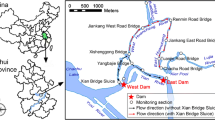
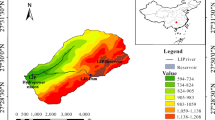
Abstract
This article investigates the hydrological response and ecological flow in the diversion area from the Hanjiang River to the Weihe River. Quantifies the impact of the inter-basin diversion project on the hydro-ecological environment of the downstream river. MIKE BASIN is initially utilized in this research to create the multi-year reservoir operating model of Sanhekou Reservoir. Then Indicators of Hydrologic Alteration (IHA) and Range of Variability Approach (RVA) are used to evaluate the change degree of hydrological indicators. Secondly, set seven different ecological flow process schemes considering ecological demand and inter-annual wetness and dryness variability. Finally, evaluate the optimization scheme by Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). According to the hydrological response results, suggestions are put forward from the perspective of engineering and non-engineering. The results show that the simulation results of the MIKE BASIN have a high degree of fitting with the design results, which verifies the rationality of the model. Under the design scheme, the overall hydrological change of the river is 72.91% and the hydrological response of the river is high changed. Scheme 6 can reduce the overall hydrological change to (56.63%) moderate change under the premise of less impact on economic benefits, and scheme 6 is the optimal scheme. The research results not only guarantee the ecological function of the river but also provide guidance and reference significance for the actual operation of the reservoir.















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The dataset on which this paper is based is too large to be retained or publicly archived with available resources. Documentation and data used to support this study are available from Geospatial Data Cloud and hydrological station data.
References
Al-Faraj FAM, Scholz M (2014) Assessment of temporal hydrologic anomalies coupled with drought impact for a transboundary river flow regime: The Diyala watershed case study. J Hydrol 517:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.05.021
Ashraf FB, Torabi HA, Marttila H et al (2016) Assessing impacts of climate change and river regulation on flow regimes in cold climate: A study of a pristine and a regulated river in the sub-arctic setting of Northern Europe. J Hydrol 542:410–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.09.016
Ban X, Shi CW, Guo H et al (2020) Impact of climate change and water conservancy projects on the hydrological situation downstream of Danjiangkou Dam. Adv Sci Technol Water Resour 40(04):1–7. https://doi.org/10.3880/j.issn.10067647.2020.04.001
Chang FX, Chen J, Zhang ZY (2007) Study on eco-environmental water demand in the upper Hanjiang River. J Yangtze River Sci Res Inst (06):18–21. https://doi.org/10.13476/j.cnki.nsbdqk.2008.01.006
Chen WD, Bao WM, Zhang Q et al (2015) Analysis of the impact of Jinjiang reservoir on downstream runoff based on IHA. J China Three Gorges Univ (Nat Sci) (37):27. https://doi.org/10.13393/j.cnki.issn.1672-948x.2015.03.006
Costigan KH, Daniels MD (2012) Damming the prairie: Human alteration of Great Plains river regimes. J Hydrol 1:444–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.04.008
Cui BL, Chang XL, Shi WY (2014) Abrupt changes of runoff and sediment load in the lower reaches of the yellow river. Water Resour 41:252–260. https://doi.org/10.1134/S009780781403004X
Cui T, Tian F, Yang T et al (2020) Development of a comprehensive framework for assessing the impacts of climate change and dam construction on flow regimes. J Hydrol 590(4):. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125358
Deng X, Li JM, Zeng HJ et al (2012) Analytic hierarchy process weight calculation method analysis and application research. J Math Pract Theory 42(07):93–100. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2012.07.012
Gao B, Li J, Wang X (2018) Analyzing changes in the flow regime of the yangtze river using the eco-flow metrics and IHA metrics. Water 10(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111552
Gao Y, Xie YH, Zou DS (2020) Hydrological changes of the three Jingjiang Estuary before and after the operation of the Three Gorges Project. Resour Enviro Yangtze Basin 29(02):479–487. https://doi.org/10.11870/cjlyzyyhj202002021
Guo WX, Li Y, Wang HX, Zha HF (2018) Based on the IHA-RVA method, the ecological hydrological situation evaluation of the downstream rivers of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin 27(09):2014–2021. https://doi.org/10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201809012
Han TG (2014) Problems and countermeasures for the conservation of aquatic biological resources in Xiaolangdi Reservoir. Henan Fisheries 98:11–12+24. CNKI: SUN: HNSC.0.2014–01–005
Hassaballah K, Jonoski A, Popescu I et al (2012) Model-based optimization of downstream impact during filling of a new reservoir: Case study of mandaya/roseires reservoirs on the Blue Nile River. Water Resour Manag 26(2):273–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9917-8
Hunt JD, Falchetta G, Zakeri B et al (2020) Hydropower impact on the river flow of a humid regional climate. Clim Change. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-020-02828-w
Ibraim F-C, Olavo P, Pierre G et al (2015) Effects of a diversion hydropower facility on the hydrological regime of the Correntes River, a tributary to the Pantanal floodplain, Brazil. J Hydrol 531(3):810–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.10.045
Kang L, Huang YY, Yang ZX et al (2010) Reservoir ecological operation model and its application. J Hydraul Eng 41(02):134–141. https://doi.org/10.13243/j.cnki.slxb.2010.02.008
