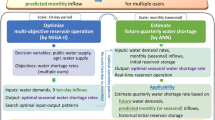
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to select the best modeling approach (simulation or optimization) for operation the water supply system using multi-criteria decision-making method. For this purpose, the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory-Earth System Models (GFDL-ESM2M) and the Model for Interdisciplinary Research on Climate-ESM (MIROC-ESM) models were selected to predict the changing trend of the climatic variables of rainfall and temperature, respectively. Then Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model and a decision support system tool named Cropwat were used to simulate water resources and consumption; and to model the behavior of the water supply system, the MODified SYMyld (MODSIM) (as simulator) and the modeling language and optimizer LINGO 18 (as optimizer) were used in the future time period (2026–2039) and the results were compared with the baseline period (1987–2000) for the Idoghmush reservoir (Iran). The results of MODSIM simulation model show that the indexes of reliability, vulnerability, reseiliency and flexibility in the future time period under the RCP2.6 emission scenario compared to the baseline time period decreased by 9%, decreased by 22%, increased by 4%, and decreased by 2%, respectively. The results of the LINGO 18 optimization model show that the reliability, vulnerability, resiliency and flexibility indexes in the future time period under the RCP2.6 emission scenario compared to the baseline time period decreased by 13%, decreased by 17%, increased by 14% and increased by 3%, respectively. Due to the different results obtained from optimization and simulation approaches for the study area, the Multi-Attributive Ideal-Real Comparative Analysis (MAIRCA) multi-criteria decision-making method was used to select a more appropriate approach. The results show that for water resources management planning, the simulation approach is given priority over the optimization approach due to its characteristics.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Authors have restrictions on sharing data.
References
Abdi-Dehkordi M, Bozorg-Haddad O, Chu X (2021) Development of a combined index to evaluate sustainability of water resources systemes. Water Resour Manage 35:2965–2985. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02880-w
Ashofteh P-S, Bozorg-Haddad O, Mariño M (2013) Climate change impact of on reservoir performance indexes in agricultural water supply. J Irrig Drain Eng 139(2):85–97. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000496
Ashofteh P-S, Golfam P, Loáiciga HA (2020) Evaluation of river water transfer alternatives with the TODIM multi-criteria decision-making method. Water Resour Manage 34:4847–4863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02694-2
Ashofteh P-S, Rajaei T, Golfam P (2017) Assessment of water resources development projects under conditions of climate change using efficiency indexes (EIs). Water Resour Manage 31(12):3723–3744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1701-y
Ashofteh P-S, Rajaei T, Golfam P, Chu X (2019) Applying climate adaptation strategies for improvement of management indexes a river reservoir irrigation system. Irrig Drain 68(3):420–432. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.2336
Ashrafi S, Kerachian R, Pourmoghim P, Behboudian M, Motlaghzadeh K (2022) Evaluating and improving sustainability of ecosystem services in river basins under climate change. Sci Total Environ 806:150702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150702
Ayağ Z, Özdemir RG (2009) A hybrid approach to concept selection through fuzzy analytic network process. Comput Ind Eng 56(1):368–379
Behboudian M, Kerachian R (2021) Evaluating the resilience of water resources management scenarios using the evidential reasoning approach: the Zarrinehrud river basin experience. J Environ Manage 284:112025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112025
Bertsekas D, Tseng P (1994) RELAX-IV: A Faster Version of the RELAX Code for Solving Minimum Cost Flow Problems. Report for NSF Grant CCR-9103804, Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge
Daba MH, You S (2020) Assessment of climate change impacts on river flow regimes in the upstream of Awash Basin Ethiopia: Based on IPCC Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) climate change scenarios. Hydrology 7(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7040098
Dau QV, Kuntiyawichai K, Adeloye AJ (2021) Future changes in water availability due to climate change projections for Houng basin, Vietnam. Environ Process 8:77–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-020-00475-y
Fadaeizadeh K, Shourian M (2019) Determination of the optimal water river basin-wide agricultural water demand quantities meeting satisfactory reliability levels. Water Resour Manage 33:2665–2676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02242-7
FAO (2009) Cropwat 8.0 for windows user guide. Rome. Italy
Forman E, Peniwati K (1998) Aggregating individual judgments and priorities with the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 108(1):165–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(97)00244-0
Golfam P, Ashofteh PS, Loáiciga HA (2019a) Evaluation of the VIKOR and FOWA multi-criteria decision making methods for climate-change adaptation of agricultural water supply. J Water Resour Manag 33(8):2867–2884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02274-z
Golfam P, Ashofteh PS, Rajaee T, Chu X (2019b) Prioritization of water allocation for adaptation to climate change using multi-criteria decision making (MCDM). J Water Resour Manag 33(10):3401–3416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02307-7
Hadian S, Shahiri Tabarestani E, Pham QB (2022) Multi Attributive Ideal-Real Comparative Analysis (MAIRCA) method for evaluating flood susceptibility in a temperate Mediterranean climate. Hydrol Sci J. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2022.2027949
