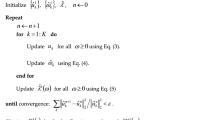Abstract
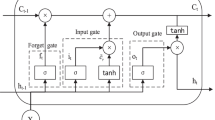
Daily inflow forecasts provide important decision support for the operations and management of reservoirs. Accurate and reliable forecasting plays an important role in the optimal management of water resources. Numerous studies have shown that decomposition integration models have good prediction capacity. Considering the nonlinearity and unsteady state of daily incoming flow data, a hybrid model of adaptive variational mode decomposition (VMD) and bidirectional long- and short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) based on energy entropy was developed for daily inflow forecast. The model was analyzed using the mean absolute error (MAE), the root means square error (RMSE), Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NSE), and correlation coefficient (r). A historical daily inflow series of the Baozhusi Hydropower Station, China, is investigated by the proposed VMD-BiLSTM with hybrid models. For comparison, BP, GRNN, ELMAN, SVR, LSTM, Bi-LSTM, EMD-LSTM, and VMD-LSTM, were adopted and analyzed for evaluation and analyzed. We found that the proposed model, with MAE = 38.965, RMSE = 64.783, and NSE = 95.7%, was superior to the other models. Therefore, the hybrid model is robust and efficient for forecasting highly nonstationary and nonlinear streamflow. It can be used as the preferred data-driven tool to predict the daily inflow flow, which can ensure the safe operation of hydropower stations in reservoirs. As an interdisciplinary field spanning both machine learning and hydrology, daily inflow forecasting can become an important breakthrough in the application of deep learning to hydrology.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
Data sources for this study are publicly available and data used for analyses are available from the authors upon request.
References
Abdelhameed AM, Daoud HG, Bayoumi M (2018) Deep convolutional bidirectional lstm recurrent neural network for epileptic seizure detection (139–143): IEEE. (Reprinted. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/NEWCAS.2018.8585542
Ahani A, Shourian M, Rahimi RP (2018) Performance assessment of the linear, nonlinear and nonparametric data-driven models in river flow forecasting. Water Resour Manag 32(2):383–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1792-5
Ali M, Khan A, Rehman NU (2018) Hybrid multiscale wind speed forecasting based on variational mode decomposition. Int T Eelectr Energy 28(1) e2466. https://doi.org/10.1002/etep.2466
Bai Y, Chen Z, Xie J, Li C (2016) Daily reservoir inflow forecasting using multiscale deep feature learning with hybrid models. J Hydrol 532:193–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.11.011
Bao H, Wang L, Li Z, Zhao L, Zhang G (2010) Hydrological daily rainfall-runoff simulation with BTOPMC model and comparison with Xin’anjiang model. Water Sci Eng 3(02):121–131
Castellano-Méndez M, González-Manteiga W, Febrero-Bande M, Manuel Prada-Sánchez J, Lozano-Calderón R (2004) Modeling of the monthly and daily behavior of the runoff of the Dallas river using Box-Jenkins and neural networks methods. J Hydrol 296(1–4):38–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.03.011
Chen L, Zhou S, Ma J, Xu M (2021) Fast kernel k-means clustering using incomplete Cholesky factorization. Appl Math Comput 402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2021.126037
Dang-Quang N, Yoo M (2021) Deep learning-based autoscaling using bidirectional long short-term memory for kubernetes. Appl Sci 11(9):3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093835
Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D (2014) Variational mode decomposition. IEEE T Signal Process 62(3):531–544. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675
Gao S, Huang Y, Zhang S, Han J, Wang G, Zhang M, Lin Q (2020) Short-term runoff prediction with GRU and LSTM networks without requiring time step optimization during sample generation. J Hydrol 589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125188
Genç O, Dağ A (2016) A machine learning-based approach to predict the velocity profiles in small streams. Water Resour Manag 30(1):43–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1123-7
Ghassemi Tari F, Hashemi Z (2018) Prioritized K-mean clustering hybrid GA for discounted fixed charge transportation problems. ComputInd Eng 126:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2018.09.019
Ghoddusi H, Creamer GG, Rafizadeh N (2019) Machine learning in energy economics and finance: A review. Energ Econ 81:709–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2019.05.006
Hadi SJ, Tombul M (2018) Forecasting daily streamflow for basins with different physical characteristics through data-driven methods. Water Resour Manag 32(10):3405–3422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-1998-1
He X, Luo J, Zuo G, Xie J (2019) Daily runoff forecasting using a hybrid model based on variational mode decomposition and deep neural networks. Water Resour manag 33(4):1571–1590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-2183-x
Hu A, Zhang K (2018) Using bidirectional long short-term memory mMethod for the height of F2 peak forecasting from Ionosonde measurements in the Australian region. Remote Sens-Basel 10(10):1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101658
Huang A, Vega-Westhoff B, Sriver RL (2019) Analyzing El Niño-Southern oscillation predictability using long-short-term-memory models. Earth Space Sci 6(2):212–221. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018EA000423
Jothiprakash V, Kote AS (2011) Effect of pruning and smoothing while using M5 model tree technique for reservoir inflow prediction. J Hydrol Eng 16(7):563–574. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000342
