Abstract
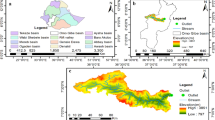
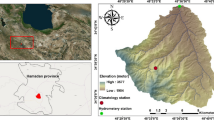
To explore the applicability of HEC-HMS and its parameter regionalization in small ungauged watersheds in hilly areas, this paper takes hydrological divisions III and IV of Henan Province as the research area. The HEC-HMS model is applied to three typical small watersheds in Luanchuan, Gaocheng and Xiahecun. On the basis of verifying the validity of the model, the regression relationships between model parameters and underlying surface characteristics are established and verified in the Zhongtang small watershed. The results show that the qualified rates of runoff depth, flood peak flow, peak occurrence time and NSE in flood simulation are higher than 75%, and the accuracy reaches the grade B level regardless of the HEC-HMS model test or the parameter regionalization method verification. In summary, the HEC-HMS model can be applied to simulate the rainfall-runoff process of small watersheds in hilly areas, and the parameter regionalization method can effectively deduce the model parameters of HEC-HMS for small ungauged watersheds in hilly areas.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data used in the study are available from the corresponding author by request.
References
Athira P, Sudheer K, Cibin R, Chaubey I (2016) Predictions in ungauged basins: an approach for regionalization of hydrological models considering the probability distribution of model parameters. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 30(4):1131–1149
Beck HE, van Dijk AIJM, de Roo A, Miralles DG, McVicar TR, Schellekens J, Bruijnzeel LA (2016) Global-scale regionalization of hydrologic model parameters. Water Resour Res 52(5):3599–3622
Cao B (2015) The Parameters regionalization research of the excess storage and excess infiltration simultaneously model. Zhengzhou University
Cislaghi A, Masseroni D, Massari C, Camici S, Brocca L (2020) Combining a rainfall-runoff model and a regionalization approach for flood and water resource assessment in the western Po Valley, Italy. Hydrol Sci J 65(3):348–370
Goswami M, O’Connor KM, Bhattarai KP (2007) Development of regionalisation procedures using a multi-model approach for flow simulation in an ungauged catchment. J Hydrol 333(2–4):517–531
Joo J, Kjeldsen T, Kim HJ, Lee H (2014) A comparison of two event-based flood models (ReFH-rainfall runoff model and HEC-HMS) at two Korean catchments, Bukil and Jeungpyeong. KSCE J Civ Eng 18(1):330–343
Oudin L, Andréassian V, Perrin C, Michel C, Nicolas LM (2008) Spatial proximity, physical similarity, regression and ungauged catchments: A comparison of regionalization approaches based on 913 French catchments. Water Resour Res 44(3)
Seckin N, Guven A (2012) Estimation of Peak Flood Discharges at Ungauged Sites Across Turkey. Water Resour Manage 26(9):2569–2581
Swain JB, Patra KC (2017) Streamflow estimation in ungauged catchments using regionalization techniques. J Hydrol 554
Tang Y, Leon AS, Kavvas ML (2020) Impact of size and location of wetlands on watershed-scale flood control. Water Resour Manage 34(5):1693–1707
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (2015) Hydrologic Engineering Center, Hydrologic Modelling System HEC-HMS. User’s Manual (version 4.1, July 2015)
U.S. Dept. Agriculture Soil Conservation Service (1972) National Engineering Handbook, Section 4, Hydrology
U.S. Soil Conservation Service (1986) Urban Hydrology for Small Watersheds (Technical Release 55). US Department of Agriculture
Verma AK, Jha MK, Mahana RK (2010) Evaluation of HEC-HMS and WEPP for simulating watershed runoff using remote sensing and geographical information system. Paddy Water Environ, 8(2):131–144
Wagener T, Wheater HS (2006) Parameter estimation and regionalization for continuous rainfall-runoff models including uncertainty. J Hydrol 320:132–154
Wagener T, Sivapalan M, Troch P et al (2007) Catchment classification and hydrological similarity. Geogr Compass 1(4):901–931
Yang M (2007) The runoff and conflux simulation research in watershed based on GIS. Taiyuan University of Technology
Yao C, Qiu ZY, Li ZJ, Hu WD, Xu J (2019) Parameter regionalization study and application of API model and Xin’ anjiang model. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences) 47(03):189–194
Yazdi J, Moghaddam MS, Saghafian B (2018) Optimal design of check dams in mountainous watersheds for flood mitigation. Water Resour Manag 32(14)
Zamoum S, Souag-Gamane D (2019) Monthly streamflow estimation in ungauged catchments of northern Algeria using regionalization of conceptual model parameters. Arab J Geosci 12(11)
Acknowledgments
We thank the Scientific and Technological Project of Henan Province (192102310228) and Think Tank Research Projects of Zhengzhou Collaborative Innovation Major Funding (Zhengzhou University) (Grant No. 2019ZZXT01) for their support.
Funding
This research was supported by the Scientific and Technological Project of Henan Province (192102310228) and Think Tank Research Projects of Zhengzhou Collaborative Innovation Major Funding (Zhengzhou University) (Grant No. 2019ZZXT01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xu Cheng: Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Writing-Original Draft, Writing-Review & Editing; Xixia Ma: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing-Original Draft, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition; Wusen Wang: Writing-Review & Editing, Formal analysis, Visualization, Investigation, Resources; Yao Xiao: Resources; Qianli Wang: Data Curation; Xinxin Liu: Data Curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Relevant research content in this paper was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee.
Consent to Participate
All of the authors consent to participate in the relevant research content in this paper.
Consent to Publish
All of the authors consent to publish the paper, and it has not been published previously nor is it being considered by any other peer-reviewed journal.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, X., Ma, X., Wang, W. et al. Application of HEC-HMS Parameter Regionalization in Small Watershed of Hilly Area. Water Resour Manage 35, 1961–1976 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02823-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02823-5