Kumar KS, Galkate RV, Tiwari HL (2018) River basin modelling for Shipra River using MIKE BASIN. ISH J Hydraul Eng 27:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2018.1534219
Li MQ, Liang XJ, Xiao CL et al (2020) Evaluation of reservoir-induced hydrological alterations and ecological flow based on multi-indicators. Water 12(7):2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12072069
Li P (2013) Research on the water resources allocation scheme above Harbin section of Songhua River Basin based on MIKE BASIN. Jilin University, Jilin
Li ZY, Liu DF, Huang Q et al (2017) Research on the ecological flow of the Hanjiang River based on various hydrological methods. J North China Univ Water Resour Electr Power (Nat Sci Ed) 38(01):8–12. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-5634.2017.01.002
Liu JH, Guo J, Zhang FH et al (2021) Study of the stormwater resources utilization in the Xiamen City based on Mike Basin. J Water Resour Res 10(3):9. https://doi.org/10.12677/JWRR.2021.103035
Liu X (2019) Assessing the impact of reservoir parameters on runoff in the Yalong River Basin using the SWAT Model. Water 11(4):643. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040643
Lu SC (2016) Research on water resources management model of Shiyang River Basin based on MIKE BASIN. Beijing: Tsinghua University. CNKI: CDMD: 2.1017.817939. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD201801&filename=1017817939.nh
Meng FC, Li QJ, Shen CS et al (2014) Water resources allocation in reclaimed water irrigation districts based on MIKE Basin model. J Irrig Drain 33(6):10–13. https://doi.org/10.13522/j.cnki.ggps.2014.06.003
Natália CLS, Emili GB, Juliana DD et al (2018) Cumulative ecological effects of a Neotropical reservoir cascade across multiple assemblages. Hydrobiologia 819(1):77–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3630-z
Oscar B, Daniel B, Francisco MC et al (2013) Effects of flow regime alteration on fluvial habitats and riparian quality in a semiarid Mediterranean Basin. Ecol Ind 30:52–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.01.042
Qi LL, Zhang B, Lai QF et al (2018) Comparative analysis of water resources rational allocation schemes based on MIKE BASIN – taking Changji Economic Circle as an example. Water Resour Hydropower Eng 49(05):16–24. https://doi.org/10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2018.05.003
Richter BD, Baumgartner JV, Powell J et al (1996) A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Soc Conserv Biol 10(4):1163–1174. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1739.1996.10041163.x
Richter BD, Baumgartner JV, Wigington R et al (1997) How Much Water Does a River Need? Freshwater Biol 37(1):231–249. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2427.1997.00153.x
Romero GQ, Moi Dieison A, Nash Liam N (2021) Pervasive decline of subtropical aquatic insects over 20 years driven by water transparency, non-native fish and stoichiometric imbalance. Biol Lett 17(6):1. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2021.0137
Swapan T, Swades P (2019) Effects of damming on the hydrological regime of Punarbhaba river basin wetlands. Ecol Eng 135:61–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.05.014
Tharme RE (2003) A global perspective on environmental flow assessment: emerging trends in the development and application of environmental flow methodologies for rivers. Wiley Online Library 19(5–6):397–441. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.736
Xu ZX, Dong ZC, Zhou JK et al (2003) Montana method for ecological water demand calculation and its application. Water Resour Hydropower Eng 11:15–17. https://doi.org/10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2003.11.005
Yang J, Wang N, Chen Y (2013) Impact of cascade hydropower development on ecological environment. J Water Resour Water Eng 24(04):58–62. CNKI:SUN:XBSZ.0.2013-04-015
Zhang HM (2017) Influence of ankang reservoir construction on reservoir aquatic ecological environment.Haerbin. Northeast For Univ. CNKI:CDMD:1.1018.249619. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CDFDLAST2019&filename=1018249619.nh
Zhang XS, Shan JH (2019) Application of improved MIKE BASIN in the calculation of reservoir regulation. Yellow River 41(12):55–58+78. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2019.12.013
Funding
This research was funded by the following projects: National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.52179025). National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51879213). Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019T120933). Basic Research Plan of Natural Science of Shaanxi Province (2019JLM-52). Planning project of science and technology of water resources of Shaanxi (2017slkj-16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tao Bai: Term, Software, Resources, Writing–Original Draft, Visualization, Project administration, Funding acquisition. Xian-ge Sun: Investigation, Data Curation, Writing–Review & Editing. Jian Wei: Validation, Formal analysis. Lianzhou Wu: Conceptualization, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
There are no relevant waivers or approvals.
Consent to Participate
Authors consent to their participation in the entire review process.
Consent to Publication
Authors allow publication if the research is accepted.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, T., Sun, XG., Wei, J. et al. Hydrological Response and Ecological Flow Optimization in Water Diversion Area of Inter-basin Water Diversion Project. Water Resour Manage 36, 5839–5865 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03309-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03309-8