Abstract
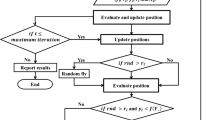
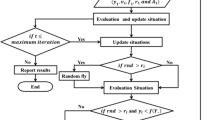
Water resources scarcity and competition among stakeholders in water allocation always highlights the optimal operation of water resources. This research examines the operation of a multi-purpose water reservoir aiming at providing agricultural, urban, industrial and environmental demands. A new evolutionary Hybrid Algorithm (integrating Bat Algorithm (BA) and Particle Swarm Algorithm (PSA)) first specified total monthly water release to meet the total monthly needs (agricultural, urban, industrial and environmental) to operate the optimal reservoir. The new Hybrid Algorithm (HA) helps BA and PSA to increase the convergence rate and achieve an optimal absolute response by eliminating the weak responses of one algorithm and substituting the strong responses of the other algorithm. Released water was then allocated to different demands based on the proportional method in the Game Theory (GT). The optimal operation of Shahid Dam Reservoir in Fars, southern Iran is the case study of this research, which has been a serious challenge for decision makers to meet various water demands. The convergence rate of HA was more than that of BA and PSA based on the results. Moreover, the HA with volumetric reliability of 0.92, 0.89, 0.79 and 0.75 was used to meet the urban, environmental, agricultural and industrial demands; while, the volumetric reliability indices of BA and PSA were less than the HA. Also, the mean water release values by the HA met different demands much better than BA and PSA in a period of five years.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhami M, Sadeghi SH, Sheikhmohammady M (2018) Making competent land use policy using a co-management framework. Land Use Policy 72:171–180
Afshar MH, Hajiabadi R (2018) A novel parallel cellular automata algorithm for multi-objective reservoir operation optimization. Water Resour Manag 32:785–803
Ahmad I, Zhang F, Liu J, Anjum MN, Zaman M, Tayyab M, Waseem M, Farid HU (2018) A linear bi-level multi-objective program for optimal allocation of water resources. PLoS One 13(2):e0192294
Anand J, Gosain AK, Khosa R (2018) Optimisation of multipurpose reservoir operation by coupling SWAT and genetic algorithm for optimal operating policy (Case study: Ganga River basin). Doctoral Dissertation, Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi
Bertoni F, Giuliani M, Castelletti A (2018) An inverse nested approach to optimize planning and operation of water reservoir systems. Proceedings of the 20th EGU General Assembly, EGU2018, Vienna
Bolouri-Yazdeli Y, Haddad OB, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Mariño MA (2014) Evaluation of real-time operation rules in reservoir systems operation. Water Resour Manag 28(3):715–729
Bozorg-Haddad O, Karimirad I, Seifollahi-Aghmiuni S, Loáiciga HA (2014) Development and application of the bat algorithm for optimizing the operation of reservoir systems. J Water Resour Plan Manag 141(8):04014097
Bozorg-Haddad O, Athari E, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Loáiciga HA (2018a) Real-time water allocation policies calculated with bankruptcy games and genetic programing. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 18(2):430–449
Bozorg-Haddad O, Athari E, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Bahrami M, Loáiciga HA (2018b) Allocation of reservoir releases under drought conditions: a conflict-resolution approach. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Water Management:1–26
Daddi T, Todaro NM, De Giacomo MR, Frey M (2018) A systematic review of the use of organization and management theories in climate change studies. Bus Strateg Environ 27:456–474
Dinar A, Hogarth M (2015) Game theory and water resources: critical review of its contributions, progress and remaining challenges. Foundations and Trends in Microeconomics 11(1–2):1–139
Du Y, Wang Z, Liu G, Chen X, Yuan H, Wei Y, Li F (2018) A cooperative game approach for coordinating multi-microgrid operation within distribution systems. Appl Energy 222:383–395
Ehteram M, Karami H, Farzin S (2018a) Reservoir optimization for energy production using a new evolutionary algorithm based on multi-criteria decision-making models. Water Resour Manag 32(7):2539–2560
Ehteram M, Karami H, Farzin S (2018b) Reducing irrigation deficiencies based optimizing model for multi-reservoir systems utilizing spider monkey algorithm. Water Resour Manag 32(7):2315–2334
