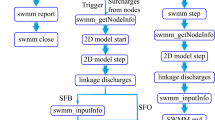
Abstract
Urban inundation is becoming increasingly severe as a result of climate change and rapid urbanization. Various urban water management practices are designed to alleviate urban inundation hazards. It is essential to better understand and model the dynamic process of surface runoff to inform the arrangement of effective strategies for urban stormwater management. A coupled hydrodynamic and rainfall-tracking model is proposed to determine spatial prioritization by identifying distributions of source areas and quantifying the contribution rate for source areas to inundating areas. Specially, the rainfall mark variable (R) is developed to trace out the pathway of runoff generated by rainfall in the proposed modeling. The coupled model is successfully validated against two idealized test cases including dissymmetric V-shaped and V-shaped catchments. Indeed, the Jinhua underpass catchment area reveals its capability in representing detailed hydrodynamic information and obtaining contribution rates of source areas to inundated areas. The approach can help recognize opportunities to determine the spatial prioritization and adaptability for city planners to complete the optimal solution schemes between the available resources and alleviating inundation.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- BMPs:
-
Best management practices
- LID:
-
Low impact development
- MCDA:
-
Multiple criteria decision analysis
- MOEA:
-
Multi-objective evolution algorithm
- NSE:
-
Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient
- R:
-
Rainfall mark variable
- RANSE:
-
Reynolds Averaged Navier–Stokes equation
- SWEs:
-
Shallow water equations
- USWM:
-
Urban stormwater management
- WSUD:
-
Water sensitive urban design
References
Abedini M, Said MAM, Ahmad F (2012) Effectiveness of check dam to control soil erosion in a tropical catchment (The Ulu Kinta Basin). CATENA 97:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.05.003
Bruwier M, Maravat C, Mustafa A, Teller J, Pirotton M, Erpicum S, Archambeau P, Dewals B (2020) Influence of urban forms on surface flow in urban pluvial flooding. J Hydrol 582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124493
Cano OM, Barkdoll BD (2017) Multiobjective, Socioeconomic, Boundary-Emanating, Nearest Distance Algorithm for Stormwater Low-Impact BMP Selection and Placement. J Water Resour Plan Manag 143:05016013. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)wr.1943-5452.0000726
Casal-Campos A, Fu G, Butler D, Moore A (2015) An Integrated Environmental Assessment of Green and Gray Infrastructure Strategies for Robust Decision Making. Environ Sci Technol 49:8307–8314. https://doi.org/10.1021/es506144f
Cristiano E, ten Veldhuis MC, Wright DB, Smith JA, van de Giesen N (2019) The Influence of Rainfall and Catchment Critical Scales on Urban Hydrological Response Sensitivity.Water Resour Res 55 3375 3390. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018WR024143
Cun C, Zhang W, Che W, Sun H (2019) Review of urban drainage and stormwater management in ancient China. Landsc Urban Plan 190:103600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2019.103600
Duan HF, Li F, Yan H (2016) Multi-Objective Optimal Design of Detention Tanks in the Urban Stormwater Drainage System: LID Implementation and Analysis. Water Resour Manag 30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1444-1
Hou J, Han H, Qi W, Guo K, Li Z, Hinkelmann R (2019) Experimental investigation for impacts of rain storms and terrain slopes on low impact development effect in an idealized urban catchment. J Hydrol 579:124176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124176
Hou J, Liang Q, Simons F, Hinkelmann R (2013a) A 2D well-balanced shallow flow model for unstructured grids with novel slope source term treatment. Adv Water Resour 52:107–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.08.003
Hou J, Simons F, Mahgoub M, Hinkelmann R (2013b) robust well-balanced model on unstructured grids for shallow water lows with wetting and drying over complex topography. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 257:126–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2013.01.015
Hou J, Wang N, Guo K, Li D, Jing H, Wang T, Hinkelmann R (2020) Effects of the temporal resolution of storm data on numerical simulations of urban flood inundation. J Hydrol 589:125100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125100