Hashimoto T, Stedinger JR, Loucks DP (1982) Reliability, resiliency and vulnerability criteria for water resources system performance evaluation. Water Resour Res 18(1):14–20. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR018i001p00014
He L, Shao F, Ren L (2020) Identifying optimal groundwater remediation strategies through a simulation-based PROMETHEE-TOPSIS approach: an application to a naphthalene-contaminated site. J Human Ecol Risk Assess: Int J 26:1550–1568. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1591267
Jamshidpey A, Shoorian M (2021) Crop pattern planning and irrigation water allocation compatiable with climate change using a coupled network flow programming-heuristic optimization model. Hydrol Sci J 66(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2020.1844889
Kuang H, Kilgur M, Hipel WK (2014) Grey-based PROMETHEE II with application to evaluation of source water protection strategies. J Inform Sci 294:376–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.09.035
Labadie J (2006) MODSIM: Decision Support System for Integrated River Basin Management”, International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software, 3rd International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software - Burlington, Vermont, USA - July 2006. https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/iemssconference/2006/all/242
Loucks DP (1997) Quantifying trends in system sustainability. Hydrol Sci J 42(4):513–530
Mandal U, Sena DR, Dhar A, Panda SN, Adhikary PP, Mishra PK (2021) Assessment of climate change and its impact on hydrologycal regimes biomass yield of a tropical river basin. Ecol Ind 126:107646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107646
Marengo JA, Chou SC, Kay G, Alves LM, Pescuero JF, Soares WR, Santos DC, Lyra AA, Sueiro G, Betts R, Chagas DJ, Gomes JL, Boustamante JF, Tavares P (2012) Development of regional future climate change scenarios in South America using the Eta CPTEC/HadCM3 climate change projections: climatology and regional analyses for the Amazon, Sao Francisco and Parana river basins. Clim Dyn 38:1829–1848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00832-011-1155-5
MATLAB (2022) “MATLAB software toolbox”, version 2022b
Nabeel A, Athar H (2020) Stochastic projection of precipitation and wet and dry spells over Pakistan using IPCC AR5 based AOGCMS. Atmos Res 234:104742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104742
Pamacur D, Vasin L, Lukovac V (2014) Selection of railway level crossing for investing in security equipment using hybrid Dematel-MAICRA model. XVI International Scientific-Expert Conference on Railways, Serbia, pp 89–92
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Info Sci 11(5):341–356
Pourmoghim P, Behboudian M, Kerachian R (2022) An uncertainty-based framework for evaluating and improving the long-term resilience of lakes under anthropogenic droughts. J Environ Manage 301:113900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113900
Rani S, Sreekesh S (2019) Evaluating the responses of streamflow under future climate change scenarios in a Western Indian Himalaya watershed. Environ Process. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-019-00361-2
Saaty TL (1977) A scaling method for priorities hierarchical structures. J Math Psychol 15(3):234–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2496(77)90033-5
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process. McGraw-Hill, New York
Shenava N, Shourian M (2018) Optimal reservoir operation with water supply enrichment and flood mitigation objectives using an optimization and simulation approach. Water Resour Manage 32:4393–4407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2068-4
Sherafatpour Z, Roozbahani A, Hasani Y (2019) Agricultural water allocation by integration of hydro-economic modeling with Bayesian Networks and Random Forest approaches. Water Resour Manage 33:2277–2299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02240-9
Theochari A-P, Feloni E, Bournas A, Batles E (2021) Hydrometeorological - hydrometric station network design using multicriteria decision analysis and GIS techniques. Environ Process 8:1099–1119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-021-00527-x
Velasquez M, Hester PT (2013) An analysis of multi-criteria decision making methods. J Int J Oper Res 10(2):56–66
Zarghami M, Fotookian MR, Safari N, Aslanzadeh A (2016) Reservoir operation using system dynamics under climate change impacts: a case study of Yamchi reservoir, Iran. Arab J Geosci 9:678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2676-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.-S. Mortezaeipooya developed the theory and performed the computations. P. Golfam verified the analytical methods. P.-S. Ashofteh and P. Golfam encouraged S.-S. Mortezaeipooya to investigate a specific aspect. P.-S. Ashofteh supervised the findings of this work, and P. Golfam helped supervise the project. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript. S.-S. Mortezaeipooya wrote the manuscript with support from P.-S. Ashofteh and P. Golfam. P.-S. Ashofteh conceived the original idea.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The paper is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. All authors have been personally and actively involved in substantial work leading to the paper, and will take public responsibility for its content.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to Publish
The participant has consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mortezaeipooya, SS., Ashofteh, PS. & Golfam, P. Selecting the Best Approach to Modeling the Performance of Water Supply System Using the Combination of Rough Set Theory with Multi-Criteria Decision Making. Water Resour Manage 36, 3129–3152 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03193-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03193-2