Fallah-Mehdipour E, Haddad OB, Mariño MA (2012) Real-time operation of reservoir system by genetic programming. Water Resour Manag 26(14):4091–4103
Faria VA, de Queiroz AR, Lima LM, Lima JW (2018) Cooperative game theory and last addition method in the allocation of firm energy rights. Appl Energy 226:905–915
Game ET, Bremer LL, Calvache A, Moreno PH, Vargas A, Rivera B, Rodriguez LM (2018) Fuzzy models to inform social and environmental indicator selection for conservation impact monitoring. Conserv Lett 11(1):e12338
Garousi-Nejad I, Bozorg-Haddad O, Loáiciga HA, Mariño MA (2016) Application of the firefly algorithm to optimal operation of reservoirs with the purpose of irrigation supply and hydropower production. J Irrig Drain Eng 142(10):04016041
Han C, Zheng B, Qin Y, Ma Y, Yang C, Liu Z et al (2018) Impact of upstream river inputs and reservoir operation on phosphorus fractions in water-particulate phases in the three gorges reservoir. Sci Total Environ 610:1546–1556
Hashimoto T, Stedinger JR, Loucks DP (1982) Reliability, resiliency and vulnerability criteria for water resources system performance evaluation. Water Resour Res 18(1):14–20
He Y, Yang J, Chen X, Lin K, Zheng Y, Wang Z (2018) A two-stage approach to basin-scale water demand prediction. Water Resour Manag 32(2):401–416
Heydari M, Othman F, Qaderi K (2015) Developing optimal reservoir operation for multiple and multipurpose reservoirs using mathematical programming. Math Probl Eng 2015(4):1–11
Jiang J, Liu X (2018) Multi-objective Stackelberg game model for water supply networks against interdictions with incomplete information. Eur J Oper Res 266(3):920–933
Kruitwagen L, Madani K, Caldecott B, Workman MH (2017) Game theory and corporate governance: conditions for effective stewardship of companies exposed to climate change risks. Journal of Sustainable Finance and Investment 7(1):14–36
Madani K, Hooshyar M (2014) A game theory–reinforcement learning (GT–RL) method to develop optimal operation policies for multi-operator reservoir systems. J Hydrol 519:732–742
Madani K, Pierce TW, Mirchi A (2017) Serious games on environmental management. Sustain Cities Soc 29:1–11
Mochizuki J, Magnuszewski P, Linnerooth-Bayer J (2018) Games for aiding stakeholder deliberation on Nexus policy issues. In: Managing Water, Soil and Waste Resources to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals, Springer, pp. 93-124
Moradi S, Mohammadi Limaei S (2018) Multi-objective game theory model and fuzzy programing approach for sustainable watershed management. Land Use Policy 71:363–371
Ostadrahimi L, Mariño MA, Afshar A (2012) Multi-reservoir operation rules: multi-swarm PSO-based optimization approach. Water Resour Manag 26(2):407–427
Skardi MJE, Afshar A, Saadatpour M, Solis SS (2015) Hybrid ACO–ANN-based multi-objective simulation–optimization model for pollutant load control at basin scale. Environ Model Assess 20(1):29–39
Steeger G, Barroso LA, Rebennack S (2014) Optimal bidding strategies for hydro-electric producers: a literature survey. IEEE Trans Power Syst 29(4):1758–1766
Shen Z, Liu P, Ming B, Feng M, Zhang X, Li H, Xie A (2018) Deriving optimal operating rules of a multi-reservoir system considering incremental multi-agent benefit allocation. Water Resour Manag 32(11):3629–3645
Taghian M, Rosbjerg D, Haghighi A, Madsen H (2013) Optimization of conventional rule curves coupled with hedging rules for reservoir operation. J Water Resour Plan Manag 140(5):693–698
Wu Y, Chen J (2013) Estimating irrigation water demand using an improved method and optimizing reservoir operation for water supply and hydropower generation: a case study of the Xinfengjiang reservoir in southern China. Agric Water Manag 116:110–121
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by Iran National Science Foundation (No. 96003777). This article has been extracted from the project of Development of Cooperative Game Theory Applications in Water Resources Conflict Resolution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarei, A., Mousavi, SF., Eshaghi Gordji, M. et al. Optimal Reservoir Operation Using Bat and Particle Swarm Algorithm and Game Theory Based on Optimal Water Allocation among Consumers. Water Resour Manage 33, 3071–3093 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02286-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02286-9