Khullar S, Singh N (2021) Water quality assessment of a river using deep learning Bi-LSTM methodology: forecasting and validation. Environ Sci Pollut R. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13875-w
Kisi O, Latifoğlu L, Latifoğlu F (2014) Investigation of empirical mode decomposition in forecasting of hydrological time series. Water Resour Manag 28(12):4045–4057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0726-8
Lin G, Chen G, Huang P, Chou Y (2009) Support vector machine-based models for hourly reservoir inflow forecasting during typhoon-warning periods. J Hydrol 372(1–4):17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.03.032
Lipton ZC, Berkowitz J, Elkan C (2015) A Critical Review of Recurrent Neural Networks for Sequence Learning
Long J, Wang X, Dai D, Tian M, Zhu G, Zhang J (2017) Denoising of UHF PD signals based on optimized VMD and wavelet transform. IET Sci Meas Technol 11(6):753–760. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-smt.2016.0510
Maheswaran R, Khosa R (2013) Wavelets-based non-linear model for real-time daily flow forecasting in Krishna River. J Hydroinform 15(3):1022–1041. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2013.135
Mohammadi K, Eslami HR, Kahawita R (2006) Parameter estimation of an ARMA model for river flow forecasting using goal programming. J Hydrol 331(1–2):293–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.05.017
Packard NH, Crutchfield JP, Farmer JD, Shaw RS (1980) Geometry from a time series. Phys Rev Lett 45(9):712–716. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.45.712
Peng L, Liu S, Liu R, Wang L (2018) Effective long short-term memory with differential evolution algorithm for electricity price prediction. Energy 162:1301–1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.05.052
Peng T, Zhang C, Zhou J, Nazir MS (2021) An integrated framework of Bi-directional long-short term memory (BiLSTM) based on sine cosine algorithm for hourly solar radiation forecasting. Energy 221:119887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.119887
Qi Y, Zhou Z, Yang L, Quan Y, Miao Q (2019) A decomposition-ensemble learning model based on LSTM neural network for daily reservoir inflow forecasting. Water resour Manag 33(12):4123–4139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02345-1
Qian Z, Pei Y, Zareipour H, Chen N (2019) A review and discussion of decomposition-based hybrid models for wind energy forecasting applications. Appl Energ 235:939–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.10.080
Ramaswamy V, Saleh F (2020) Ensemble based forecasting and optimization framework to optimize releases from water supply reservoirs for flood control. Water Resour Manag 34(3):989–1004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02481-8
Rezaie-Balf M, Kim S, Fallah H, Alaghmand S (2019) Daily river flow forecasting using ensemble empirical mode decomposition-based heuristic regression models: Application on the perennial rivers in Iran and South Korea. J Hydrol 572:470–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.03.046
Rockafellar RT (1973) A dual approach to solving nonlinear programming problems by unconstrained optimization. Math Program 5(1):354–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01580138
Santra AS, Lin J (2019) Integrating long short-term memory and genetic algorithm for short-term load forecasting. Energies 12(11):2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112040
Tan Q, Lei X, Wang X, Wang H, Wen X, Ji Y, Kang A (2018) An adaptive middle and long-term runoff forecast model using the EEMD-ANN hybrid approach. J Hydrol 567:767–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.01.015
Wang H, Yu L, Tian S, Peng Y, Pei X (2019) Bidirectional LSTM Malicious webpages detection algorithm based on convolutional neural network and independent recurrent neural network. Appl Intell 49(8):3016–3026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-019-01433-4
Xu B, Zhou F, Li H, Yan B, Liu Y (2019) Early fault feature extraction of bearings based on Teager energy operator and optimal VMD. Isa T 86:249–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2018.11.010
Yaseen ZM, El-shafie A, Jaafar O, Afan HA, Sayl KN (2015) Artificial intelligence-based models for stream-flow forecasting: 2000–2015. J Hydrol 530:829–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.10.038
Yin J, Deng Z, Ines AVM, Wu J, Rasu E (2020) Forecast of short-term daily reference evapotranspiration under limited meteorological variables using a hybrid bi-directional long short-term memory model (Bi-LSTM). Agr Water Manage 242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106386
Zhang J, Zhu Y, Zhang X, Ye M, Yang J (2018) Developing a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) based model for predicting water table depth in agricultural areas. J Hydrol 561:918–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.04.065
Zuo G, Luo J, Wang N, Lian Y, He X (2020) Decomposition ensemble model based on variational mode decomposition and long short-term memory for streamflow forecasting. J Hydrol 585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124776
Funding
the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFB0905204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: FuGang LI. Methodology: FuGang LI. Writing—Original Draft Preparation, FuGang LI and WeiBin Huang. Writing–Review & Editing, ShiJun Chen, and GuangWen Ma. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LI, F., MA, G., CHEN, S. et al. An Ensemble Modeling Approach to Forecast Daily Reservoir Inflow Using Bidirectional Long- and Short-Term Memory (Bi-LSTM), Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD), and Energy Entropy Method. Water Resour Manage 35, 2941–2963 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02879-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02879-3