Abstract
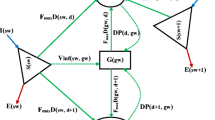
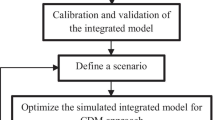
The use of irrigation water extracted from aquifers with submerged pumps is essential to ensure agricultural production mainly in water-scarce regions.. However, the use of the water source requires of a considerable energy consumption by water user associations (WUAs) being key factor to consider due to their high share of total management, operation, and maintenance costs. In this work, a new tool (MOPWE, model to optimize water extraction) to optimize the water and energy use of wells in WUAs was developed. MOPWE was applied to a real WUA located in Castilla-La Mancha region (southeast of Spain). This WUA utilizes groundwater as water source that is extracted from several different wells of different characteristics (discharges, water table levels, efficiency, variable speed drives…).. Therefore, these kind of WUAs must decide not only which well to activate at a certain time but also at what frequency the variable-speed drive should run the pump. With the aim of aiding decision-making in groundwater abstraction, a new management model (MOPWE), which is based on multi-objective genetic algorithms and is implemented in MATLAB®. This model helps determine the optimal daily management of a WUA with multiple underground supply sources and focuses on the management of wells while considering the water reservoir level. After 18,000 generations of the genetic algorithm, the pareto front was obtained with the best WUA managements achieving a water and energy savings of 25% and 54%, respectively. At the end of the irrigation season, the optimal total energy consumption per unit of water applied was 38% lower than that achieved by the current management. Results showed that a more realistic approach can be implemented when several water supplies operate jointly under a collaborative principle.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carrión F, Sanchez-Vizcaino J, Corcoles JI, Tarjuelo JM, Moreno MA (2016) Optimization of groundwater abstraction system and distribution pipe in pressurized irrigation systems for minimum cost. Irrig Sci 34:145–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-016-0489-5
Córcoles J, Gonzalez Perea R, Izquiel A, Moreno M (2019) Decision support system tool to reduce the energy consumption of water abstraction from aquifers for irrigation. Water 11:323. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020323
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6:182–197
Fernández García I, Moreno MA, Rodríguez Díaz JA (2014) Optimum pumping station management for irrigation networks sectoring: case of Bembezar MI (Spain). Agric Water Manag 144:150–158
González Perea R, Camacho Poyato E, Montesinos P, Rodríguez Díaz JA (2016) Optimization of irrigation scheduling using soil water balance and genetic algorithms. Water Resour Manag 30:2815–2830
Jury WA, Vaux HJ (2007) The emerging global water crisis: managing scarcity and conflict between water users. Adv Agron 95:1–76
Khadra R, Moreno MA, Awada H, Lamaddalena N (2016) Energy and hydraulic performance-based Management of Large-Scale Pressurized Irrigation Systems. Water Resour Manag 30:3493–3506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1365-z
Li Z, Quan J, Li XY, Wu XC, Wu HW, Li YT, Li GY (2016) Establishing a model of conjunctive regulation of surface water and groundwater in the arid regions. Agric Water Manag 174:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.04.030
Lima FA, Martínez-Romero A, Tarjuelo JM, Córcoles JI (2018) Model for management of an on-demand irrigation network based on irrigation scheduling of crops to minimize energy use (part I): model development. Agric Water Manag 210:49–58
Moreno MA, Córcoles JI, Moraleda DA, Martinez A, Tarjuelo JM (2010a) Optimization of underground water pumping. J Irrig Drain Eng 136:414–420. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000229
Moreno MA, Ortega JF, Córcoles JI, Martínez A, Tarjuelo JM (2010b) Energy analysis of irrigation delivery systems: monitoring and evaluation of proposed measures for improving energy efficiency. Irrig Sci 28:445–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-010-0206-8
Zeinali M, Azari A, Heidari MM (2020) Multiobjective Optimization for Water Resource Management in Low-Flow Areas Based on a Coupled Surface Water-Groundwater Model. J Water Resour Plan Manag 146. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001189
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge to the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science (MEC) for funding the AGL2017-82927-C3-2-R (Co-funded by FEDER) and to the Regional Government of Castilla-La Mancha for funding the project SBPLY-19-18501-000080. We would also like to acknowledge to the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities for funding the Juan de la Cierva-Formacion grant to Rafael González Perea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perea, R.G., Moreno, M.Á., da Silva Baptista, V.B. et al. Decision Support System Based on Genetic Algorithms to Optimize the Daily Management of Water Abstraction from Multiple Groundwater Supply Sources. Water Resour Manage 34, 4739–4755 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02687-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02687-1