceptron artificial neural network (MLP-ANN). Chemom Intell Lab Syst 155:73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2016.03.031
Jakarni FM, Muniandy R, Hassim S, Mahmud AR (2010) Analysis of stone mastic asphalt (SMA) slab dimensions for evaluation of the newly developed roller compactor (Turamesin). Pertanika J Sci Technol 18(1):13–22
Karunanayake C, Gunathilake MB, Rathnayake U (2020) Inflow forecast of Iranamadu Reservoir, Sri Lanka, under projected climate scenarios using artificial neural networks. Appl Comput Intell Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8821627
Lai V, Malek MA, Abdullah S, Latif SD, Ahmed AN (2020) Time-series prediction of sea level change in the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia from the supervised learning approach. Int J Des Nat Ecodyn. https://doi.org/10.18280/ijdne.150314
Liaw A, Wiener M (2002) R news 2(3):18–22. ISSN: 1609-3631
Mandal S, Mahapatra SS, Adhikari S et al (2015) Modeling of arsenic (III) removal by evolutionary genetic programming and least square support vector machine models. Environ Process 2:145–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-014-0050-6
McCulloch WS, Pitts WA (1943) logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys 5:115–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478259
Mirjalili S (2015) How effective is the Grey Wolf optimizer in training multi-layer perceptrons. Appl Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-014-0645-7
Panda AK, Rapur JS, Tiwari R (2018) Prediction of flow blockages and impending cavitation in centrifugal pumps using Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithms based on vibration measurements. Meas J Int Meas Confed 130:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.07.092
Pereira HR, Meschiatti MC, de Matos Pires RC, Blain GC (2018) On the performance of three indices of agreement: An easy-to-use r-code for calculating the willmott indices. Bragantia 77(2):394–403. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4499.2017054
Qasem SN, Samadianfard S, Kheshtgar S, Jarhan S, Kisi O, Shamshirband S, Chau KW (2019) Modeling monthly pan evaporation using wavelet support vector regression and wavelet artificial neural networks in arid and humid climates. Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech 13(1):177–187. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2018.1564702
Rahimzad M, MoghaddamNia A, Zolfonoon H et al (2021) Performance comparison of an LSTM-based deep learning model versus conventional machine learning algorithms for streamflow forecasting. Water Resour Manag 35:4167–4187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02937-w
Ravindran SM, Bhaskaran SKM, Ambat SKN (2021) A deep neural network architecture to model reference evapotranspiration using a single input meteorological parameter. Environ Process 8:1567–1599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-021-00543-x
Tauqeer HM, Turan V, Farhad M, Iqbal M (2022) Sustainable agriculture and plant production by virtue of biochar in the era of climate change. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Ahammed GJ, Nahar K (eds) Managing plant production under changing environment. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5059-8_2
Tehrany MS, Pradhan B, Jebur MN (2013) Spatial prediction of flood susceptible areas using rule based decision tree (DT) and a novel ensemble bivariate and multivariate statistical models in GIS. J Hydrol 504:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.09.034
Tikhamarine Y, Malik A, Kumar A, Souag-Gamane D, Kisi O (2019) Estimation of monthly reference evapotranspiration using novel hybrid machine learning approaches. Hydrol Sci J 64(15):1824–1842. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2019.1678750
Tikhamarine Y, Souag-Gamane D, Najah Ahmed A, Kisi O, El-Shafie A (2020) Improving artificial intelligence models accuracy for monthly streamflow forecasting using grey Wolf optimization (GWO) algorithm. J Hydrol 582(Dec 2019):124435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124435
Wang L, Huang X, Fang NF, Niu YH, Wang TW, Shi ZH (2019) Selective transport of soil organic and inorganic carbon in eroded sediment in response to raindrop sizes and inflow rates in rainstorms. J Hydrol 575(Oct 2018):42–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.05.033
Yang T, Asanjan AA, Welles E, Gao X, Sorooshian S, Liu X (2017) Developing reservoir monthly inflow forecasts using artificial intelligence and climate phenomenon information. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017WR020482
Zhou P, Li Z, Snowling S, Baetz BW, Na D, Boyd G (2019) A random forest model for inflow prediction at wastewater treatment plants. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 33(10):1781–1792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-019-01732-9
Zounemat-Kermani M, Ramezani-Charmahineh A, Razavi R et al (2020) Machine learning and water economy: a new approach to predicting dams water sales revenue. Water Resour Manag 34:1893–1911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02529-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing – original draft, Software and Formal Analysis: Yahia Mutalib Tofiq; Methodology: Ahmed El-Shafie; Supervision: Ali Najah Ahmed; Writing – review & editing: Sarmad Dashti Latif, Writing- review & edit: Pavitra Kumar.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tofiq, Y.M., Latif, S.D., Ahmed, A.N. et al. Optimized Model Inputs Selections for Enhancing River Streamflow Forecasting Accuracy Using Different Artificial Intelligence Techniques. Water Resour Manage 36, 5999–6016 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03339-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03339-2