Ilderomi AR, Vojtek M, Vojteková J, Pham QB, Kuriqi A, Sepehri M (2022) Flood prioritization integrating picture fuzzy-analytic hierarchy and fuzzy-linear assignment model. Arab J Geosci 15(13):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10404-y
Jia H, Wang Z, Zhen X, Clar M, Yu SL (2017) China’s sponge city construction: A discussion on technical approaches. Front Environ Sci Eng 11:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-017-0984-9
Jiang J, Liang Q, Xia X, Hou J (2021) A coupled hydrodynamic and particle-tracking model for full-process simulation of nonpoint source pollutants. Environ Model Softw 136:104951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2020.104951
Li B, Hou J, Li D, Yang D, Han H, Bi X, Wang X, Hinkelmann R, Xia J (2021a) Application of LiDAR UAV for High-Resolution Flood Modelling. Water Resour Manag 35:1433–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02783-w
Li C, Peng C, Chiang PC, Cai Y, Wang X, Yang Z (2019) Mechanisms and applications of green infrastructure practices for stormwater control: A review. J Hydrol 568:626–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.10.074
Li J, Yao Y, Ma M, Li Y, Xia J, Gao X (2021b) A Multi-Index Evaluation System for Identifying the Optimal Configuration of LID Facilities in the Newly Built and Built-up Urban Areas. Water Resour Manag 35:2129–2147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02830-6
Liu Y, Cibin R, Bralts VF, Chaubey I, Bowling LC, Engel BA (2016) Optimal selection and placement of BMPs and LID practices with a rainfall-runoff model. Environ Model Softw 80:281–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2016.03.005
Qi W, Ma C, Xu H, Chen Z, Zhao K, Han H (2021) Low Impact Development Measures Spatial Arrangement for Urban Flood Mitigation: An Exploratory Optimal Framework based on Source Tracking. Water Resour Manag 35:3755–3770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02915-2
Vercruysse K, Dawson DA, Glenis V, Bertsch R, Wright N, Kilsby C (2019a) Developing spatial prioritization criteria for integrated urban flood management based on a source-to-impact flood analysis. J Hydrol 578:124038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124038
Vercruysse K, Dawson DA, Wright N (2019b) Interoperability: A conceptual framework to bridge the gap between multifunctional and multisystem urban flood management. J Flood Risk Manag 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12535
Wang X, Kingsland G, Poudel D, Fenech A (2019) Urban flood prediction under heavy precipitation. J Hydrol 577:123984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.123984
Xu T, Engel BA, Shi X, Leng L, Jia H, Yu SL, Liu Y (2018) Marginal-cost-based greedy strategy (MCGS): Fast and reliable optimization of low impact development (LID) layout. Sci Total Environ 640–641:570–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.358
Xu T, Jia H, Wang Z, Mao X, Xu C (2017) SWMM-based methodology for block-scale LID-BMPs planning based on site-scale multi-objective optimization: a case study in Tianjin. Front Environ Sci Eng 11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-017-0934-6
Yazdi J, Neyshabouri SS (2014) Identifying low impact development strategies for flood mitigation using a fuzzy-probabilistic approach. Environ Model Softw 60:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.06.004
Funding
This work is partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52079106), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0402704).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology: J. Hou, X. Wang; Writing-original draft preparation: X. Wang; Material preparation, collection and analysis: X. Wang, D. Li,; Supervision: B. Li, X. Gao, Y. Liu; Funding acquisition: J. Hou.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
The authors are indeed informed and agree to publish.
Competing Interests
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled “A coupled hydrodynamic and rainfall-tracking model for source-to-impact analysis in urban inundation”.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Hou, J., Li, D. et al. A Coupled Hydrodynamic and Rainfall-tracking Model for Source-to-impact Analysis in Urban Inundation. Water Resour Manage 36, 5581–5598 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03319-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03319-6