Abstract
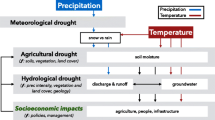
Climate change and human activity are the two major drivers that can alter hydrological cycle processes and influence the characteristics of hydrological drought in river basins. The present study selects the Wei River Basin (WRB) as a case study region in which to assess the impacts of climate change and human activity on hydrological drought based on the Standardized Runoff Index (SRI) on different time scales. The Generalized Additive Models in Location, Scale and Shape (GAMLSS) are used to construct a time-dependent SRI (SRIvar) considering the non-stationarity of runoff series under changing environmental conditions. The results indicate that the SRIvar is more robust and reliable than the traditional SRI. We also determine that different driving factors can influence the hydrological drought evolution on different time scales. On shorter time scales, the effects of human activity on hydrological drought are stronger than those of climate change; on longer time scales, climate change is considered to be the dominant factor. The results presented in this study are beneficial for providing a reference for hydrological drought analysis by considering non-stationarity as well as investigating how hydrological drought responds to climate change and human activity on various time scales, thereby providing scientific information for drought forecasting and water resources management over different time scales under non-stationary conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control 19(6):716–723. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705
van Buuren S, Fredriks M (2001) Worm plot: a simple diagnostic device for modelling growth reference curves. Stat Med 20(8):1259–1277. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.746
Chang JX, Wang YM, Istanbulluoglu E et al (2015) Impact of climate change and human activities on runoff in the Weihe River basin, China. Quat Int 380:169–179
Dai AG (2011) Drought under global warming: a review. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Clim Chang 2(1):45–65. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcc.81
Dai AG (2013) Increasing drought under global warming in observations and models. Nat Clim Chang 3(2):171–171. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1811
Duan QY, Sorooshian S, Gupta V (1992) Effective and efficient global optimization for conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour Res 28(4):1015–1031. https://doi.org/10.1029/91WR02985
Engeland K, CY X, Gottschalk L (2005) Assessing uncertainties in a conceptual water balance model using Bayesian methodology. Hydrol Sci J Des Sci Hydrol 50(1):45–63
Hamed KH, Rao AR (1998) A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J Hydrol 204(1–4):182–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(97)00125-X
Hao ZC, Singh VP (2015) Drought characterization from a multivariate perspective: a review. J Hydrol 527:668–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.05.031
Heim RR (2002) A review of twentieth-century drought indices used in the United States. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83(8):1149–1165
Huang SZ, Chang JX, Huang Q, Chen YT (2014) Spatio-temporal changes and frequency analysis of drought in the Wei River basin, China. Water Resour Manag 28(10):3095–3110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0657-4
Kendall MG (1975) Rank correlation methods. Griffin, London
Kirono DGC, Kent DM, Hennessy KJ, Mpelasoka F (2011) Characteristics of Australian droughts under enhanced greenhouse conditions: results from 14 global climate models. J Arid Environ 75(6):566–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2010.12.012
Lin QC, Li HE (2010) Influence and guarantee on ecological basic flow of Weihe River from Baojixia water diversion. J Arid Land Resour Environ 24(11):114e119 in Chinese
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13(3):245–259. https://doi.org/10.2307/1907187
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In proceedings of the 8th conference on applied climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January
Milly PCD, Betancourt J, Falkenmark M, Hirsch RM, Kundzewicz ZW, Lettenmaier DP, Stouffer RJ (2008) Climate change - stationarity is dead: whither water management? Science 319(5863):573–574. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1151915
Mishra AK, Singh VP (2010) A review of drought concepts. J Hydrol 391(1–2):204–216
Mittal N, Bhave AG, Mishra A, Singh R (2016) Impact of human intervention and climate change on natural flow regime. Water Resour Manag 30(2):685–699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1185-6
Nalbantis I, Tsakiris G (2009) Assessment of hydrological drought revisited. Water Resour Manag 23(5):881–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9305-1
Pettitt AN (1979) A non-parametric approach to the change-point problem. J R Stat Soc 28(2):126–135
Rigby RA, Stasinopoulos DM (2005) Generalized additive models for location, scale and shape. J R Stat Soc Ser C: Appl Stat 54(3):507–544. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9876.2005.00510.x
Santhi C, Arnold JG, Williams JR, Hauck LM, Dugas WA (2001) Application of a watershed model to evaluate management effects on point and nonpoint source pollution. T Asae 44(6):1559–1570
Sheffield J, Wood EF (2007) Characteristics of global and regional drought, 1950-2000: analysis of soil moisture data from off-line simulation of the terrestrial hydrologic cycle. J Geophys Res-Atmos 112:D17
Sheffield J, Wood EF, Roderick ML (2012) Little change in global drought over the past 60 years. Nature 491(7424):435–438. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11575
Shukla S, Wood AW (2008) Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought. Geophys Res Lett 35(2):226–236
Van Loon AF, Tijdeman E, Wanders N et al (2014) How climate seasonality modifies drought duration and deficit. J Geophys Res 119(8):4640–4656
Villarini G, Serinaldi F, Smith JA, Krajewski WF (2009) On the stationarity of annual flood peaks in the continental United States during the 20th century. Water Resour Res 45(8):2263–2289
Wanders N, Wada Y (2015) Human and climate impacts on the 21st century hydrological drought. J Hydrol 526:208–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.10.047
Wang GS, Xia J, Chen J (2009) Quantification of effects of climate variations and human activities on runoff by a monthly water balance model: a case study of the Chaobai River basin in northern China. Water Resour Res 45(7):206–216
Wang YX, Li JZ, Feng P, Chen FL (2015) Effects of large-scale climate patterns and human activities on hydrological drought: a case study in the Luanhe River basin, China. Nat Hazards 76(3):1687–1710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1564-y
Wen L, Rogers K, Ling J, Saintilan N (2011) The impacts of river regulation and water diversion on the hydrological drought characteristics in the lower Murrumbidgee River, Australia. J Hydrol 405(3–4):382–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.05.037
Xia J, Wang GS, Tan G, Ye AZ, Huang GH (2005) Development of distributed time-variant gain model for nonlinear hydrological systems. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 48(6):713–723. https://doi.org/10.1360/03yd0183
Ye AZ, Duan QY, Zhan CS, Liu ZF, Mao YN (2013) Improving kinematic wave routing land model scheme in community land model. Hydrol Res 44(5):886–903. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2012.145
Zhan CS, Jiang SS, Sun FB, Jia YW, Niu CW, Yue WF (2014) Quantitative contribution of climate change and human activities to runoff changes in the Wei River basin, China. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 18(8):3069–3077. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-18-3069-2014
Zhang XB, Harvey KD, Hogg WD, Yuzyk TR (2001) Trends in Canadian streamflow. Water Resour Res 37(4):987–998. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000WR900357
Zhang YF, Guan DX, Jin CJ et al (2011) Analysis of impacts of climate variability and human activity on streamflow for a river basin in northeast China. J Hydrol 410(3–4):239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.09.023
Zhu Y, Wang W, Singh VP, Liu Y (2016) Combined use of meteorological drought indices at multi-time scales for improving hydrological drought detection. Sci Total Environ 571:1058–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.096
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41501030 and 41571028) and the Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Hydrology-Water Resources and Hydraulic Engineering (No. 2016490211). We are very grateful to the editors and two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and constructive suggestions that helped us to greatly improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, L., Xia, J. & She, D. Analysis of Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Hydrological Drought: a Case Study in the Wei River Basin, China. Water Resour Manage 32, 1421–1438 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1877-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1877-1